Word to the reader: That is the sixteenth in a sequence of articles I am publishing right here taken from my guide, “Investing with the Pattern.” Hopefully, you can see this content material helpful. Market myths are usually perpetuated by repetition, deceptive symbolic connections, and the entire ignorance of info. The world of finance is filled with such tendencies, and right here, you may see some examples. Please remember the fact that not all of those examples are completely deceptive — they’re generally legitimate — however have too many holes in them to be worthwhile as funding ideas. And never all are instantly associated to investing and finance. Get pleasure from! – Greg
Whereas the world of finance believes danger is measured by volatility (customary deviation), it’s my perception that lack of capital is danger, and never volatility.
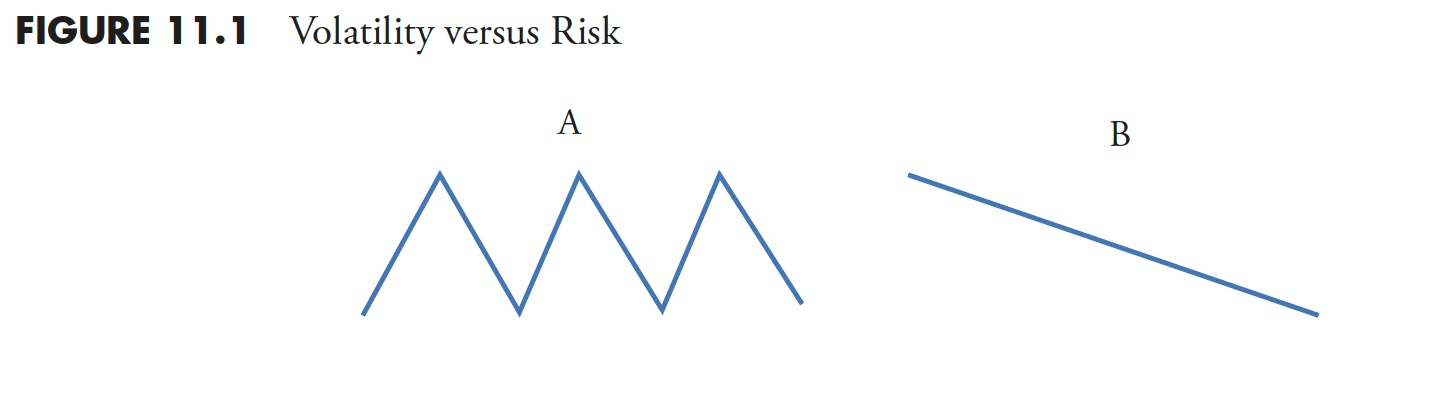
In Determine 11.1, instance A ends the place it begins with zero acquire or loss, but fashionable finance says it’s dangerous as a result of it’s risky. Instance B exhibits the tip worth decrease than the start worth, so it exhibits a loss; fashionable finance, on this occasion, would say there isn’t a danger as a result of there isn’t a volatility. I believe you may draw your individual conclusions.
Volatility can contribute to danger, nevertheless it can also contribute to cost features. Lack of capital is straightforward and affordable to make use of as a danger measure, and on this chapter, danger is outlined by drawdown.
What Is Drawdown?
- Drawdown is the share that worth has moved down from its earlier all-time excessive worth.
- Drawdown is danger.
- Drawdown is systematic danger.
- Drawdown is lack of capital.
- Drawdown can last more than you may.
- Drawdown can damage your retirement plans.
Drawdown Terminology
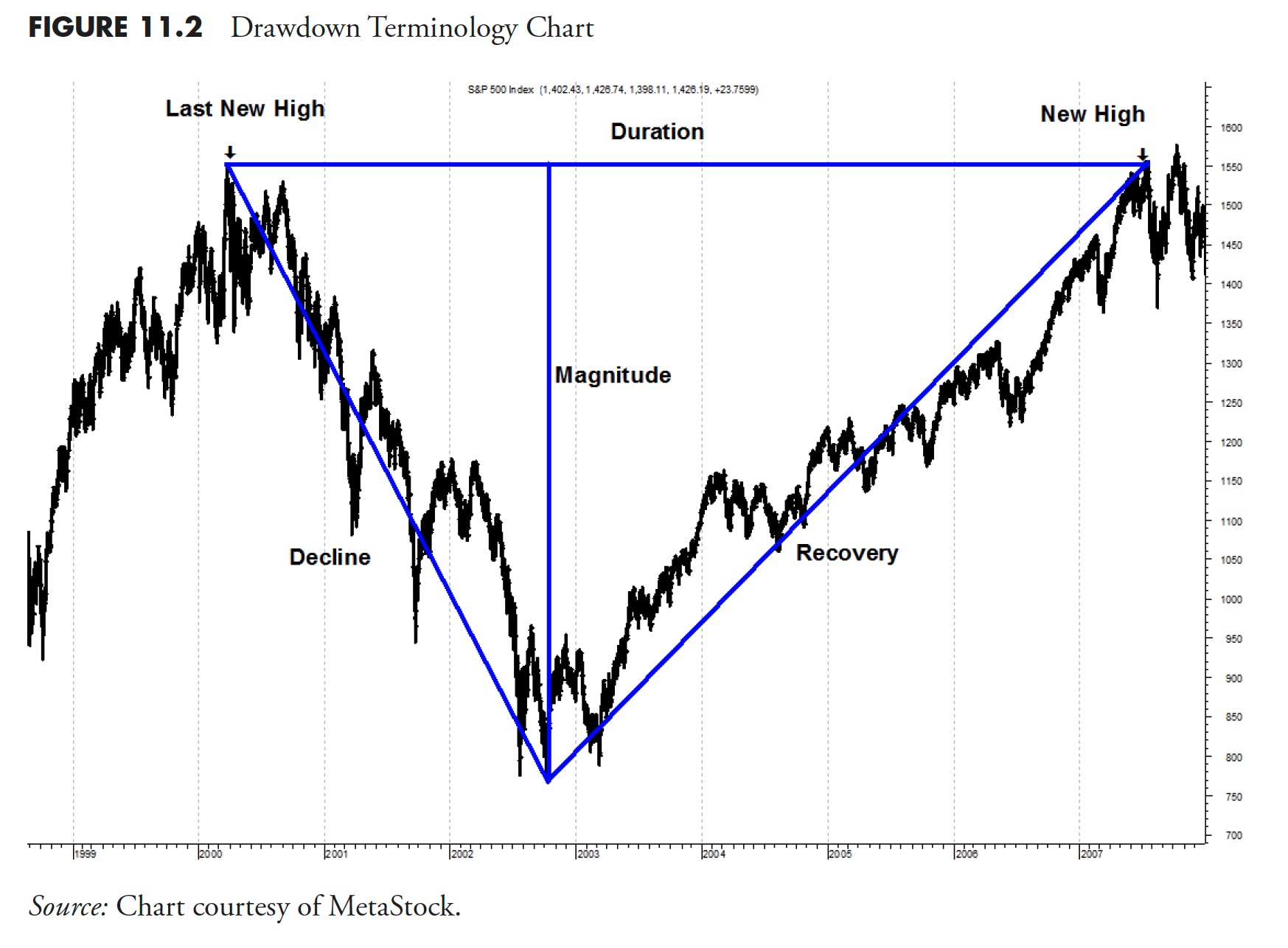
The next describes the nomenclature utilized in Determine 11.2.
- Drawdown Magnitude is the share that worth has moved down from its earlier all-time excessive.
- Drawdown Decline is the period of time the market declined from an all-time excessive to the trough.
- Drawdown Period is the overall period of time that it took the worth to get better to is earlier all-time excessive.
- Drawdown Restoration is the time it took from the trough to get again to an all-time excessive.
Though the terminology for drawdowns is subjective, I will stick to those that Sam Stovall (Commonplace & Poor’s) makes use of, as they’re nearly as good as any. I’ve usually thought another time period for bear markets larger than -40% can be good, corresponding to Tremendous Bear, however I’ve different battles to struggle. See Desk 11.1.
The Arithmetic of Drawdown and Equal Return
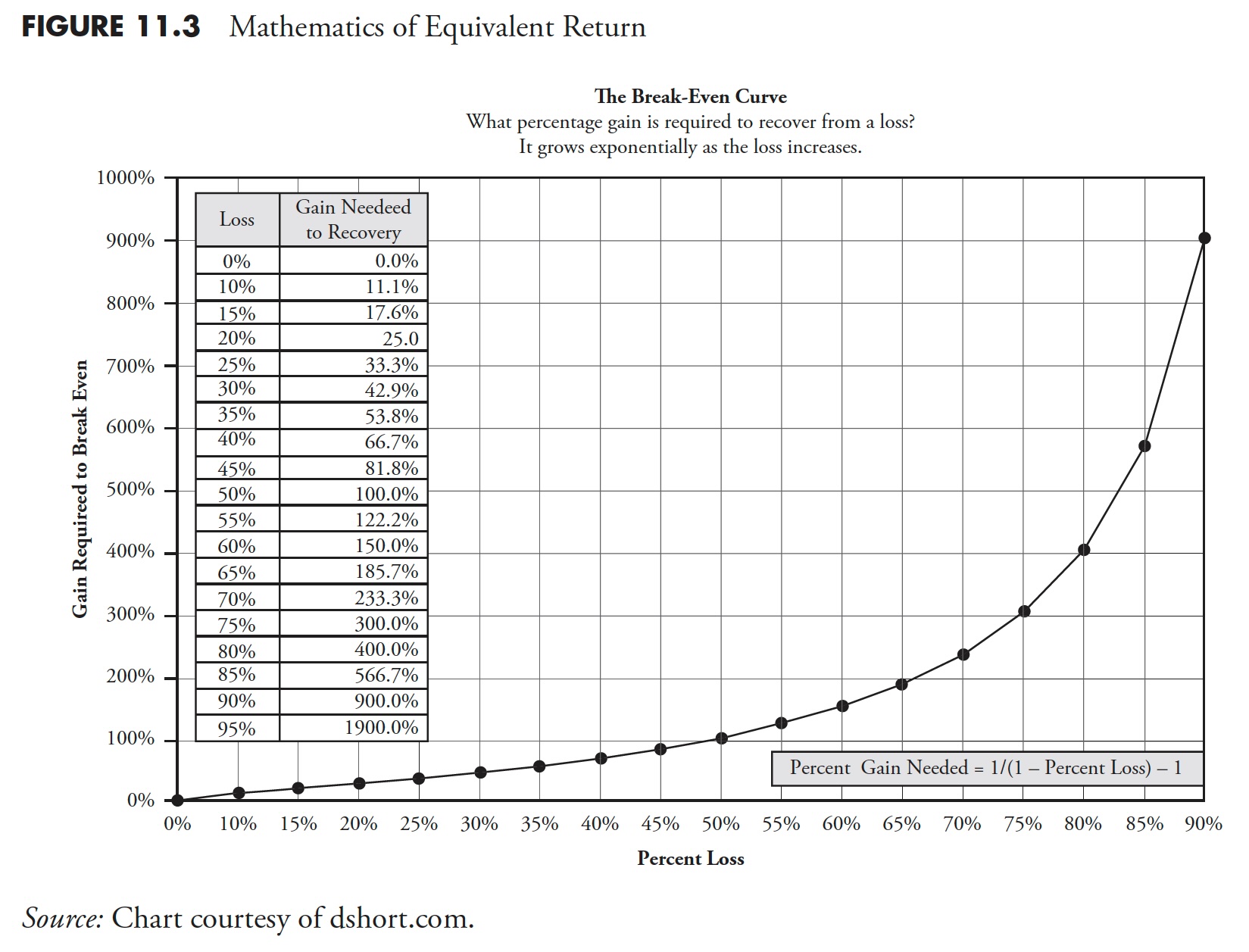
Recovering from a extreme drawdown takes a rare return simply to get again to the place you had been. That is generally known as equal return and is represented by this formulation:
P.c Drawdown /(1 – P.c Drawdown ) – 1
If you do not have a calculator or desk useful, simply divide the % decline by its complement (100 – %), after which mentally place the decimal within the applicable place. That is finest accomplished in privateness and never on a stage in entrance of many individuals.
From Determine 11.3, you may see that for those who lose 50%, then it takes a 100% acquire to get again to even. When was the final time you doubled your cash? A 100% acquire is similar as doubling your cash. The bear market that started on October 9, 2007 dropped greater than 55%; you may see that to get better. it takes a acquire of greater than 122% to get again to even. One factor the graphic clearly exhibits is that, the bigger the loss, the larger the acquire required to get better.
Cumulative Drawdown
Determine 11.4 is an instance of cumulative drawdown. The road that strikes throughout the tops of the worth information (prime plot) solely strikes up with the information and sideways when the information doesn’t transfer up; in different phrases, it’s consistently reflecting the worth’s all-time excessive worth. The underside plot is the share decline from that all-time excessive line. At any time when that line is on the prime, it signifies that worth within the prime plot is at its all-time excessive. As the road within the backside plot declines, it strikes in percentages of the place it was final at its all-time excessive worth.
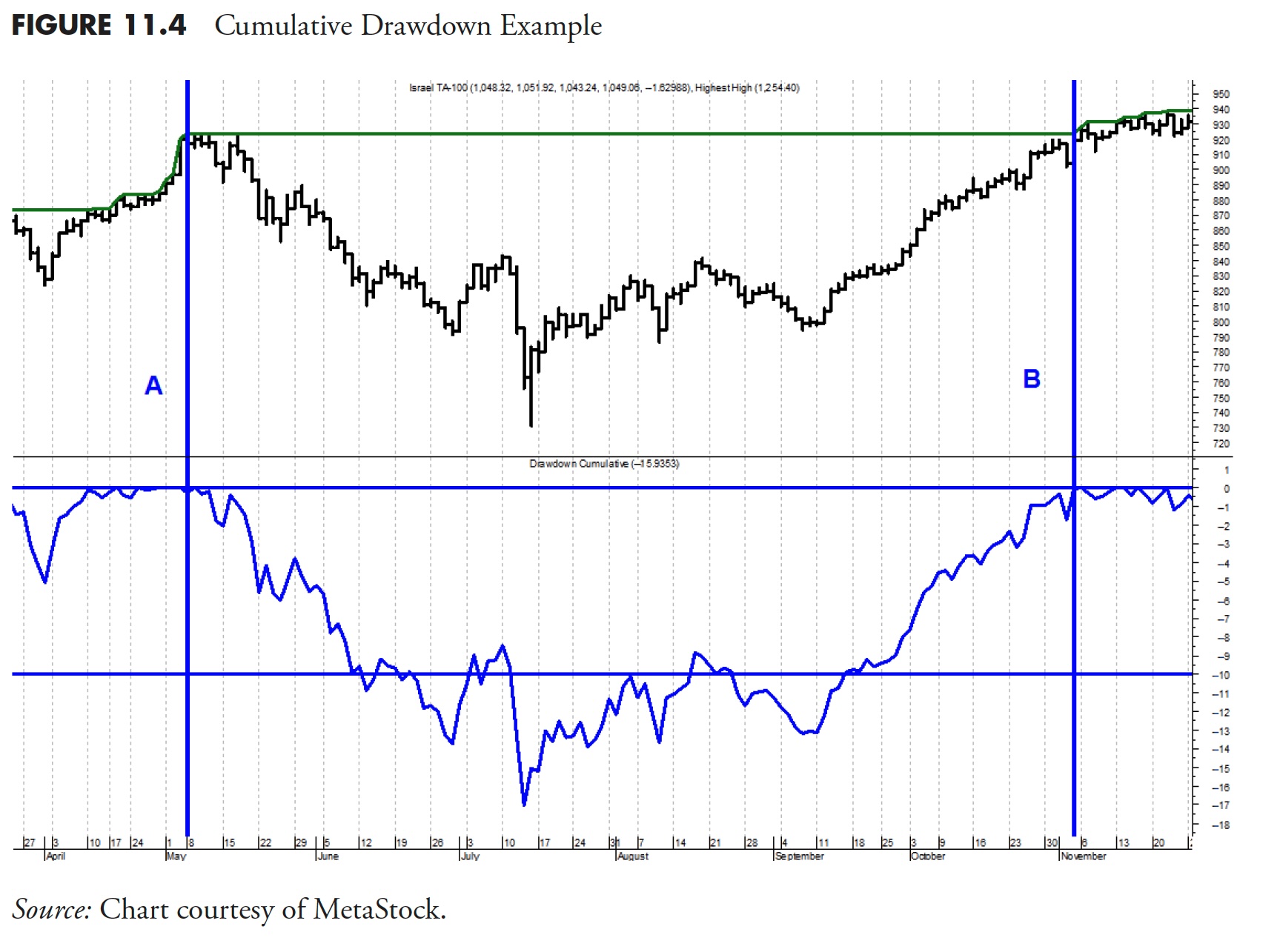
Within the instance proven, a brand new all-time excessive in worth is reached on the vertical line labeled A. The underside plot exhibits that, as costs transfer down from that time, the drawdown additionally strikes along with worth. The horizontal line that goes by way of the decrease a part of the drawdown plot is at -10%. You’ll be able to’t learn the dates on the backside, nevertheless it took nearly six months earlier than the costs recovered to level B after which moved above the extent they’d reached at level A. That is an instance of drawdown that had a magnitude of -17%, proven by the bottom level reached on the drawdown line within the backside plot. The drawdown additionally lasted (period) nearly six months, as proven by the point between line A and line B.
