Untangling tax legal guidelines can really feel like navigating a maze, particularly whenever you’re making an attempt to decipher what looks like a wholly new language. When filling out your tax type, one time period that used to play a significant function in particular person tax returns was “private exemption.”
This exemption allowed people to deduct a certain amount from their complete revenue when figuring their taxable revenue whereas finishing their tax kinds. It performed an important function in shaping tax liabilities and influencing monetary methods.
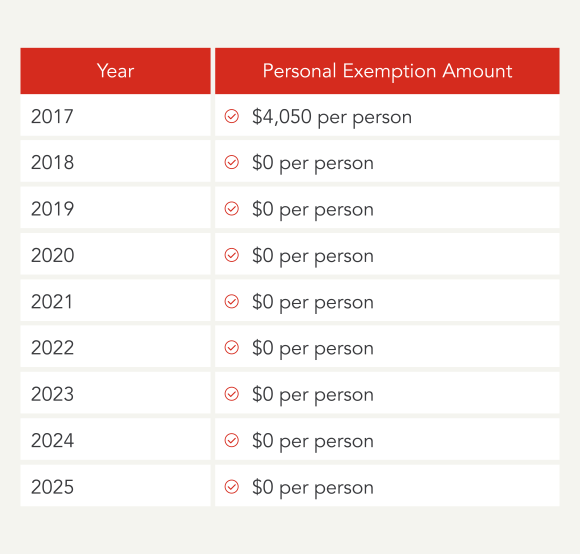
Nonetheless, tax regulation modifications have been fairly vital and the Tax Cuts and Jobs Acts in 2017 eradicated this exemption. Now, that may change in 2025, however for tax 12 months 2023, there aren’t any private exemptions.
This main shift has possible modified the way you strategy your taxes. That can assist you get a greater understanding of their impression, let’s check out the historic function of private exemptions and what their absence means for present tax planning.
What’s a private exemption?
A private exemption was a hard and fast deduction that was subtracted out of your complete revenue. You and every member of your loved ones have been entitled to at least one private exemption. These private exemptions would cut back your complete taxable revenue.
The private exemption helped scale back the burden of financially supporting your self and dependents by decreasing taxable revenue. Nonetheless, there have been just a few exceptions. For instance, in case you might be claimed as a dependent, you couldn’t declare the private exemption.
Even in case you certified for a private exemption, it didn’t imply you have been in a position to declare the complete quantity. Primarily based in your adjusted gross revenue (AGI), you’ll start to part out at a sure threshold.
Within the 2017 tax 12 months, if a single filer’s AGI was above $261,500, the private exemption was lowered. It could part out fully for an AGI above $384,000.
Important modifications occurred with the implementation of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, signed into regulation in 2017. In consequence, people may not declare a selected greenback quantity as a private exemption for:
- Themselves
- Their spouses
- Their dependents
What’s the private exemption for 2024?
In 2024, the private exemption continues to face at $0. That is as a result of provision enacted in 2017 by the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act.
The private exemption isn’t relevant for tax returns starting after December 31, 2017, and earlier than January 1, 2026.
How did the Tax Cuts & Jobs Act have an effect on private exemptions?
The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act was signed in 2017 and went into impact in 2018 (for the tax 12 months of 2017.) A few of the provisions included within the invoice will revert again after 2025 until prolonged. Key modifications embrace new tax charges, elevated normal deductions, and updates to varied deductions akin to:
- State and native taxes
- Mortgage curiosity
- Charitable contributions
The kid tax credit score was expanded, and the “kiddie tax” has new standards. Notable modifications additionally have an effect on:
- Alimony
- Different Minimal Tax (AMT)
- Obamacare mandate penalties
- Therapy of 529 Plan funds
Understanding these modifications is essential for navigating the evolving tax panorama.
Among the many different tax regulation modifications, the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act eradicated private exemptions beginning after December 31, 2017, till January 1, 2026. Previous to the Act, taxpayers may deduct a private exemption for:
- Themselves
- Their partner
- Every dependent from their adjusted gross revenue

How have private exemptions labored prior to now?
Up to now, private exemptions have been utilized to every particular person and the dependents that every particular person may declare on their tax return.