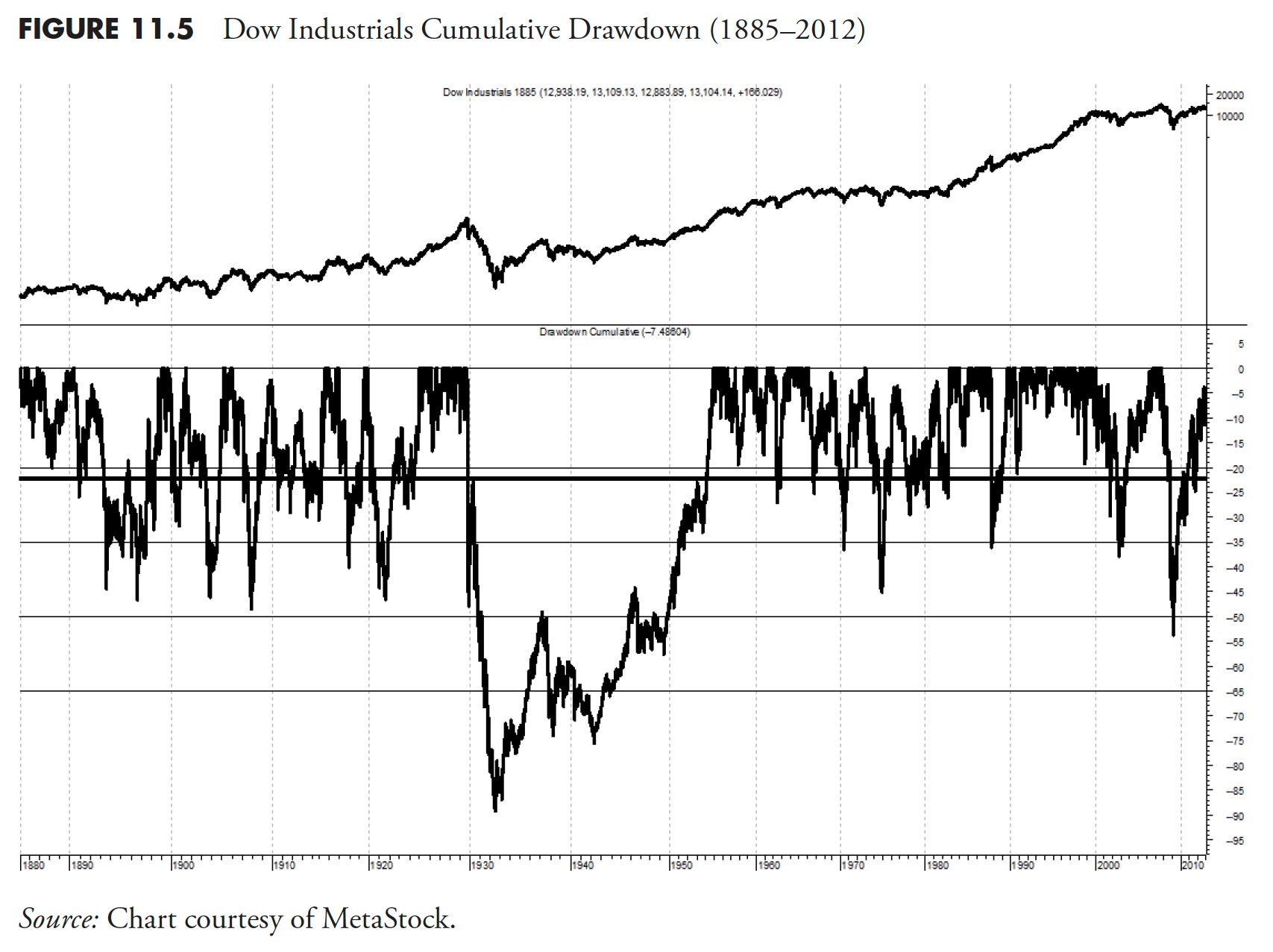
Determine 11.5 exhibits the share of drawdown over your entire historical past of the Dow Industrials since 1885. The highest portion is the Dow Industrials, plotted utilizing semi-log scaling, and the underside plot is the drawdown share. The darker horizontal line by way of the underside plot is the imply or common of the drawdown over the total time interval since 1885. Its worth is -22.1%. The opposite horizontal strains are proven at zero (prime line), -20%, -35%, -50%, and -65%, I believe the factor that stands out from this chart is that the interval from 1929 by way of 1954 suffered an unlimited drawdown, not solely in magnitude but in addition in period. The low was on June 28, 1932 at -88.67%. The equal return to get again to even from that time was a acquire of greater than 783%. That’s the reason it took nearly 25 years to perform.
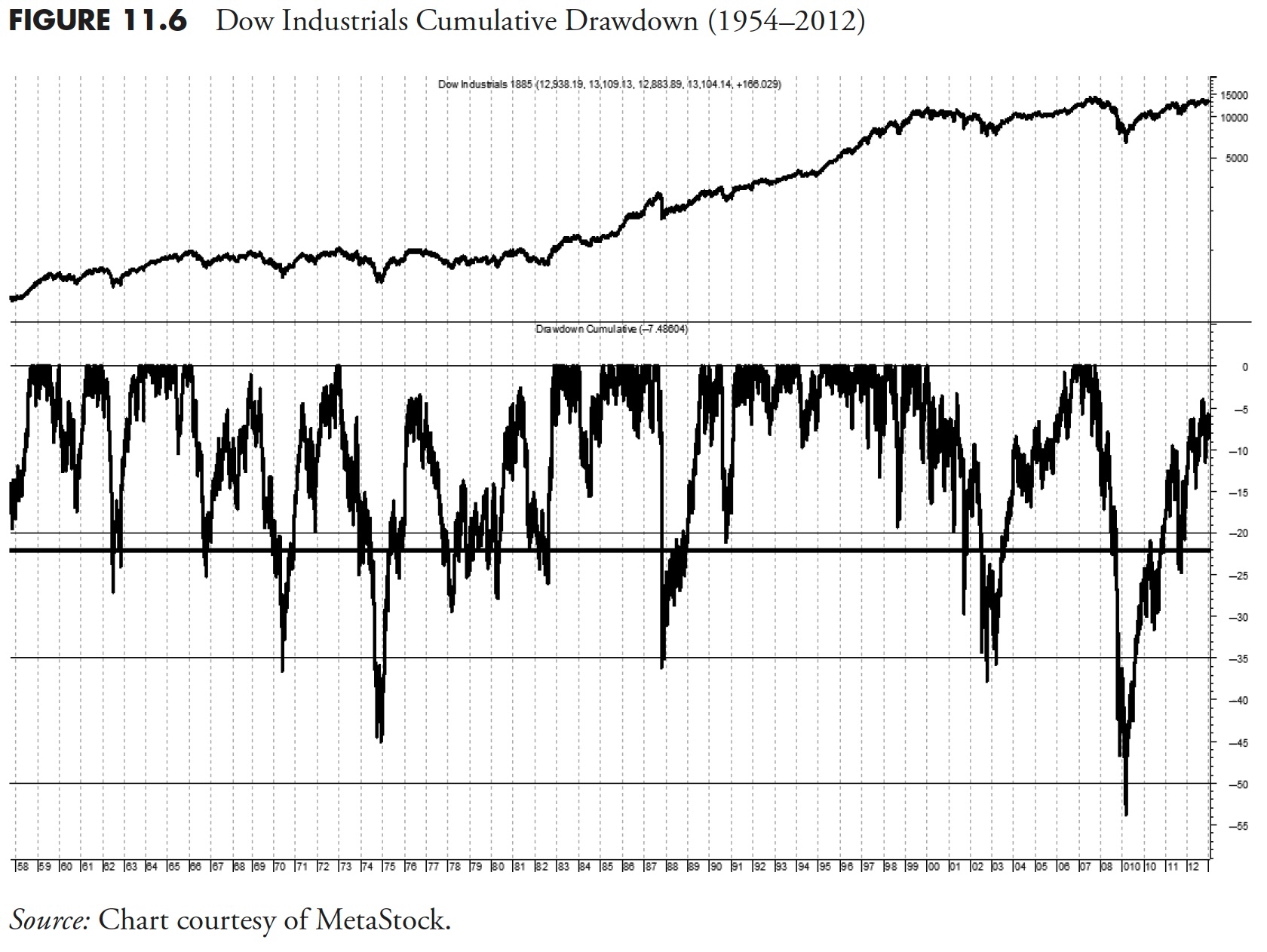
As a result of the Melancholy-era drawdown distorts the opposite drawdowns, Determine 11.6 exhibits precisely the identical information since about 1954, eliminating the scaling impact from the -88% Melancholy-era drawdown. The drawdown in 2008 clearly stands out as the most important in fashionable occasions at -53.78% on March 9, 2009. As of this writing (in 2013), that drawdown has but to get better. It needs to be famous that the entire time that the drawdown line within the backside plot will not be again as much as the highest (0%), the market is in a “state of drawdown,” which is famous by the period, not simply the quantity of the decline, which is the magnitude.
Bear in mind: Each bear market ends, however hardly ever when you’re nonetheless attempting to select the underside.
S&P 500 Drawdown Evaluation
The next information is from the S&P 500 Index, not adjusted for dividends or inflation, over the interval from December 30, 1927, by way of December 31, 2012. It was a interval that consisted of 21,353 market days and 1,016.81 calendar months. The S&P 500 has been extensively considered one of the best single gauge of the large-cap U.S. equities market because the index was first printed in 1957 and backfilled to 1927 with the S&P 90. The index has greater than US$5.58 trillion benchmarked, with index property comprising roughly US$1.31 trillion of this complete. The index contains 500 main corporations in main industries of the U.S. financial system, capturing 75% protection of U.S. equities.
Drawdown Decline — S&P 500
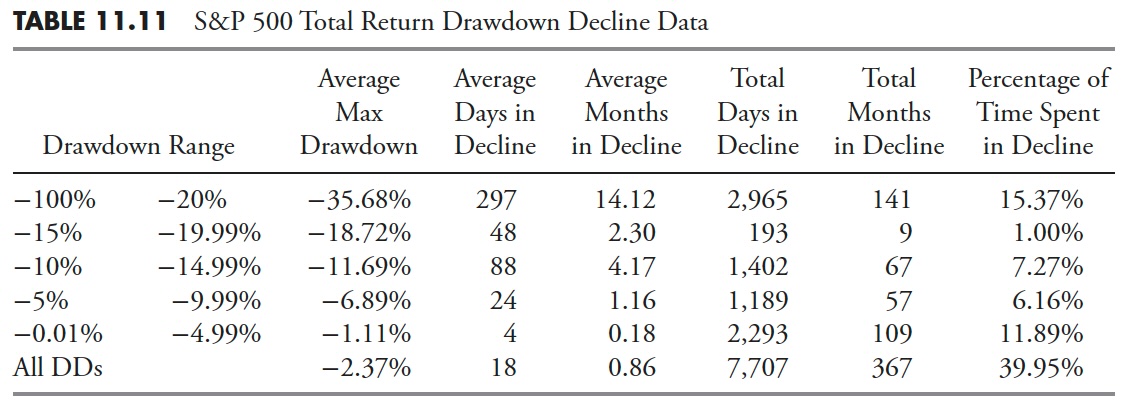
Desk 11.2 is concentrated solely on the share decline of the assorted drawdowns. The columns within the desk are outlined as follows:
- Drawdown vary. That is the share of drawdown decline, divided into varied ranges which make up the rows within the desk. The highest row of knowledge is for drawdowns with declines larger than 20%, and the underside row is the information for all drawdowns.
- Common max drawdown. That is the typical of all of the drawdowns for the share decline within the first column.
- Common days in decline. That is the typical variety of market days that the drawdowns had been within the decline whose share decline is outlined by the primary column.
- Common months in drawdown. That is merely a calculation of dividing the typical market days in decline by 21, which is the typical variety of market days monthly, which yields calendar months.
- Whole days in decline. That is the sum of all the times the actual decline vary was in decline.
- Whole months in decline. That is the overall market days in decline divided by 21.
- Share of time spent in decline. That is the share of time that the declines had been in a state of decline based mostly on the overall variety of market days for the interval of study.
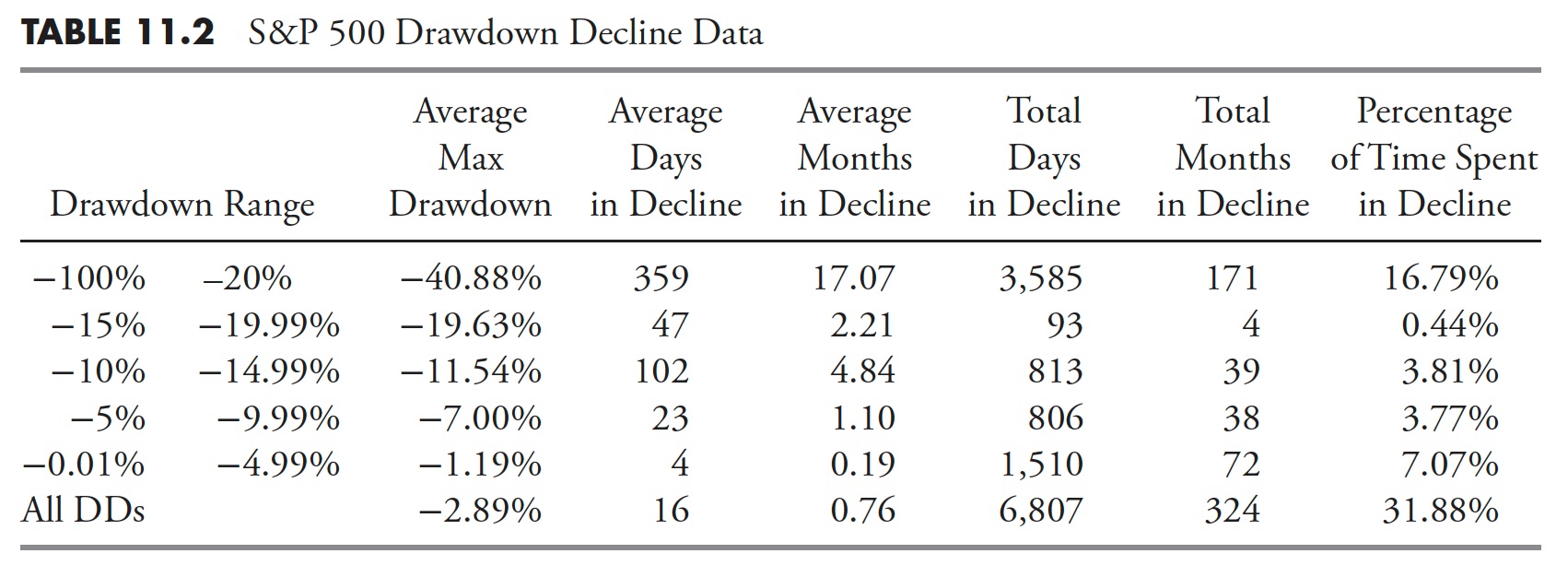
From Desk 11.2, you may see that every one drawdowns larger than 20%, that are additionally referred to as bear markets, had been in a state of decline for nearly 17% of the time; in different phrases, bear market declines accounted for 17% of the overall time from 1927 to 2012. The underside row within the desk above exhibits that every one drawdowns (DD), it doesn’t matter what their magnitude, spent nearly 32% of the time declining.
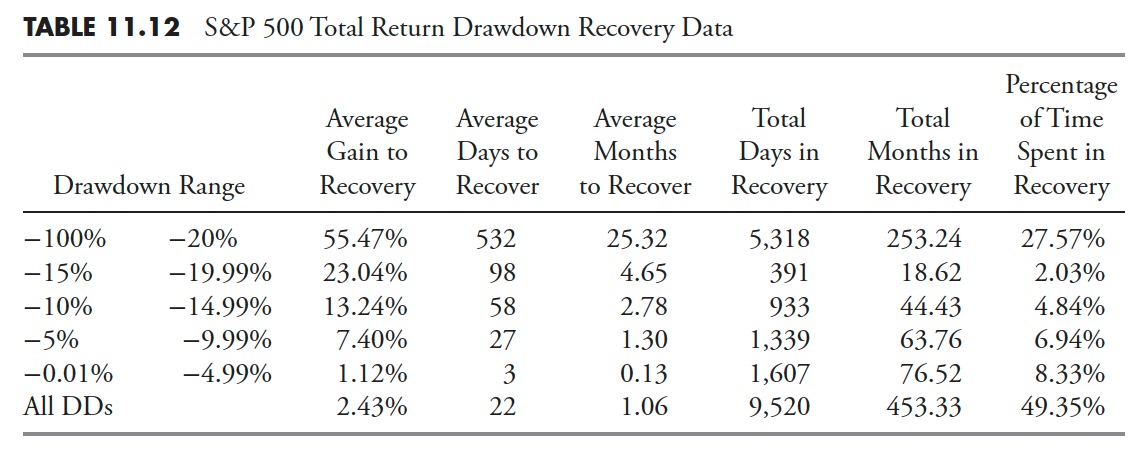
Drawdown Restoration — S&P 500
Drawdown restoration is the time period used to outline the time spent from when a drawdown bottoms (hits its absolute lowest level and best share of decline) and fully recovers (will get again as much as the place the drawdown started). The columns in Desk 11.3 are just like the Drawdown Decline desk in Desk 11.2; we’re simply discussing the final portion of the drawdown right here as an alternative of the primary portion.
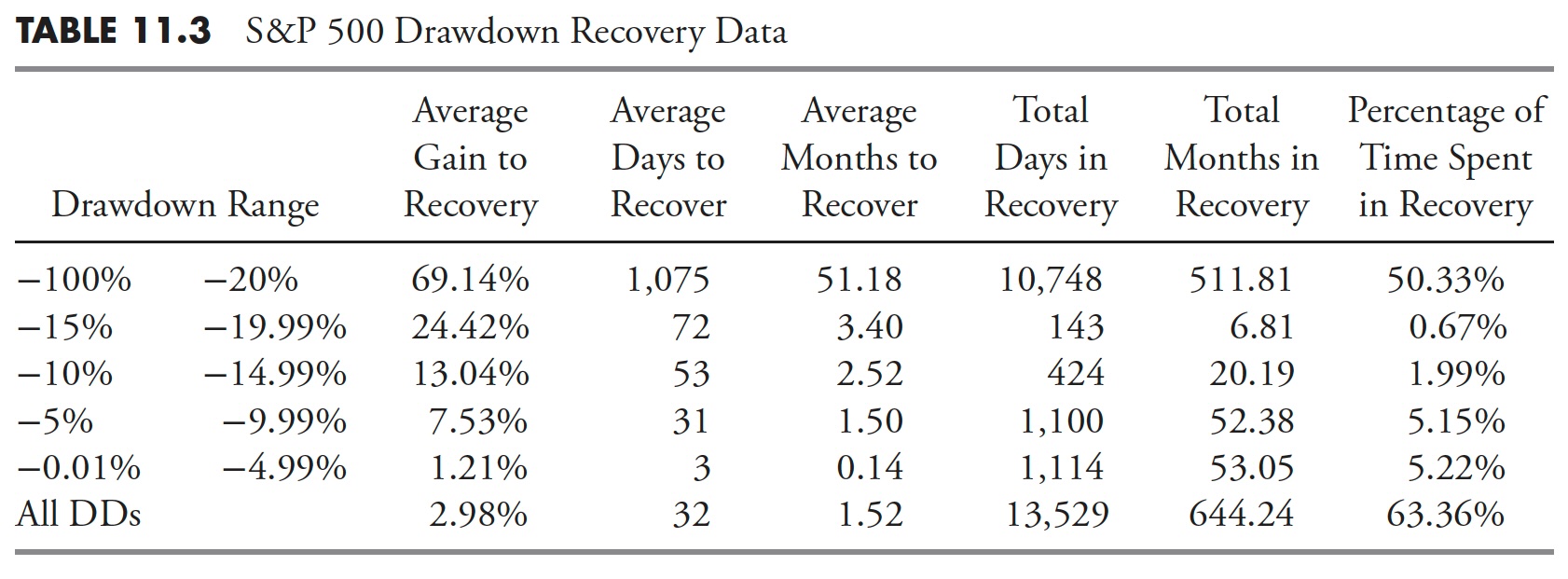
Following the same dialogue as was accomplished within the Drawdown Decline evaluation, we are able to see that Drawdown Recoveries the place the magnitude of the drawdown was larger than 20% took greater than 50% of the overall time to get better. Do not forget that recoveries from declines all the time take longer than the declines. That is usually outlined by the truth that declines (promoting) are extra emotionally pushed so normally are faster and extra abrupt.
There’s a new column within the Drawdown Restoration desk referred to as Common Acquire to Restoration. That is the share of acquire (restoration) wanted to get again to the place the drawdown started. See the sooner a part of this part that talks about equal return for extra info. From Desk 11.3, you may see that for drawdowns larger than 20%, on common, it takes a acquire of greater than 69% to get again to even. Bear in mind we’re coping with averages in these tables. Elsewhere within the guide are tables displaying every of the drawdowns that had been larger than 20%.
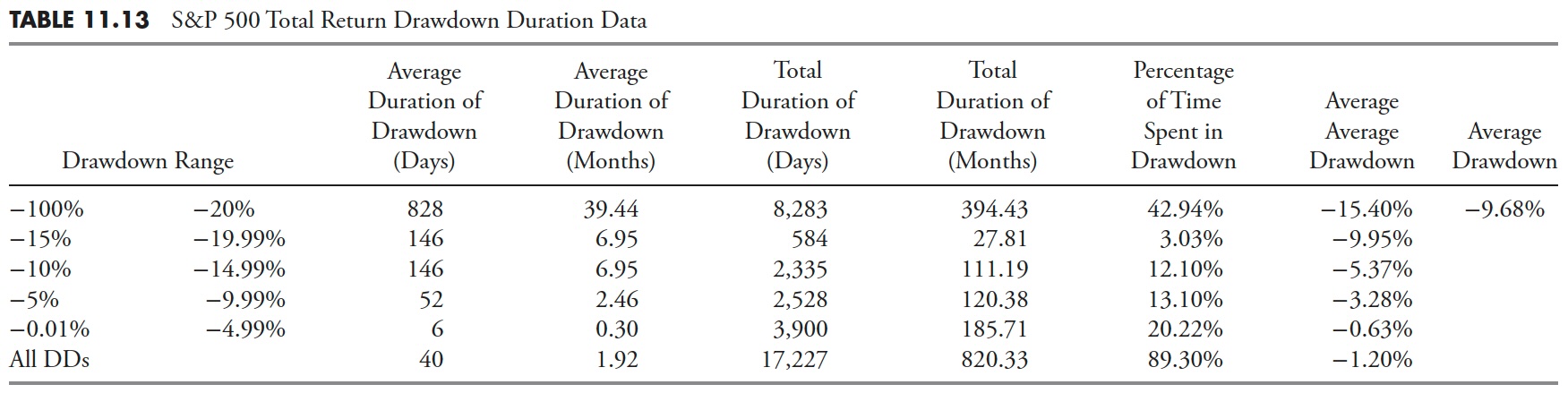
Drawdown Period — S&P 500
Drawdown Period is proven in Desk 11.4; that is the overall period of time {that a} full drawdown occurred. The earlier two tables handled the decline and the restoration, this desk is the overall of these two.
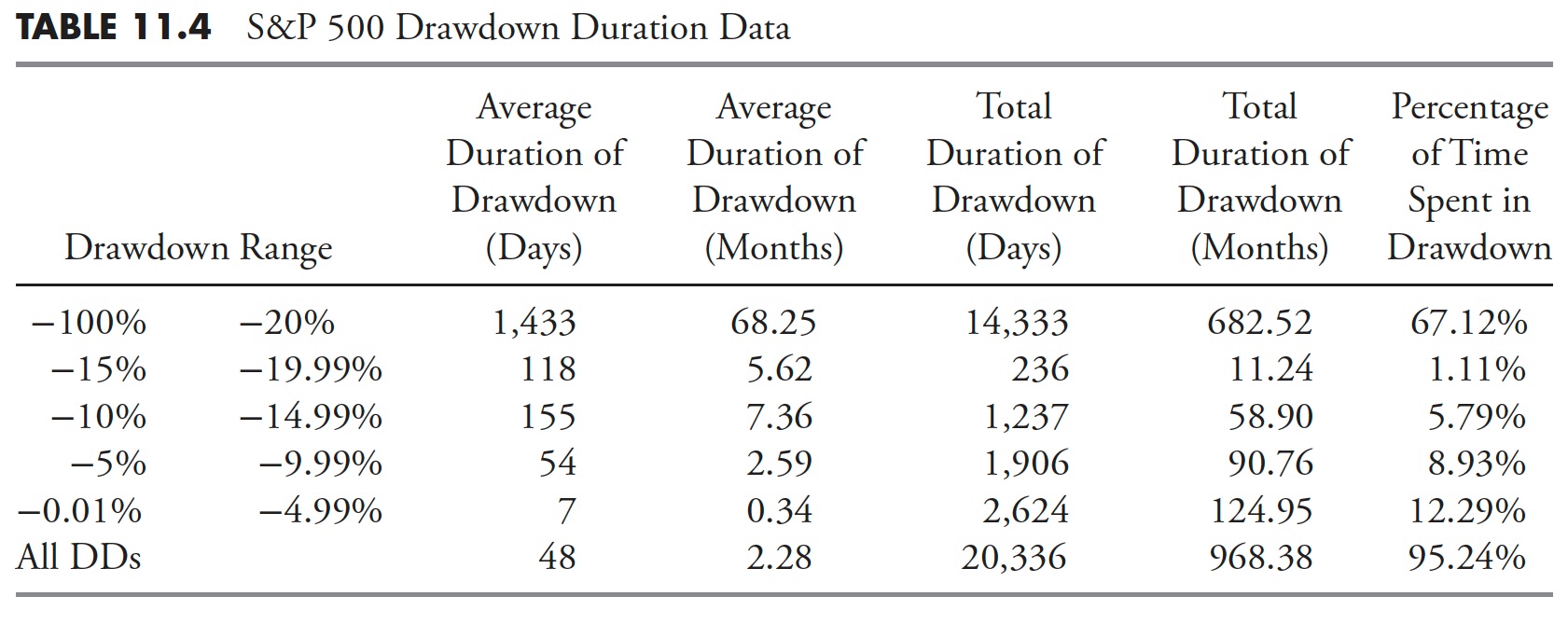
Drawdowns of larger than 20% averaged 1,433 days, which is greater than 68 months, or about 5-6 years. The full variety of days of all drawdowns larger than 20% was 14,333 market days, or 682 months, which is greater than 56 years. Now the true eye-catcher on this desk is the final row, which exhibits all drawdowns whatever the share decline. It exhibits that the market from 1927 to 2012 was in a state of drawdown for greater than 95% of the time. In different phrases, the market was making new all-time highs lower than 5% of the time.
The Drawdown Message — S&P 500
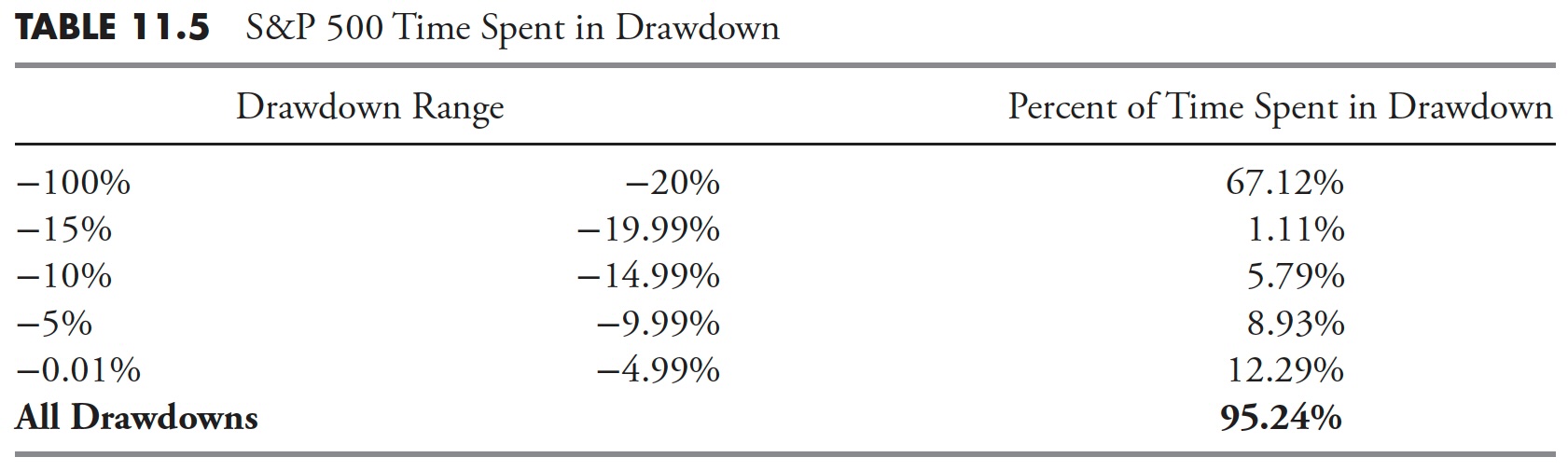
With all of the above tables in regards to the varied phases of drawdown, the data taken from the Drawdown Period desk in Desk 11.5 is the true message from this Drawdown Evaluation; the share of time that the market, on this case the S&P 500 Index, has spent in a state of drawdown. In different phrases, the period of time that the market has spent simply to get again to the place it had already been earlier than is what most people don’t understand. Even for those who eradicated the noise, that are the drawdowns of lower than 5%, the market has been in a state of drawdown for 82-95% of the time.
Various Methodology
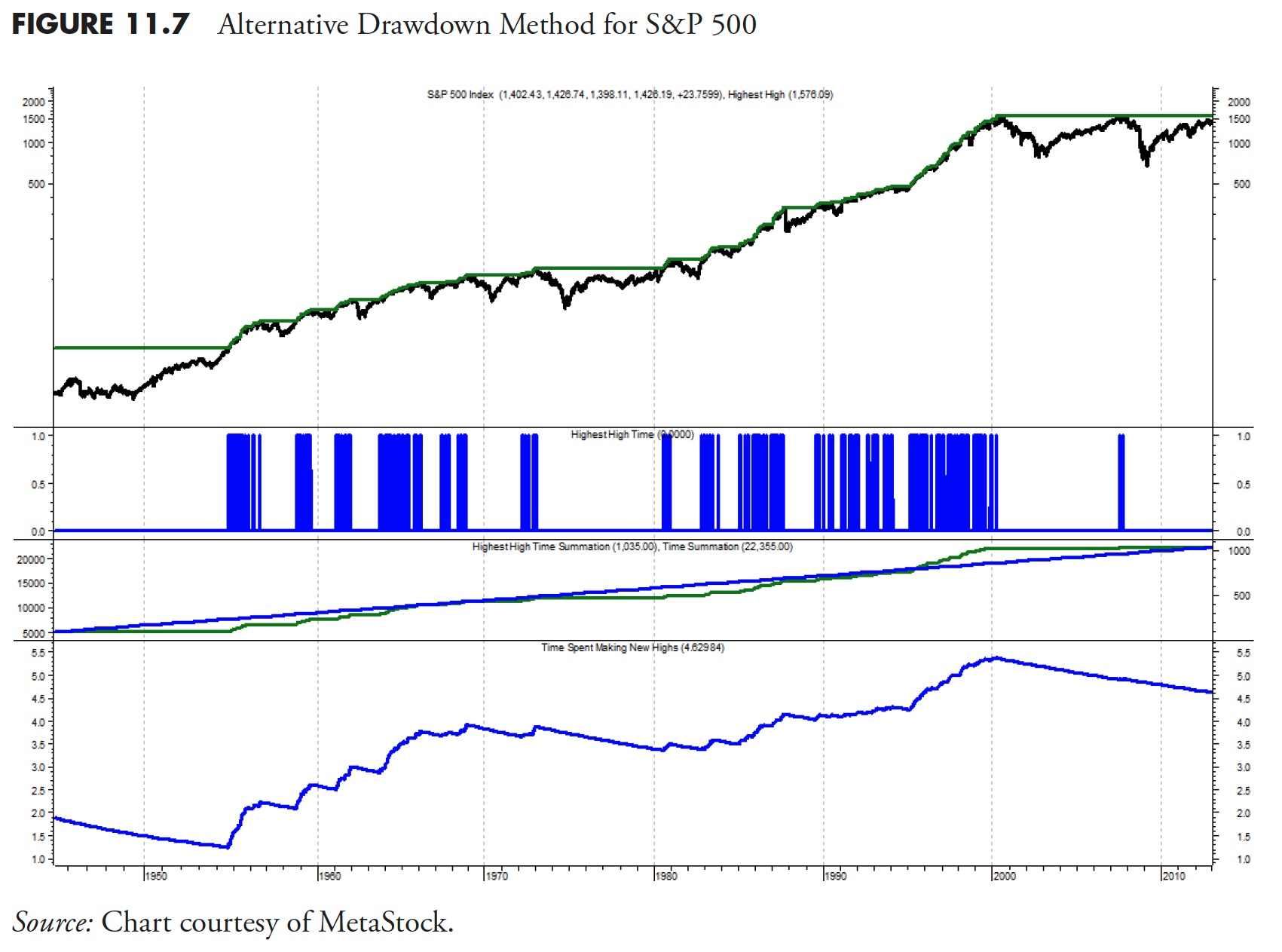
Determine 11.7 and the evaluation under exhibits an alternate methodology to validate this drawdown evaluation. On this mathematical course of, the period of time spent making new all-time highs was calculated utilizing the identical S&P 500 information. The highest plot is the S&P 500 worth proven plotted utilizing semi-log scaling. The jagged line that strikes alongside the highest of the information is a line representing the all-time excessive worth. It solely strikes up when the S&P is making a brand new all-time excessive, and strikes sideways when the S&P is declining under its earlier all-time excessive. The second plot is a calculation to establish solely the times by which the all-time excessive line within the prime plot was shifting upward; in different phrases, the times by which the S&P 500 was making a brand new all-time excessive. The third plot has two strains; one is a summation of the second plot or the working sum of all the times making a brand new all-time excessive in worth. The second line within the third plot is simply calculating all the times of knowledge within the S&P 500 by utilizing the straightforward idea of Shut worth not equal to zero after which doing the working summation. The underside plot is the % of the brand new all-time highs summation to the overall of all days of knowledge. You’ll be able to see (belief me) that the share of time the S&P 500 was making new all-time highs is 4.63%. Within the earlier drawdown evaluation, it was proven that every one drawdowns contained 95.24 % of the information. 100% – 95.24% = 4.76%, which suggests there may be solely a 0.13% distinction between the 2 completely impartial calculations.