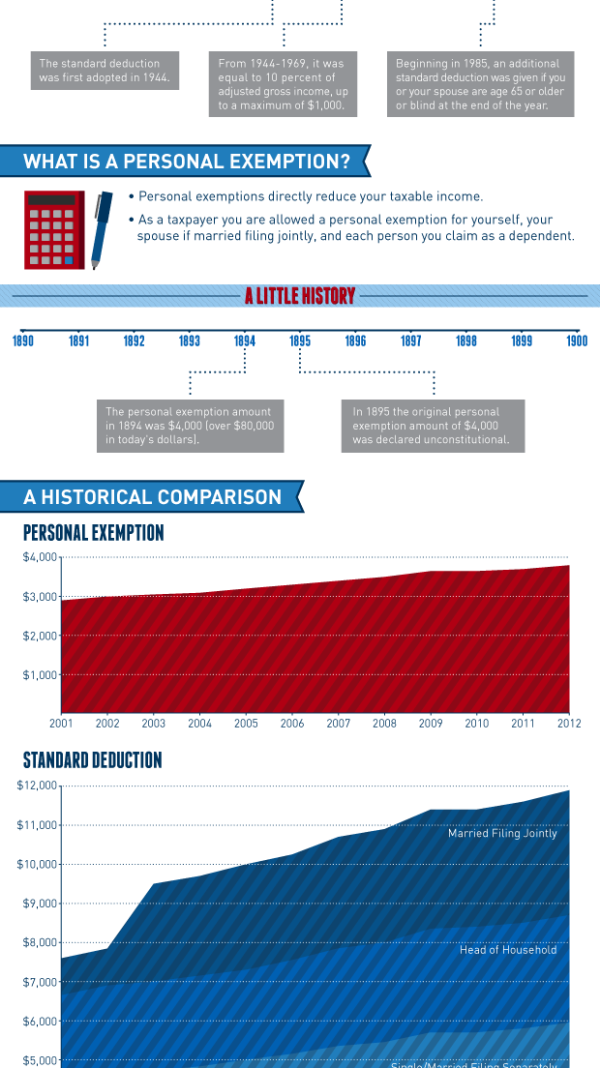
Sometimes, every particular person was entitled to at least one private exemption for themselves. This solely utilized if they might not be claimed as a depending on one other taxpayer’s return. For the tax 12 months of 2017, the private exemption stood at $4,050 per particular person.
A dependent is a qualifying baby or relative. See the previous tips listed under.
Qualifying youngsters below the previous private exemption guidelines
For a qualifying baby:
- The eligible baby would have wanted to fall below one in every of these classes: your son, daughter, stepchild, foster baby, brother, sister, half-sibling, step-sibling, or a descendent of any of them.
A toddler that was legally adopted would’ve additionally certified.
- Particular age standards ought to’ve utilized: the kid is both below 19 years previous on the finish of the 12 months and youthful than you or a full-time pupil below 24 years previous on the finish of the 12 months and youthful than you.
A toddler that was completely and completely disabled would’ve certified no matter age.
- The kid should have resided with you for greater than half of the 12 months. Exceptions existed for momentary absences as a result of sickness or journey, newborns or deceased youngsters in the course of the 12 months, kidnapped youngsters, and people of divorced or separated mother and father.
- The kid can’t have supplied greater than half of their very own assist for the 12 months, together with fundamental wants akin to room and board.
- The kid can’t have filed a joint tax return with every other particular person for the 12 months.

Claiming a toddler below the previous private exemption guidelines
In instances the place two taxpayers each believed a toddler certified below the previous standards, particular tie-breaker guidelines would’ve apply:
- If just one taxpayer was the kid’s guardian, they’re handled because the qualifying baby of that guardian.
- If each mother and father claimed the kid however filed individually, the IRS considers which guardian lived with the kid the longest in the course of the tax 12 months.
- If the time was equal, the kid would’ve been handled because the qualifying baby of the guardian with the upper adjusted gross Revenue (AGI).
- If no guardian was claiming the kid, they’re handled because the qualifying baby of the taxpayer with the very best AGI.
- If no guardian claimed the kid, they usually have been eligible to take action, the kid would’ve been handled because the qualifying baby of the taxpayer with the very best AGI, supplied it surpasses that of any eligible mother and father.
If all else failed, the taxpayers may have reached an settlement between themselves relating to who could declare the kid.
Qualifying relative below the previous private exemption guidelines
That is also referred to as the “not qualifying baby check.” The next standards should’ve utilized:
- A toddler can’t have been your qualifying relative in the event that they already certified because the qualifying baby of one other taxpayer.
- Your relative should have fulfilled one in every of two circumstances: both resided with you all through your entire 12 months as a family member or have a specified relationship with you. Whereas fast members of the family naturally meet this requirement, it additionally encompasses half-siblings, step-siblings, and in-laws.
- The relative’s gross revenue for the 12 months should not have exceeded the revenue threshold of the tax 12 months.
- You should have contributed greater than half of your relative’s complete assist in the course of the 12 months to satisfy this criterion.