Common Drawdown — S&P 500
A further calculation has been added to Desk 11.4 — S&P 500 Drawdown Period Knowledge, proven in Desk 11.6 as two new columns. These are the typical of the typical drawdown for every share class, and the overall common of all drawdowns.
Whereas the information within the earlier tables breaks down the drawdowns over varied ranges of share of decline, a standard mistake on this planet of finance is to give attention to a time period referred to as most drawdown when evaluating two points, corresponding to two mutual funds. One should remember the fact that most drawdown is a one-time remoted occasion and could possibly be deceptive.
Right here is an instance: Let’s assume we’re two mutual funds, every with a 20-year historical past of web asset worth (NAV). Fund A has a most drawdown of 45% and Fund B has a most drawdown of 30%. Which fund do you like? Most will say that Fund B is healthier as a result of it has a smaller most drawdown. And they might be appropriate, however I believe they should view extra info from the 20 years of knowledge. For example Fund B had 12 extra drawdowns of 25% every and Fund A had extra drawdowns, with the most important being solely 12%. Now which fund do you want? Whereas the utmost drawdown is larger on Fund A, the entire remaining drawdowns are significantly lower than these for Fund B. This is the reason I want to take a look at Common Drawdown, as proven in Desk 11.6.
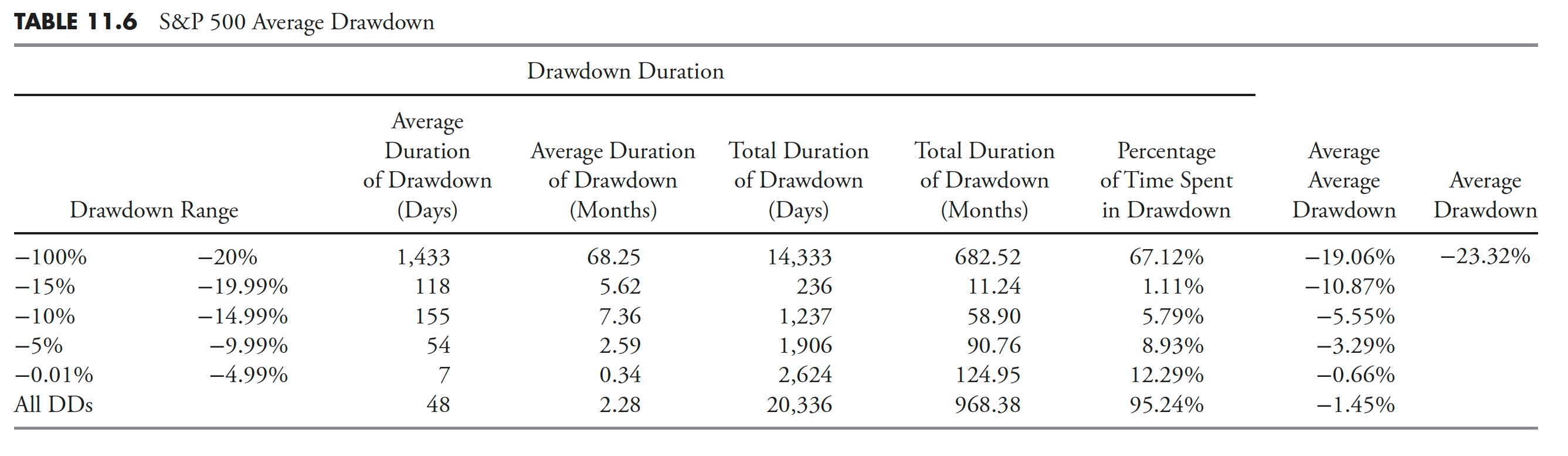
Distribution of Drawdowns — S&P 500
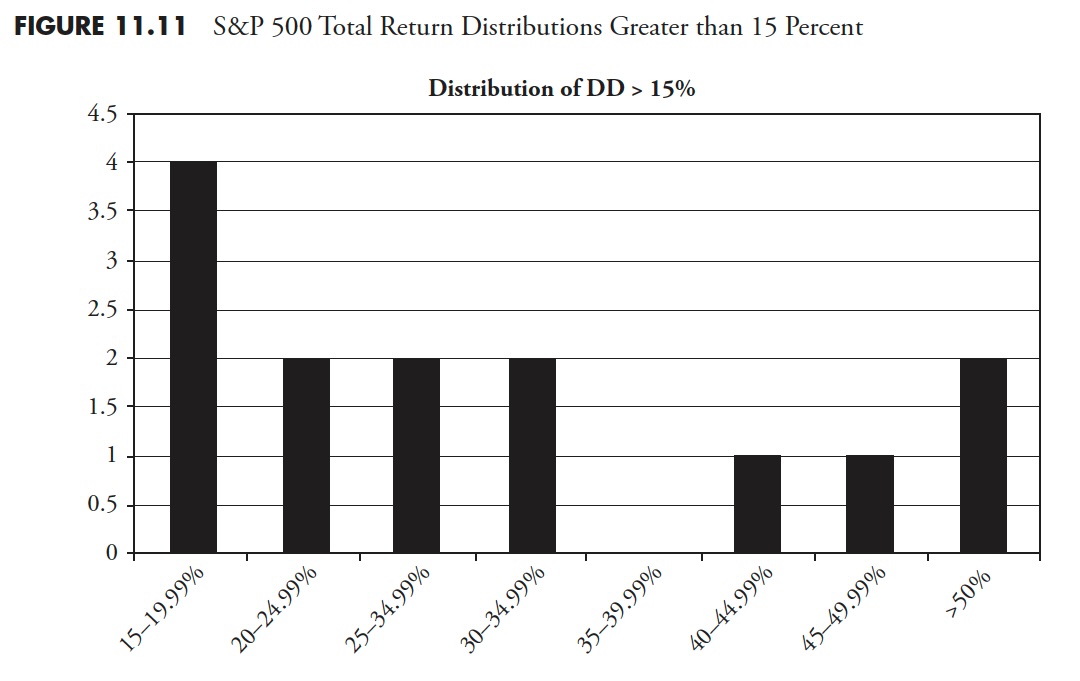
Determine 11.8 exhibits all drawdowns that had been larger than 15%. You’ll be able to see that for the interval from 1927 to 2012, the S&P 500 had 2 drawdowns within the 15–19.99% vary, 2 within the 20–24.99% vary, and so forth, for a complete of 12 draw-downs of magnitude larger than 15%. Apparently, there have been no drawdowns within the 40–44.99% vary. I might guess that after a market has declined over 40%, it creates a lot concern it can’t cease till it strikes additional first.
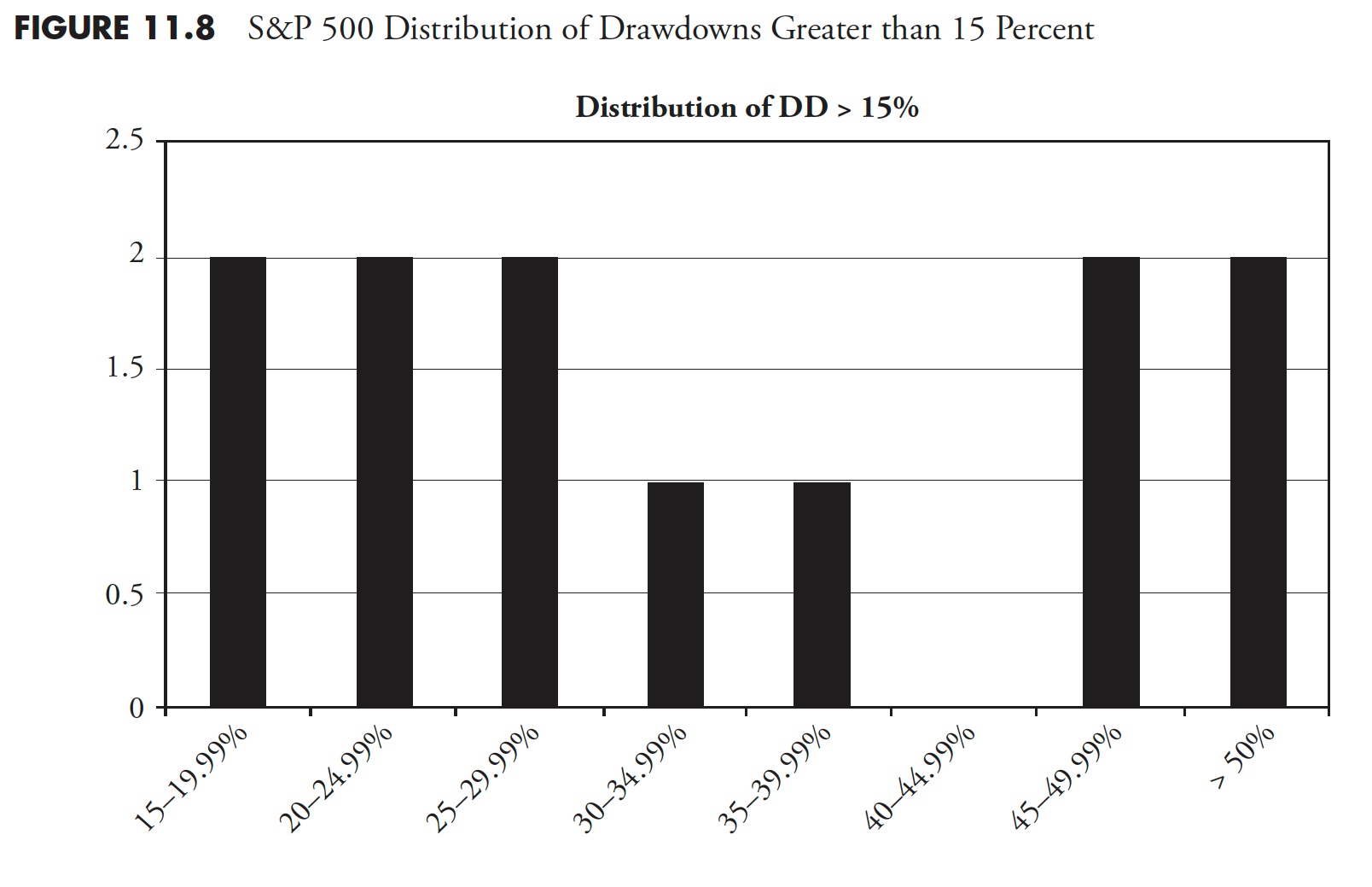
Determine 11.9 exhibits all drawdowns, irrespective of how small. You’ll be able to see that there have been 424 drawdowns, with 369 of them lower than 5%. 5 % declines are usually thought-about simply noise and a part of the market pricing mechanism. Drawdowns between 5% and 10% are thought-about pullbacks; there have been 35 pullbacks throughout this era. Corrections are drawdowns between 10% and 20%; you may see that there have been 10 (complete of 10–14.99% and 15–19.99%). There have been 10 drawdowns of 20% or larger. Additionally discover that Determine 11.8 is mirrored in Determine 11.9, simply that 3 extra distribution percentages had been added to the left.
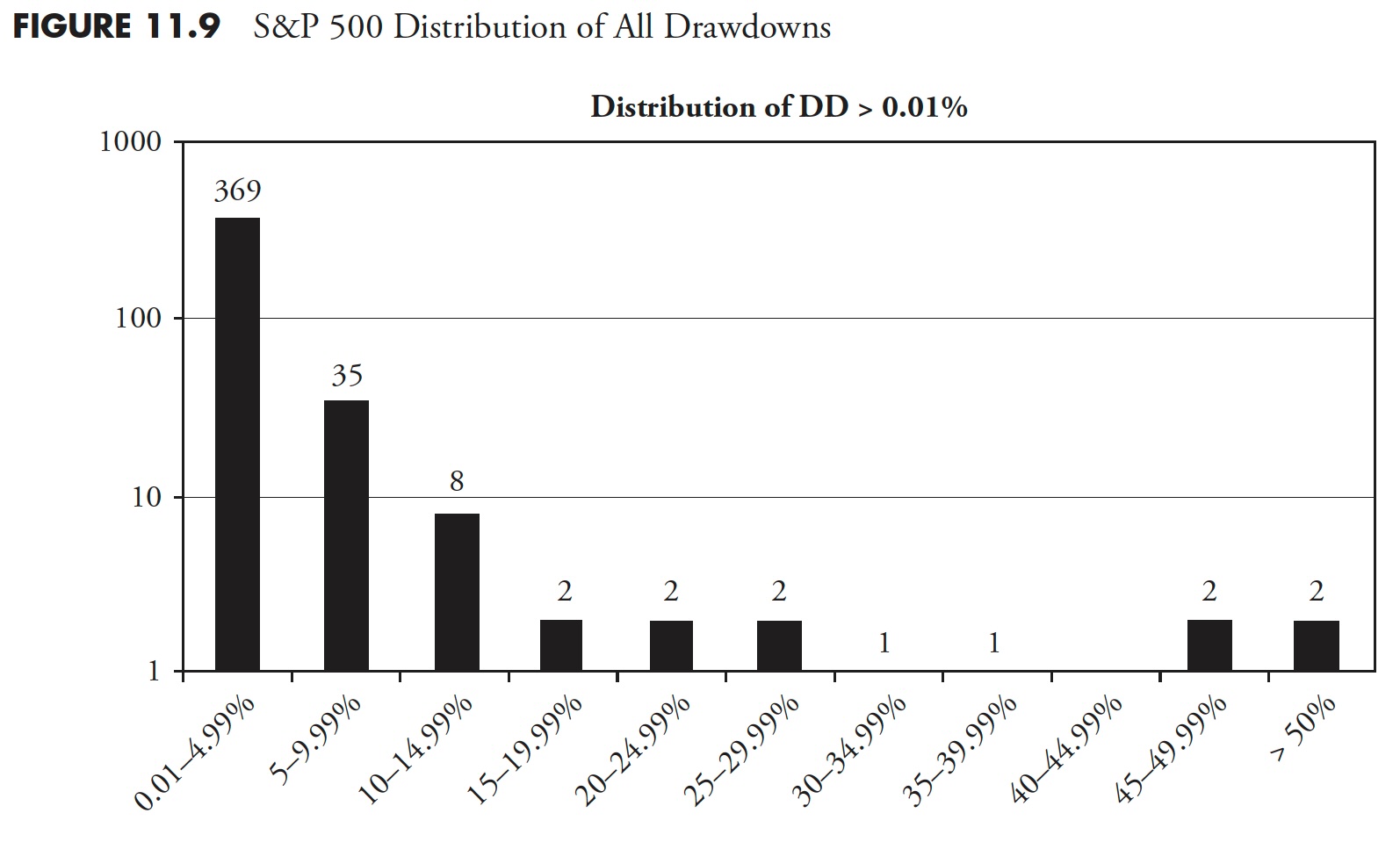
Cumulative Drawdown for S&P 500
Determine 11.10 exhibits you a visible of all drawdowns through the evaluation interval. The 1929 drawdown is clearly distinctive not solely in magnitude of decline, but in addition period; a lot in order that it skews the visible impact of the remaining drawdowns.
S&P 500 Index Excluding the 1929 Bear Market
Usually it’s good to take away some statistical outliers, corresponding to the large drawdown/bear market that started in 1929 and lasted till 1954, 25 years complete. The tables that comply with (Desk 11.7, Desk 11.8, and Desk 11.9) present the S&P 500 from 1927 to 2012 with precisely the identical information because the earlier respective tables; nevertheless, this time, the Nice Melancholy drawdown has been faraway from the information.