So as to formally declare a dependent as a private exemption in your tax return, you should have supplied:
- Their identify
- Social Safety quantity
- Relationship to you
If you happen to’re utilizing tax preparation software program or a tax skilled, you possible needed to present the beginning dates of your dependents.
As well as, private exemptions may have additionally utilized to married {couples}. For a married couple who filed a joint revenue tax return, an exemption may have been claimed for the partner.
If you happen to have been married and submitting a separate tax return, the exemption may have be claimed for the partner below the circumstances that the partner:
- Had no gross revenue
- Wasn’t submitting a tax return
- Couldn’t have been claimed as a dependent by another person
What’s the distinction between an exemption vs. deduction?
Though each exemptions and deductions scale back your complete taxable revenue, they differ from each other in vital methods.
The variety of exemptions you would have certified for depended in your submitting standing and the variety of dependents you had. Then again, now you both declare a normal deduction or an itemized deduction. deductions are tied to your bills. Whenever you declare a normal deduction it’s arguably simpler since you don’t need to preserve observe of bills and you are taking normal deduction in your submitting standing. The 2023 normal deduction is $13,850 for single taxpayers ($20,800 if you’re submitting head of family or $27,700 for these married submitting collectively). Some widespread examples of deductions for these itemizing deductions embrace pupil mortgage curiosity deduction in case you’re repaying pupil loans, contributions to certified charitable organizations, or curiosity paid on your house mortgage.
The usual deduction for single filers was $6,350 within the tax 12 months 2017 when private exemptions have been nonetheless allowed.
How are you going to decrease your tax invoice?
In the case of taxes, there are many nuances that make it troublesome to navigate tax legal guidelines. Though you possibly can’t use a private exemption now, there are nonetheless different methods to avoid wasting in your taxes and enhance your tax refund.
Listed here are just a few ideas to make sure most financial savings come tax time:
Perceive deductions
Successfully using deductions is essential to minimizing your tax invoice. Determine any eligible bills, keep correct information, and select between itemized and normal deductions based mostly on most profit. Strategically time deductible bills and leverage tax-advantaged accounts to cut back taxable revenue.
There are a variety of itemized deductions to contemplate trying into, akin to:
- Medical and dental bills
- Mixed complete of state and native revenue taxes
- Mortgage curiosity
- Charitable contributions
- Casualty losses throughout a nationally declared catastrophe
Contribute to retirement
You may decrease your tax invoice by decreasing your taxable revenue. One strategic transfer is reaching the utmost contribution quantity for pre-tax plans like a 401(ok) or IRA.
Chances are you’ll need to think about changing your conventional IRA to a Roth IRA. In contrast to a standard IRA, transformed quantities from a Roth IRA usually don’t incur federal revenue taxes on certified distributions, supplied that:
- A minimal of 5 years has handed since your preliminary Roth IRA contribution or conversion.
- You’re 59½ or older.
Discover completely different funding methods
You would possibly need to look into placing a few of your revenue towards investments. With a buy-and-hold technique, you possibly can get pleasure from deferred capital features.
Observe that in case your modified adjusted gross revenue reaches $200,000 or extra ($250,000 or extra if married submitting collectively), you’re accountable for a 3.8% Internet Funding Revenue Tax (NIIT). Relying on which is decrease, this may apply to both:
- Your web funding revenue
- The quantity of your modified adjusted gross revenue (MAGI) that surpasses the $200,000 threshold for single or head of family ($250,000 for married submitting collectively)
Observe that particular exclusions apply, so that you’ll need to seek the advice of your tax advisor.
Embrace clear vitality
Enacted in 2022, The Inflation Discount Act allotted billions for clear vitality tax credit and different efforts to handle local weather change. As a person, one thing to notice is the potential for substantial tax credit doubtlessly price hundreds of {dollars} for:
- Buying new or used electrical or hybrid clear automobiles
- Putting in residential vitality property
- Different environmentally pleasant initiatives
There are some restrictions. You’ll need to seek the advice of together with your tax advisor to find out which credit apply to you.
Work with a monetary advisor or use instruments
You need to think about working with a monetary advisor who’s well-versed in tax issues. A monetary advisor will help information you in your taxable revenue. They’ll additionally advise you on taxes that may impression your investments.
You can even use any variety of tax calculators or instruments to hurry up the method.
Understanding the nuances of tax legal guidelines is crucial relating to tax planning. This contains private exemptions. Nonetheless, you don’t have to stress about understanding these tax legal guidelines. It doesn’t matter what strikes you made final 12 months, TurboTax will make them rely in your taxes. Whether or not you need to do your taxes your self or have a TurboTax skilled file for you, we’ll ensure you get each greenback you deserve and your largest potential refund – assured.
32 responses to “What Is a Private Exemption & Ought to You Use It?”