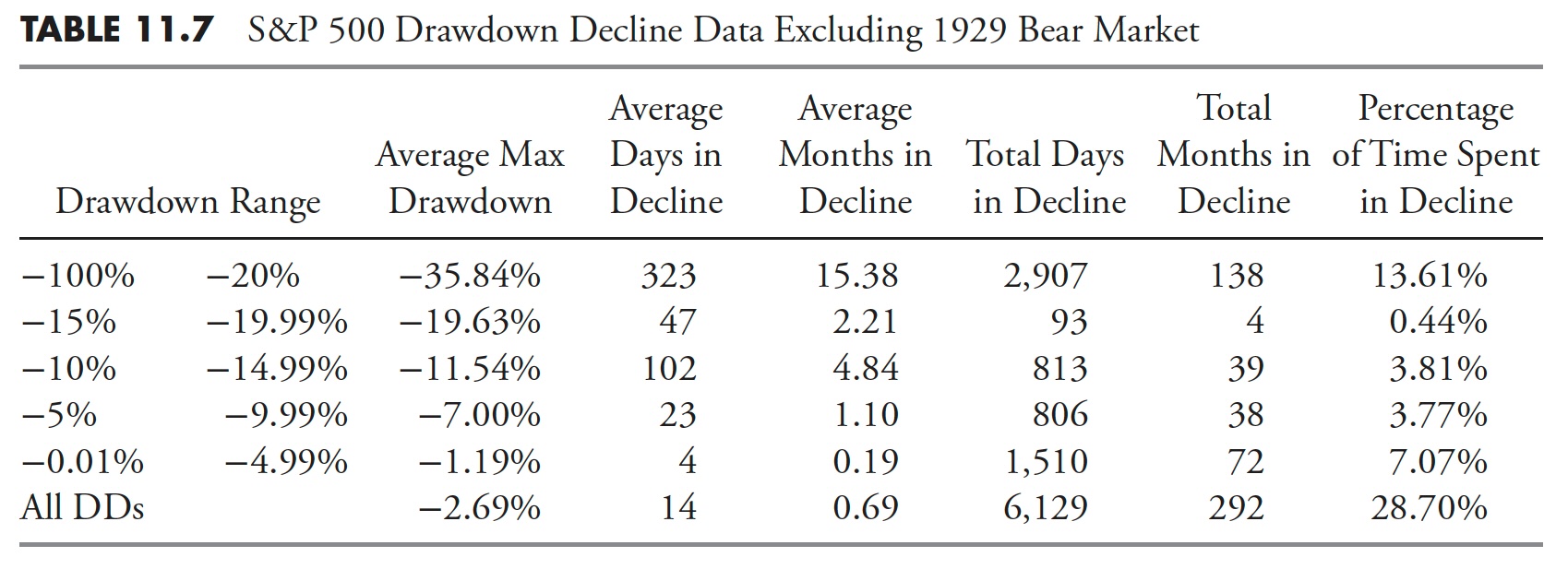
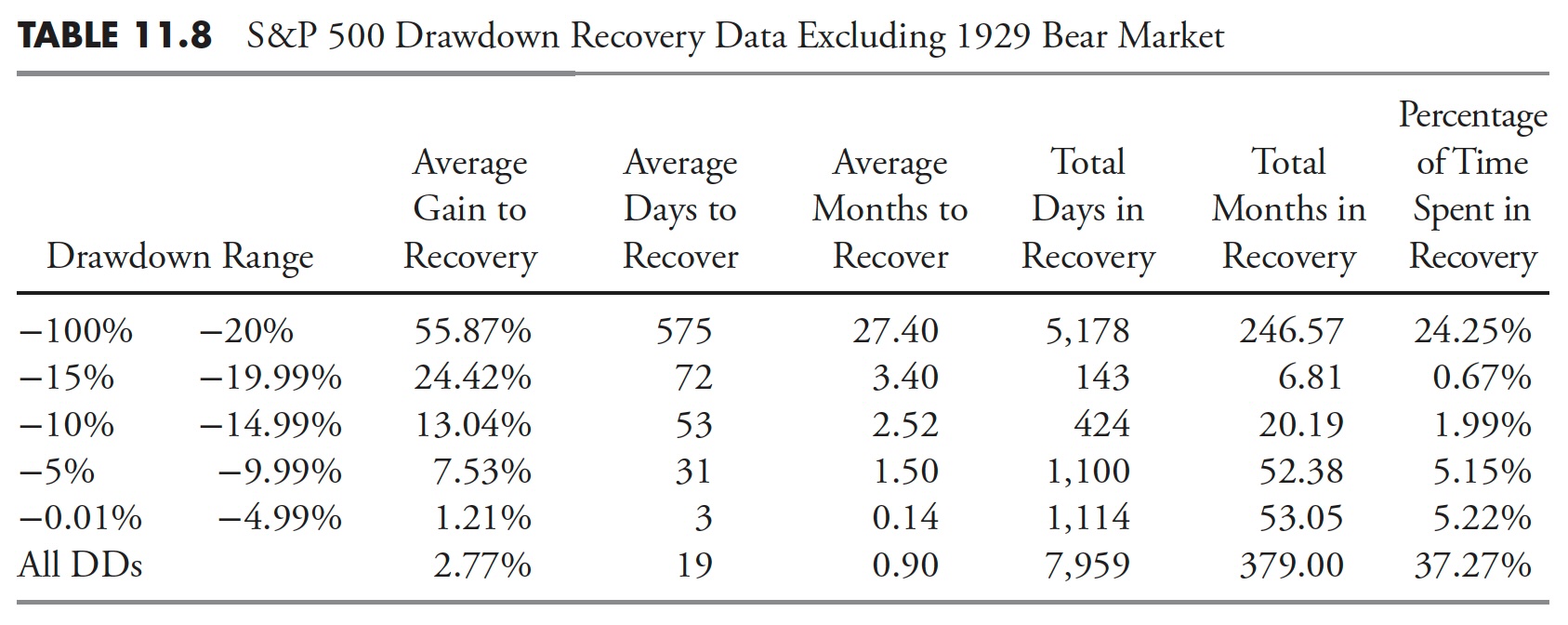
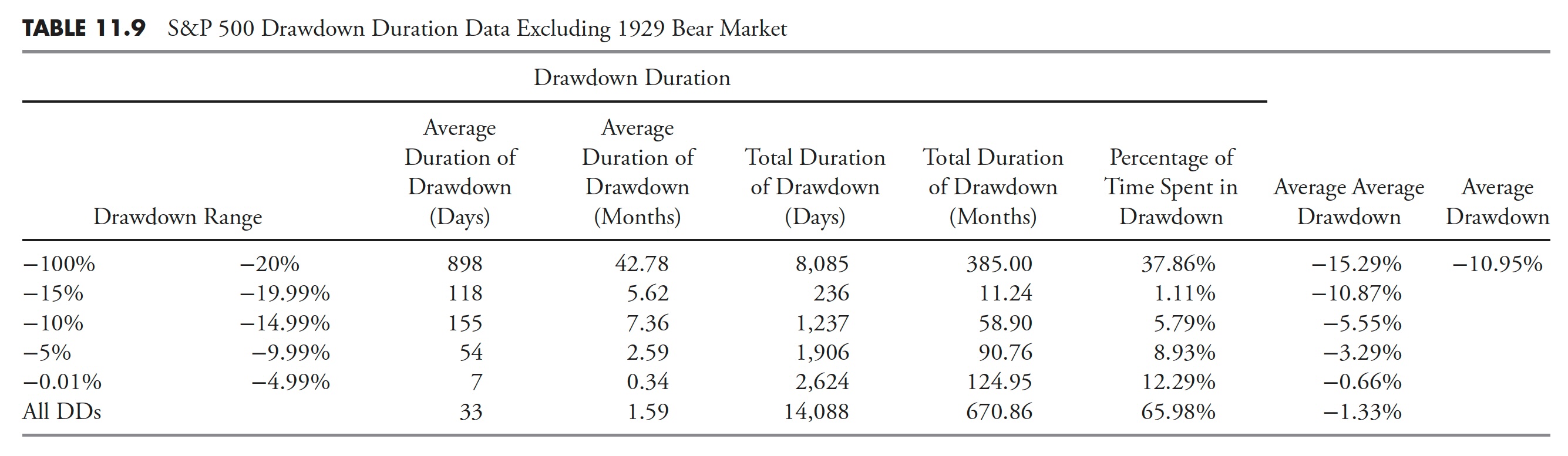
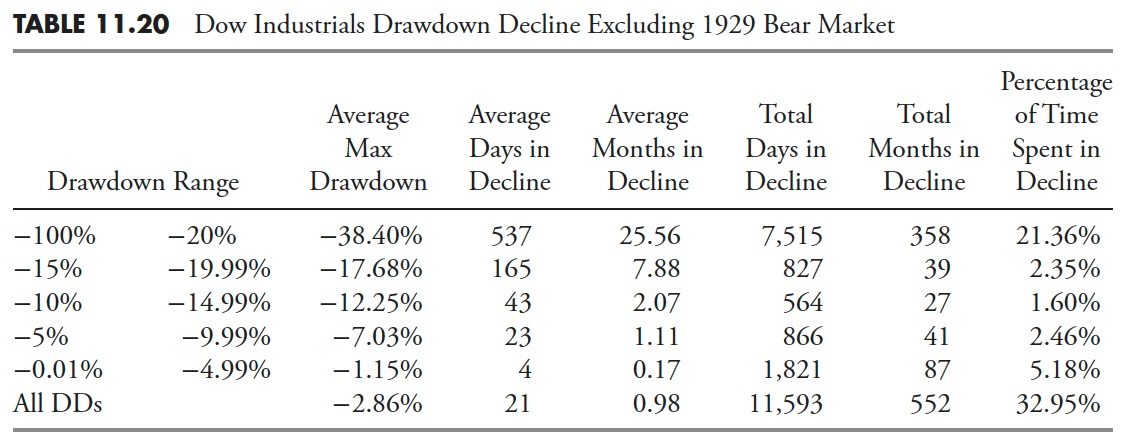
The Common Max Drawdown has decreased from -40.88% to solely -35.84% for drawdowns greater than 20%. You’ll be able to have a look at the numbers for the remaining columns and see that they’re all diminished, nevertheless, not by practically as a lot as I might have guessed previous to doing the evaluation.
Restoration information appears to have been diminished considerably extra when eradicating the 1929 Melancholy drawdown. It is because not solely was the magnitude of that bear market over -86%, nevertheless it additionally lasted for greater than 25 years.
As a result of the Restoration numbers had been considerably diminished with the removing of the 1929 bear market, it additionally stands to purpose that the period numbers would even be considerably diminished. And Desk 11.9 confirms that’s the case.
Drawdowns Higher than 20% are Bear Markets
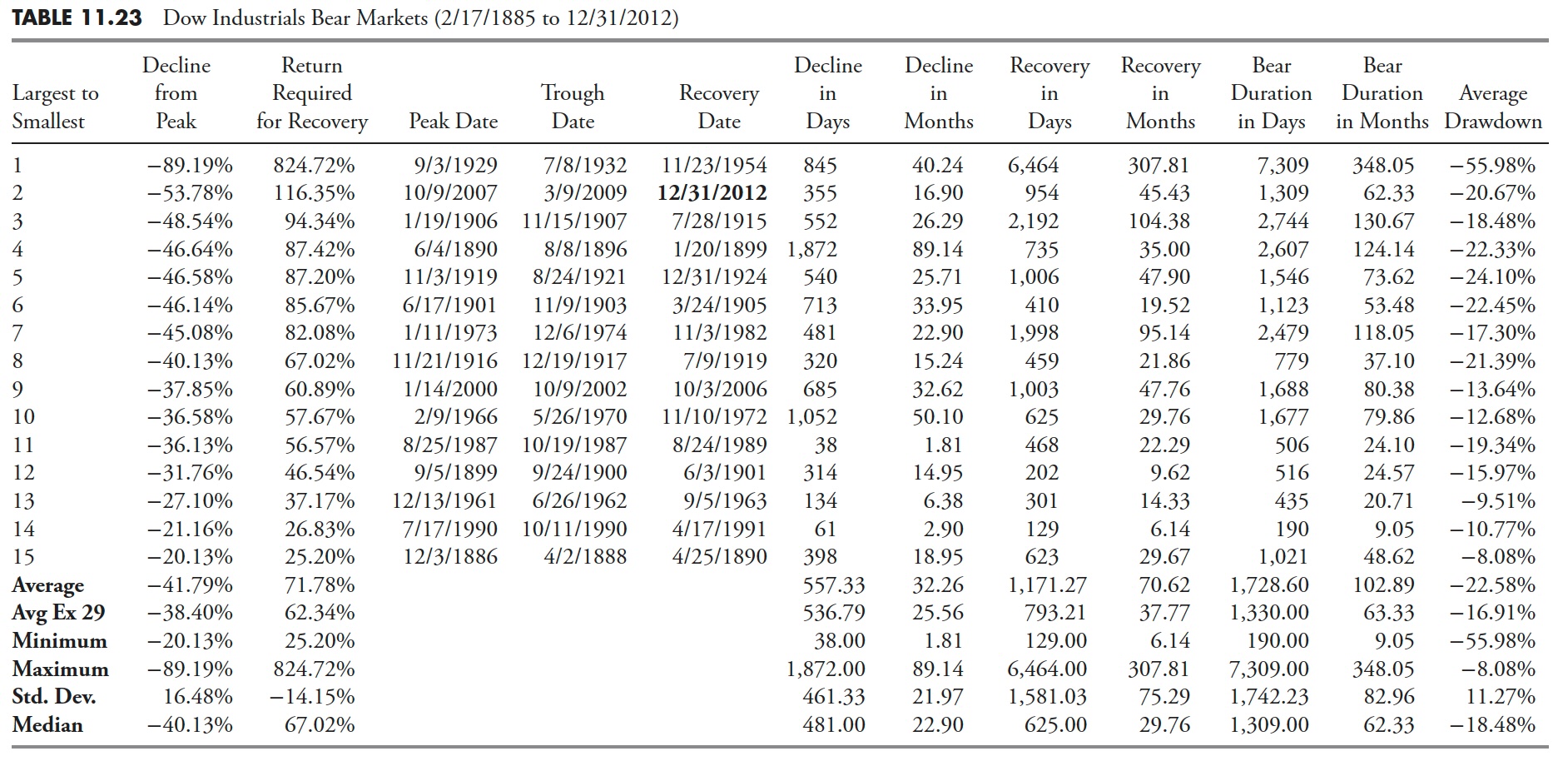
Though that is additionally proven in earlier chapters, it’s applicable to incorporate with this part of the guide on Drawdown Evaluation as a result of bear markets are merely drawdowns of 20% or larger. Desk 11.10 exhibits all of the drawdowns (bear markets) of 20% or larger within the S&P 500 Index since 12/30/1927. Here’s a transient description of the statistics which are on the backside of Desk 11.10.
- Common. The identical because the imply in statistics; add all values after which divide by the variety of gadgets.
- Avg Ex 29. That is the Common with the 1929 bear market eliminated because it skews the information considerably.
- Minimal. The minimal worth in that column.
- Most. The utmost worth in that column.
- Std. Dev. That is customary deviation or sigma, which is a measure of the dispersion of the values within the column. About 65% of the values will fall inside one customary deviation of the imply, and 95% will fall inside two customary deviations of the imply.
- Median. If the information is extensively dispersed or has asymptotic outlier information, that is normally a greater measure for central tendency than Common.
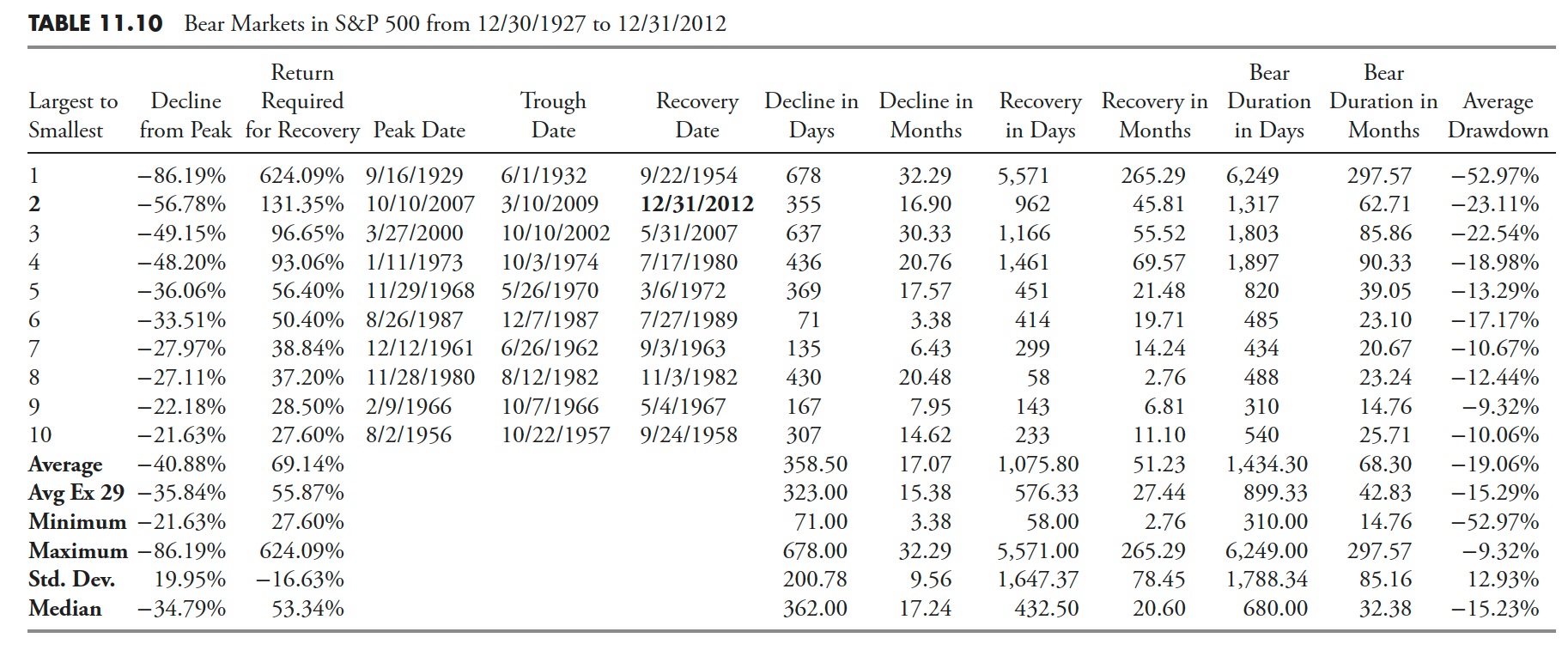
The quantity two drawdown as of 12/31/2012 continues to be in progress. Whereas its magnitude of decline was -56.78%, the period continues to be in progress and solely fourth in rank as the present quantity 3 and 4 drawdowns, whereas not as steep, lasted longer.
S&P Whole Return Evaluation
This information will not be as sturdy as the worth information, however does replicate the fact of the markets for buy-and-hold or index investing, by which one obtained and reinvests the dividends earned by the person shares that make up the index. This information begins on March 31, 1936, so due to this fact is not going to embody the Nice Melancholy drawdown that started in 1929. Tables 11.11 by way of 11.13, Figures 11.11 and 11.12, and Desk 11.14 comply with the format of the previous sections.
Drawdown Decline — S&P Whole Return
Drawdown Restoration — S&P Whole Return
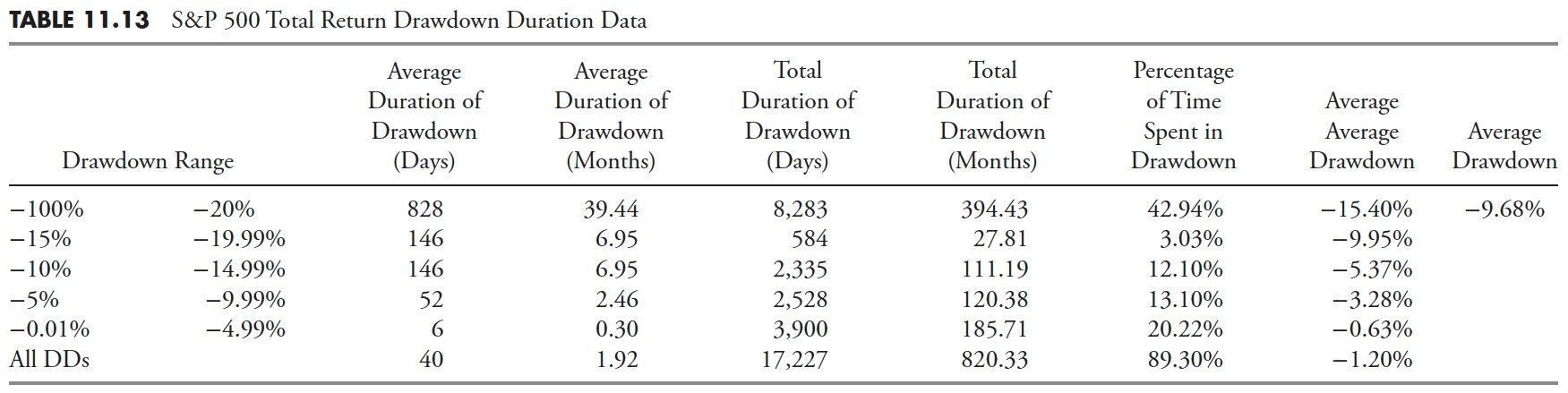
Drawdown Period — S&P Whole Return
Distribution of Drawdowns Higher than 15% — S&P Whole Return
Distribution of All Drawdowns — S&P Whole Return
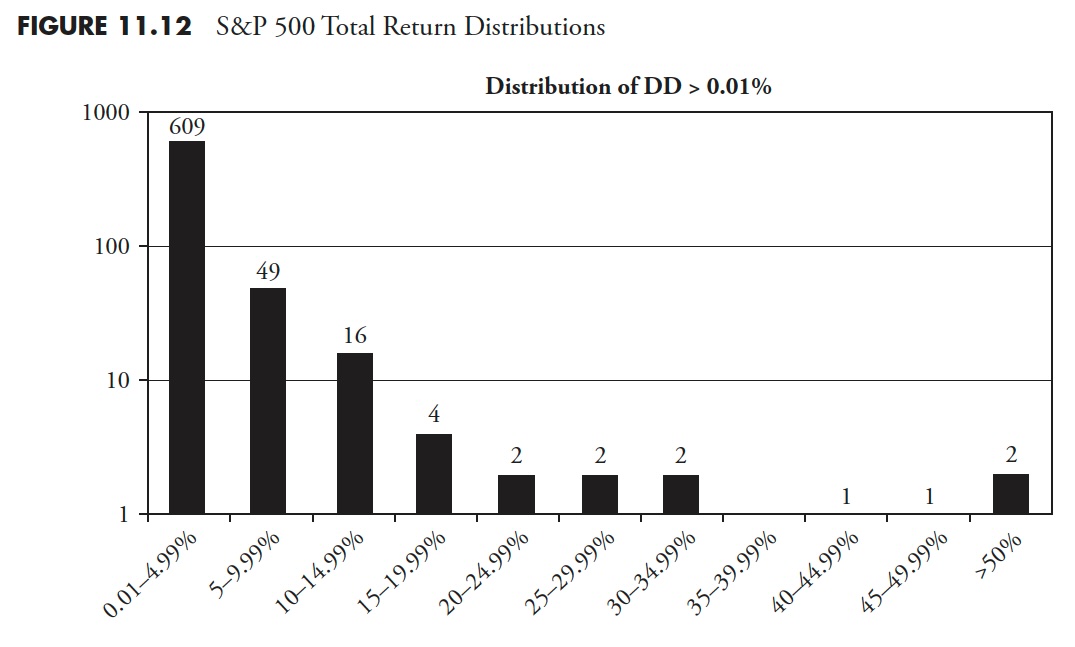
Drawdown Period — S&P Whole Return
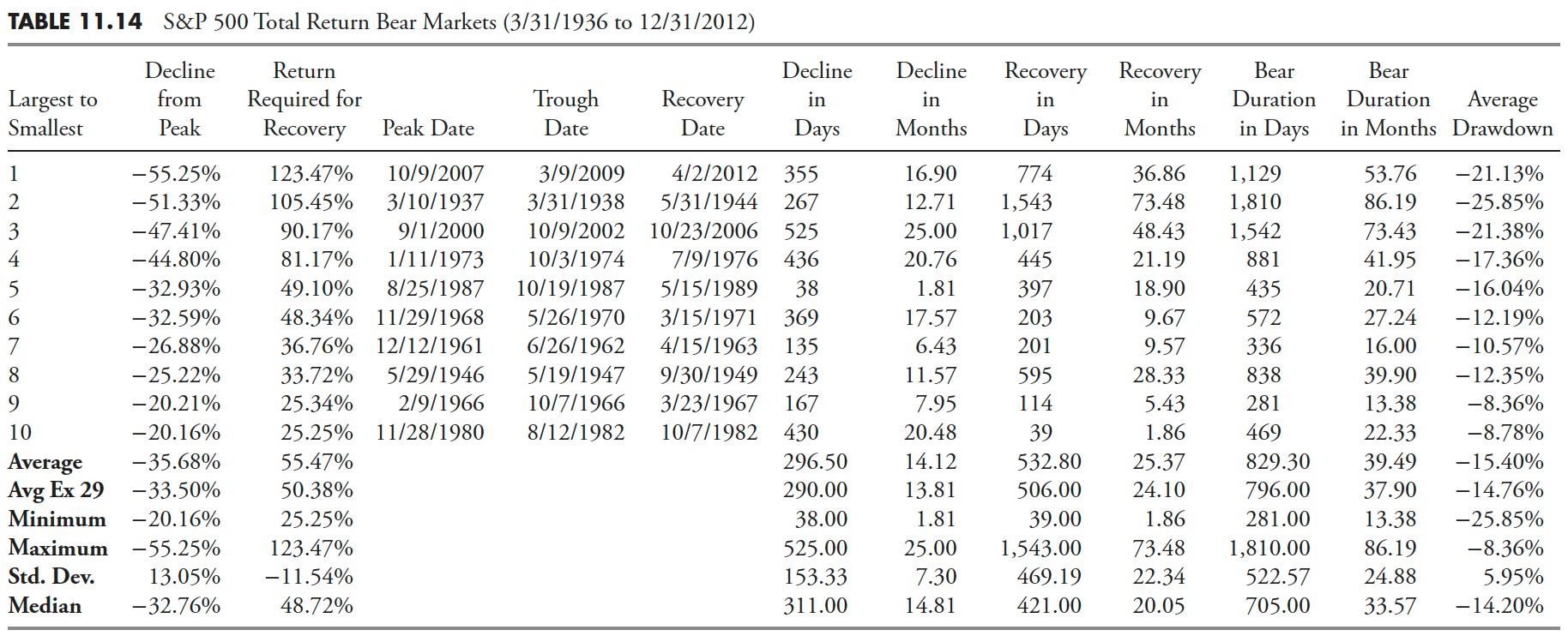
Bear Markets — S&P Whole Return
Dow Jones Industrial Common Drawdown Evaluation
This part follows the identical order and format of the earlier part on the S&P 500 Index drawdown; the one distinction is that the evaluation is completed on the Dow Jones Industrial Common. (See Tables 11.15 by way of 11.19, Figures 11.13 by way of 11.15, and extra Tables 11.20 by way of 11.23.)
The Dow Jones Industrial Common, additionally known as The Dow, is a price-weighted measure of 30 U.S. blue-chip corporations. The Dow covers all industries excluding transportation and utilities, that are lined by the Dow Jones Transportation Common and Dow Jones Utility Common. Though inventory choice will not be ruled by quantitative guidelines, a inventory sometimes is added to the Dow provided that the corporate has a wonderful popularity, demonstrates sustained progress and is of curiosity to a lot of buyers. Sustaining sufficient sector illustration inside the indexes can also be a consideration within the choice course of.
The next information is from the Dow Jones Industrial Common, not adjusted for dividends or inflation, over the interval from February 17, 1885, by way of December 31, 2012. The drawdown evaluation for the Dow Industrials consists of 35,179 market days, which interprets into 1,675.19 calendar months.
Drawdown Decline — Dow Jones Industrial Common
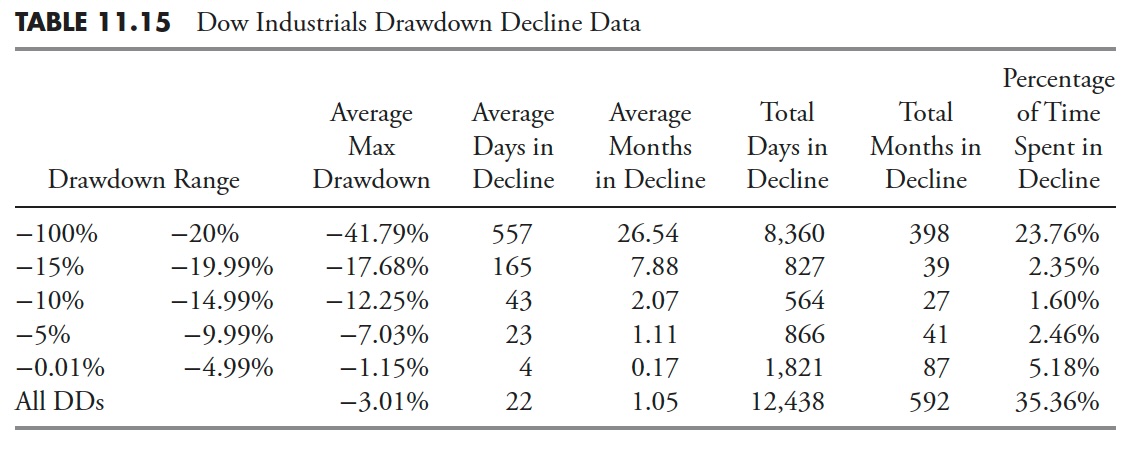
Drawdown Restoration — Dow Jones Industrial Common
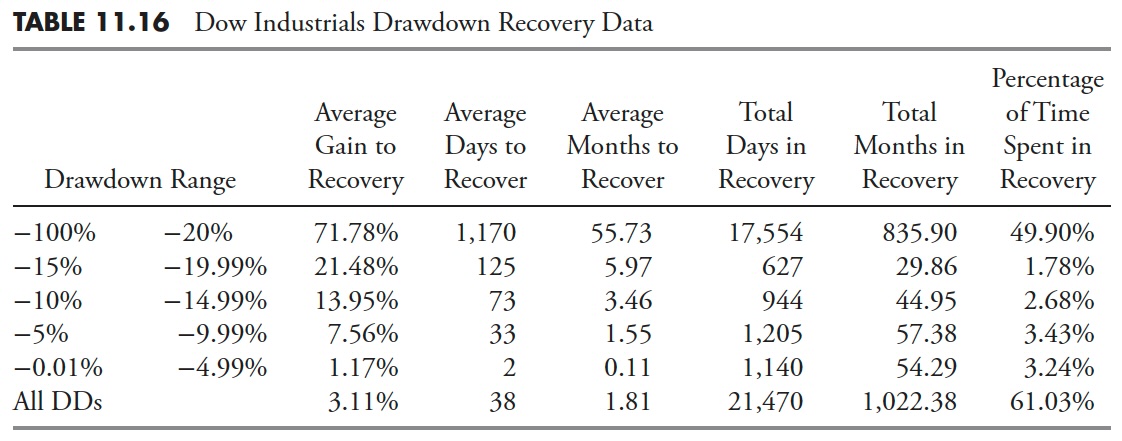
Drawdown Period — Dow Jones Industrial Common
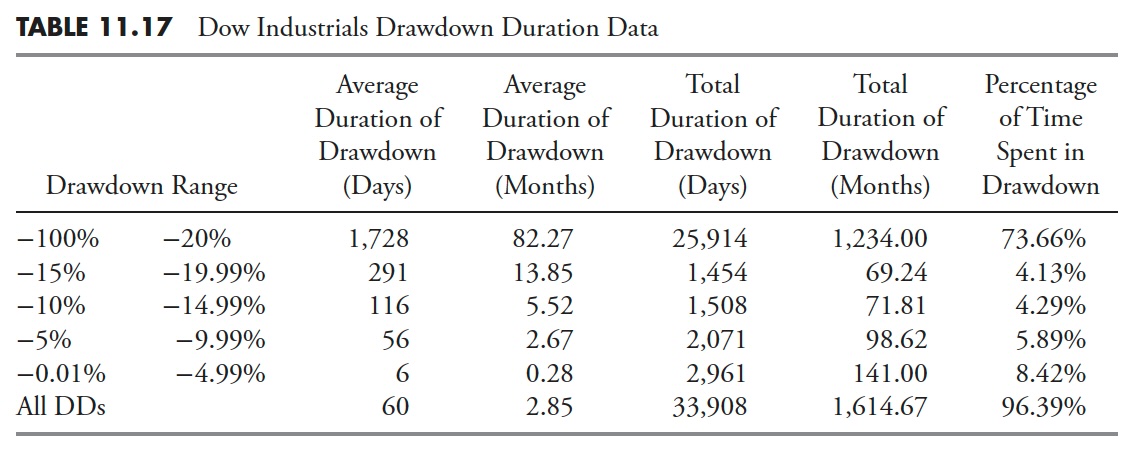
The Drawdown Message — Dow Jones Industrial Common
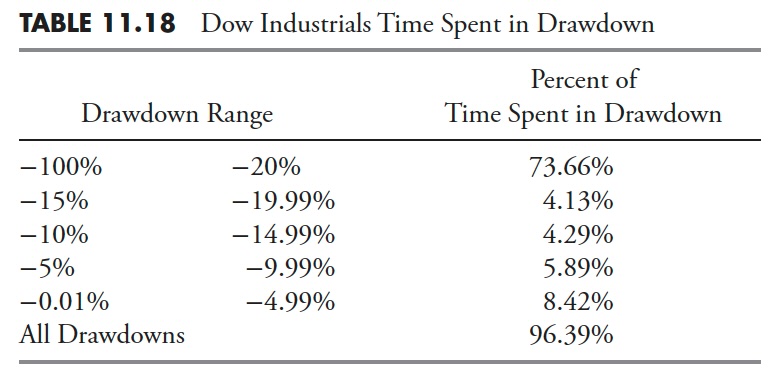
Common Drawdown — Dow Jones Industrial Common
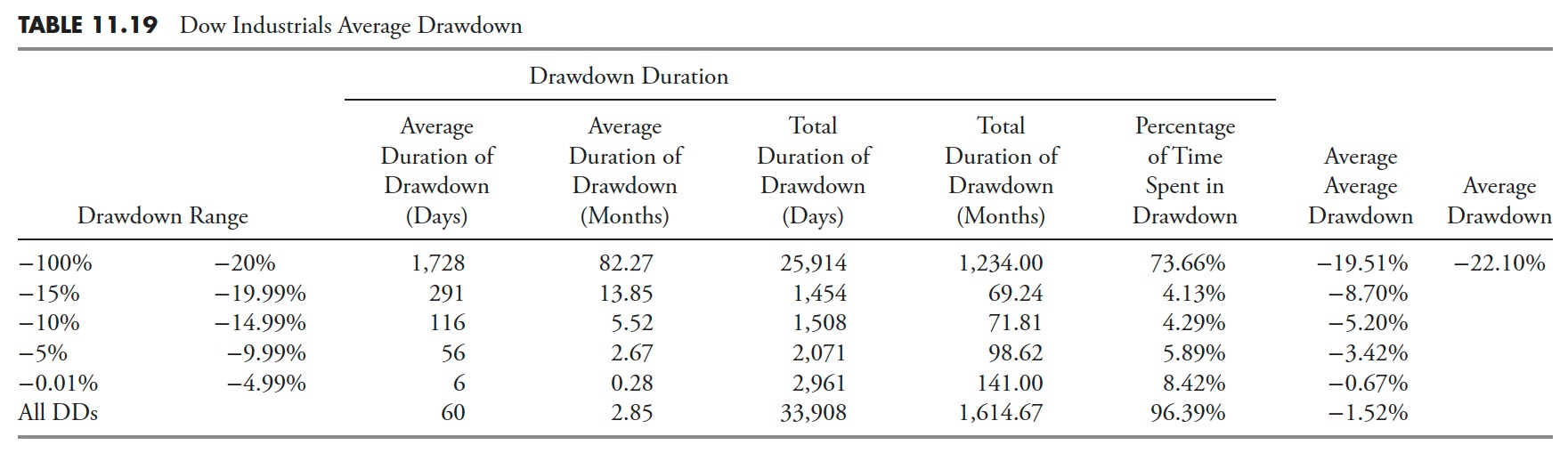
Distribution of Drawdowns — Dow Jones Industrial Common
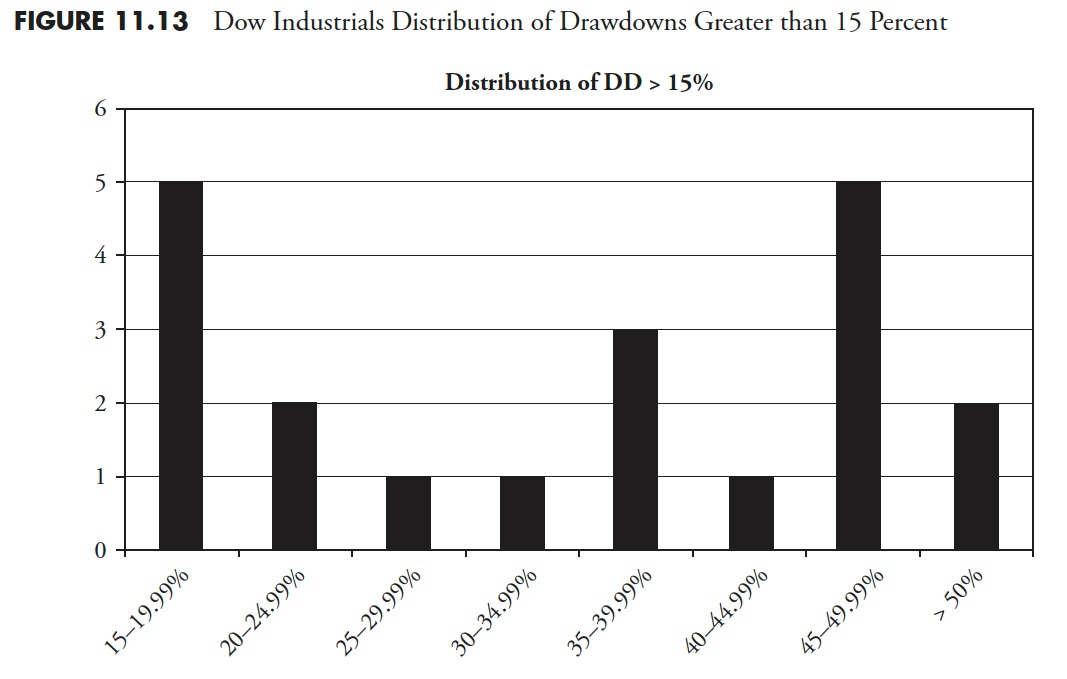
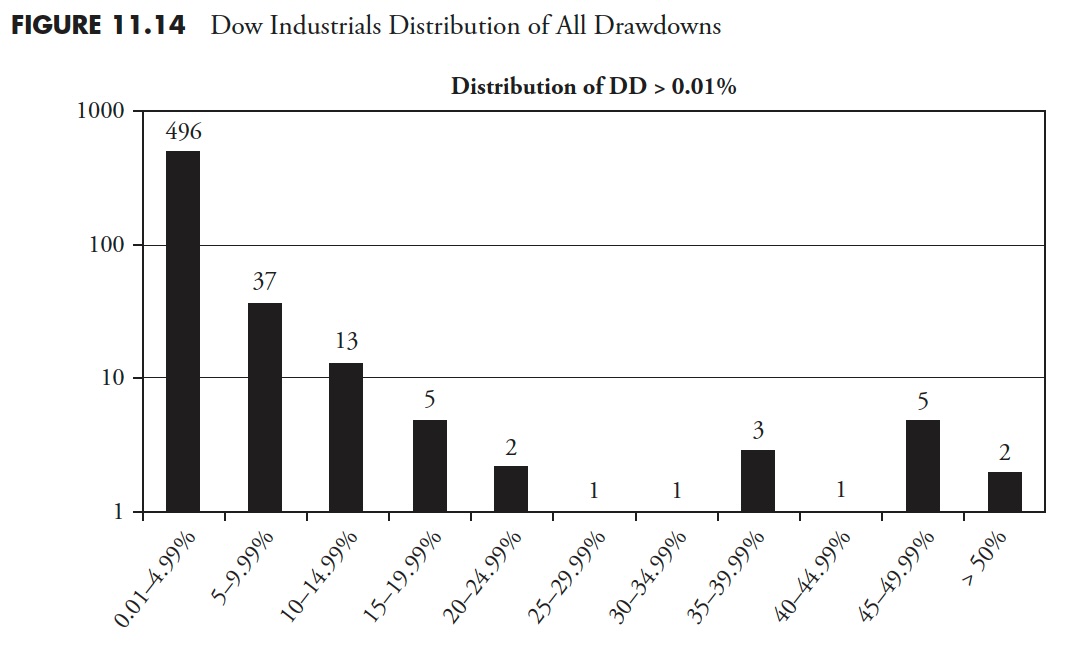
Cumulative Drawdown for Dow Industrials
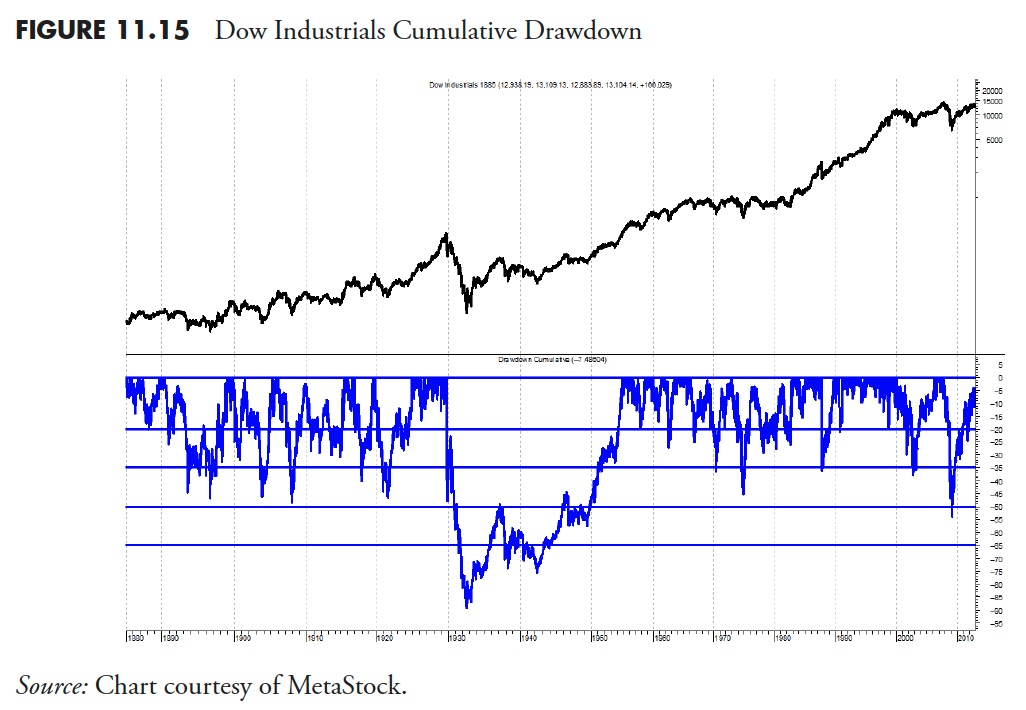
Dow Industrials Excluding the 1929 Bear Market
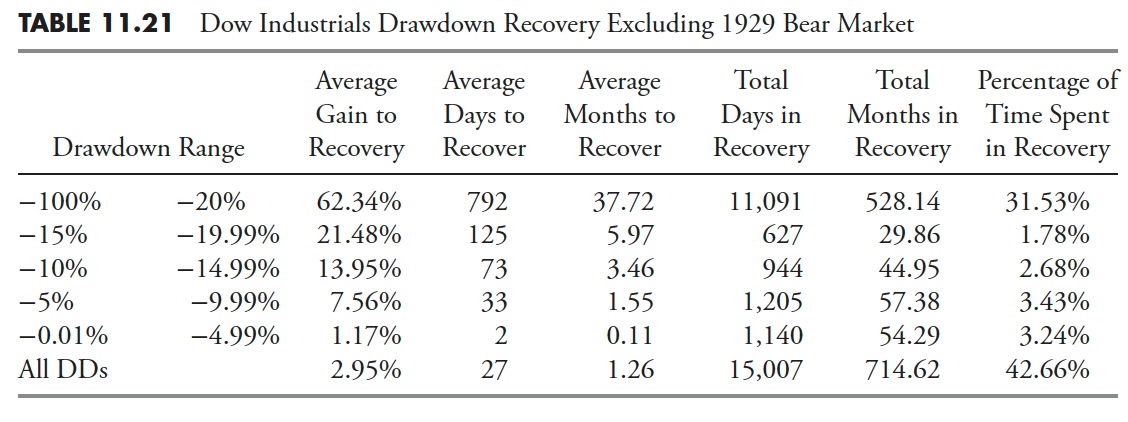
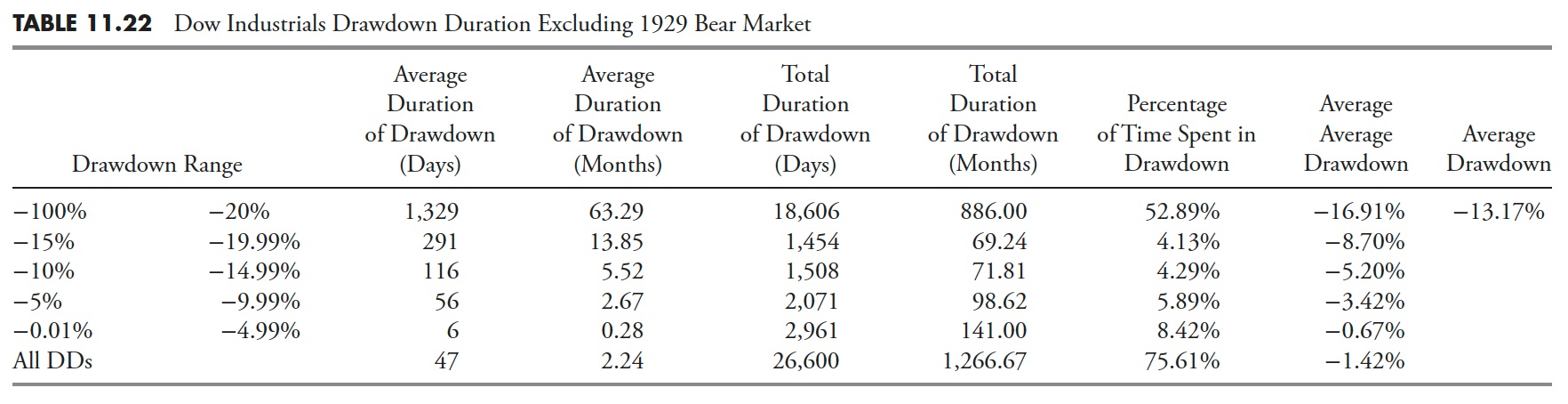 Drawdowns Higher than 20% are Bear Markets
Drawdowns Higher than 20% are Bear Markets
Dow Industrials Whole Return Evaluation
This information is just out there starting on March 31, 1963. (See Tables 11.24 by way of 11.26 and Figures 11.16 and 11.17, adopted by Desk 11.27.)
Drawdown Decline — Dow Industrials Whole Return
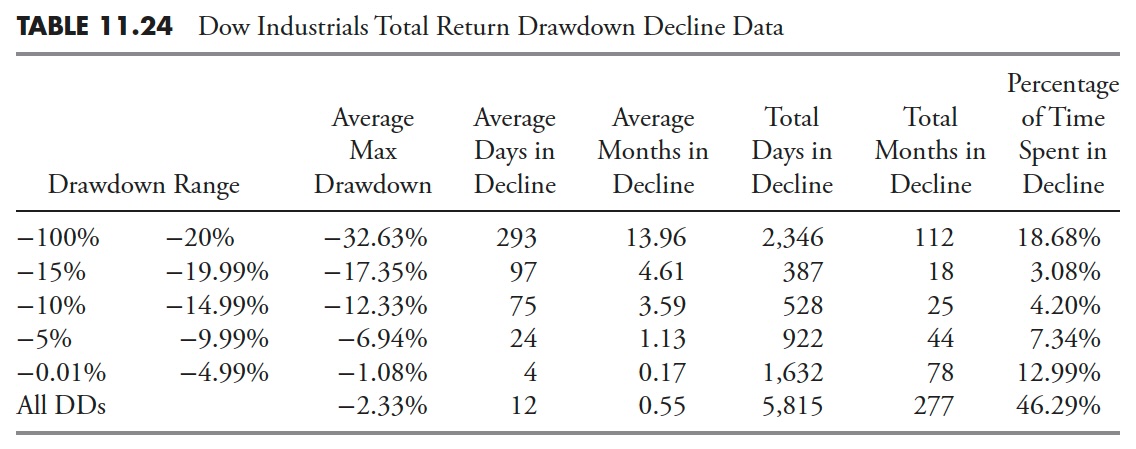
Drawdown Restoration — Dow Industrials Whole Return
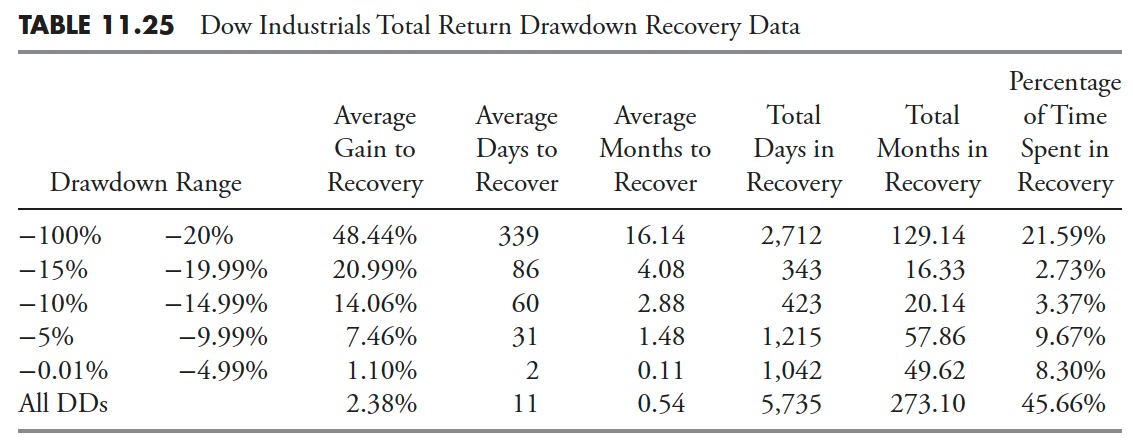
Drawdown Period — Dow Industrials Whole Return
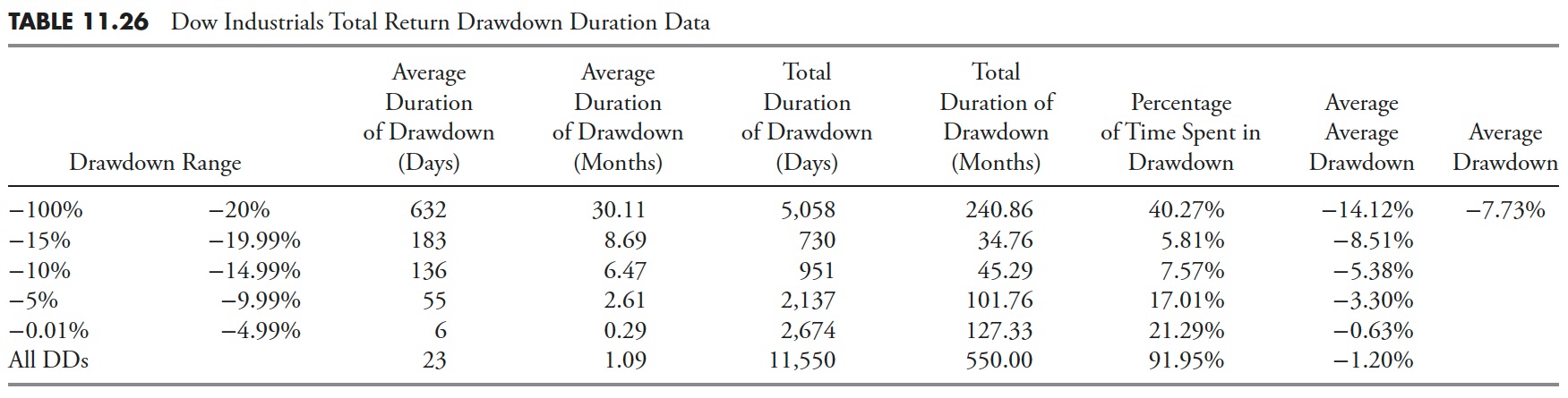
Distribution of Drawdowns — Dow Industrials Whole Return
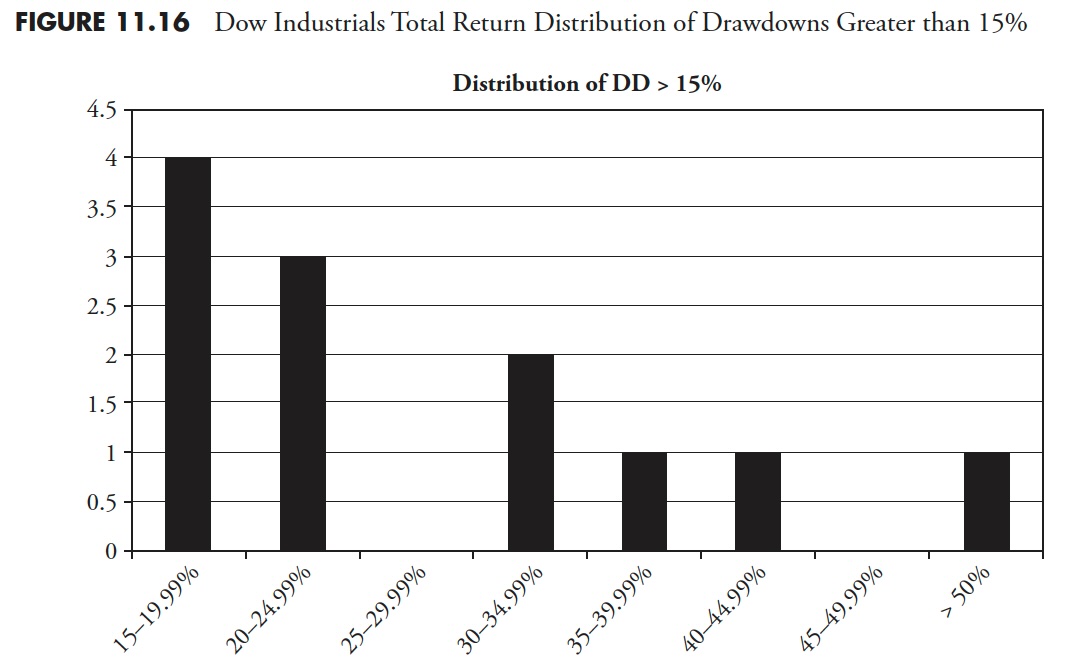
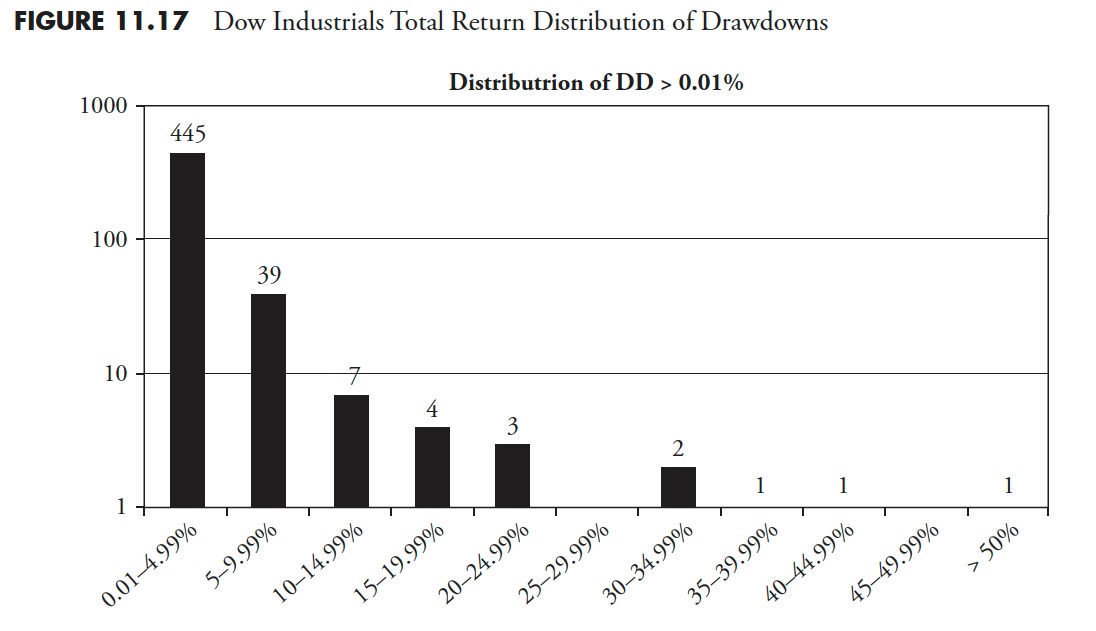
Bear Markets for Dow Industrials Whole Return
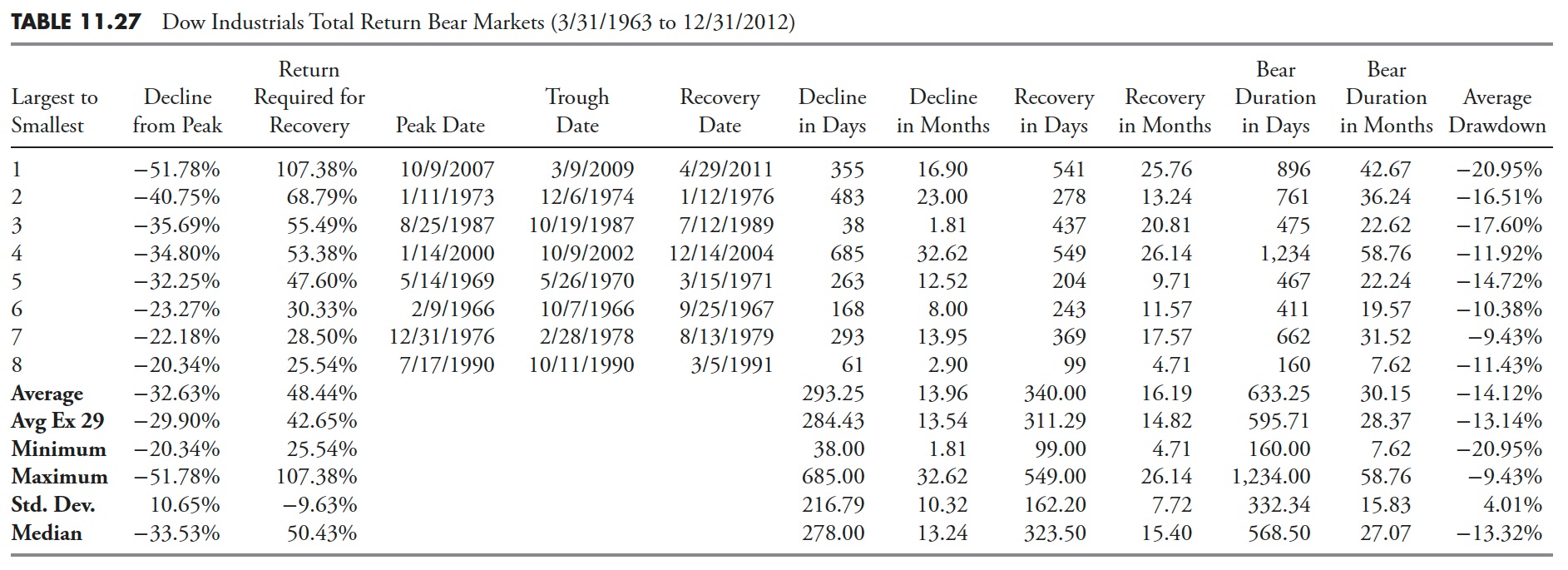
Gold Drawdown
Drawdowns should not restricted to the inventory market; they are often analyzed on any time sequence information.
Determine 11.18 is a chart of gold. This exhibits the worth of gold within the prime plot since 1967 and its cumulative drawdown within the backside plot. The 2 horizontal strains within the drawdown plot are at -20% and -50%. I believe it’s clear that anybody who purchased gold within the Hunt Brothers 1981 silver period, and likewise the ending of the distinctive inflationary interval of the Seventies, held an funding from 1980 till 2008 earlier than the worth of gold recovered. Twenty-eight years is a extremely very long time to carry a loser. With gold’s current surge to new highs (as of 2013), the time worth of cash would most likely proceed to erode this 1980 funding, despite the fact that these people are a minimum of feeling higher now.
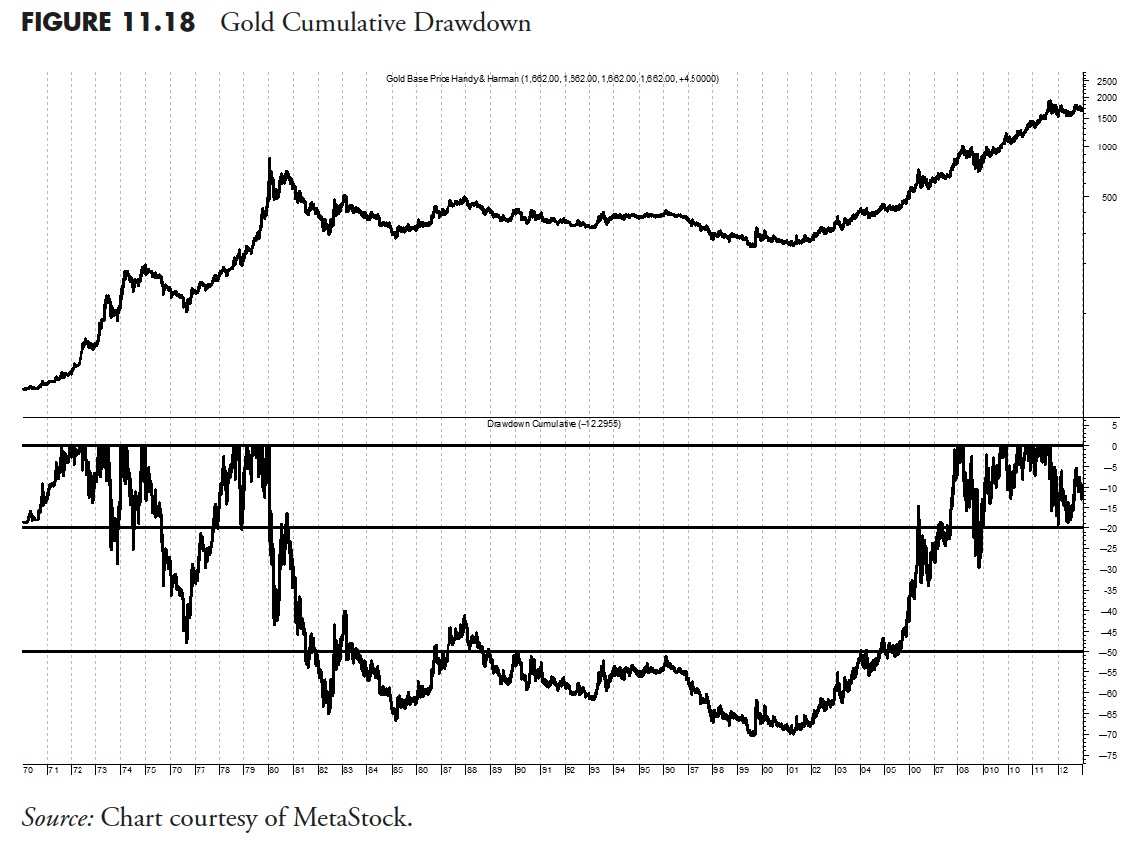
Japan’s Nikkei 225 Drawdown
Determine 11.19 is of the Japanese inventory market and its drawdown. I believe at this level no commentary is required, as you may see that the Nikkei began dropping in late 1989 and is down within the -75% space because the finish of 2008.
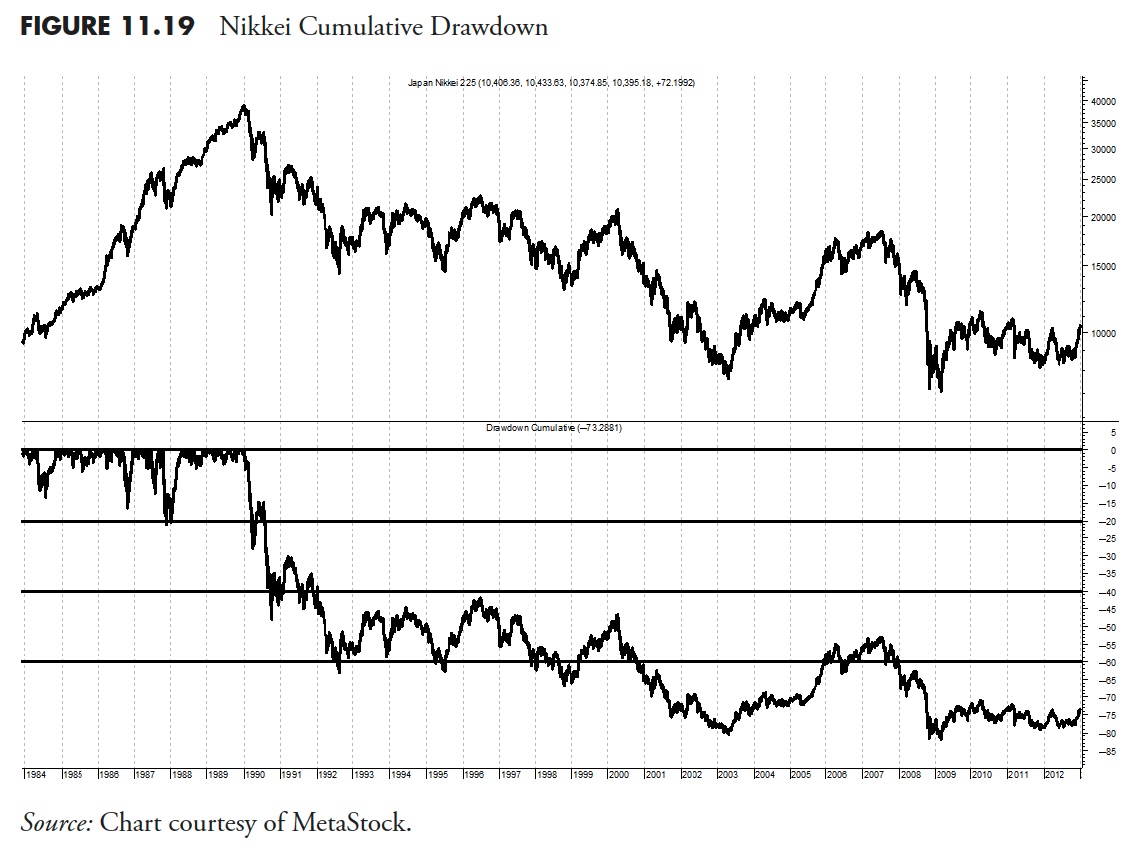
Copper Drawdown
Copper is also known as Physician Copper, as many assume it’s a measure of financial exercise, particularly within the development business. Determine 11.20 is a chart of copper since 1971, with its cumulative drawdown within the backside plot. Clearly, copper as an funding has spent an unlimited period of time in a state of drawdown.
Drawdown Depth Evaluator (DIE)
In an try to additional consider the ache of drawdown, I’ve created an indicator that measures not solely the magnitude of the drawdown, but in addition the period. Bear in mind, it’s not simply how huge the drop in worth is, but in addition how lengthy it takes to get better.
Determine 11.21 helps you perceive how this idea works. The highest plot is a worth sequence, the center plot (with the circles) is the cumulative drawdown, and the underside plot is the Drawdown Depth Evaluator (DIE). You’ll be able to see at level A on the center plot {that a} drawdown started and didn’t finish till level D, which, on this instance (Client Staples), means a time interval from the tip of 1998 till the center of 2006. You additionally see that the DIE was at zero at level A and once more at level D (vertical strains). From the center plot of cumulative drawdown, you may see that the purpose of most drawdown is at level B (early 2000), which additionally corresponded with an preliminary peak in DIE. The center plot of drawdown exhibits level C, which occurred in early 2003 and isn’t as little as level B; in reality, on this instance, level B is -32.5% and level C is -27.4%. Nonetheless, if you have a look at the underside plot of DIE, the best level is at level C. It is because despite the fact that level C occurred three years after level B, the ache of holding an funding throughout this time elevated as a result of the drawdown was nonetheless important, despite the fact that it wasn’t at its most. After level C, you may see that the drawdown slowing began to lower, however didn’t get again to its place to begin (A) for greater than three years (level D). DIE represents the ache of drawdown utilizing not solely magnitude, but in addition, and equally essential, the period.
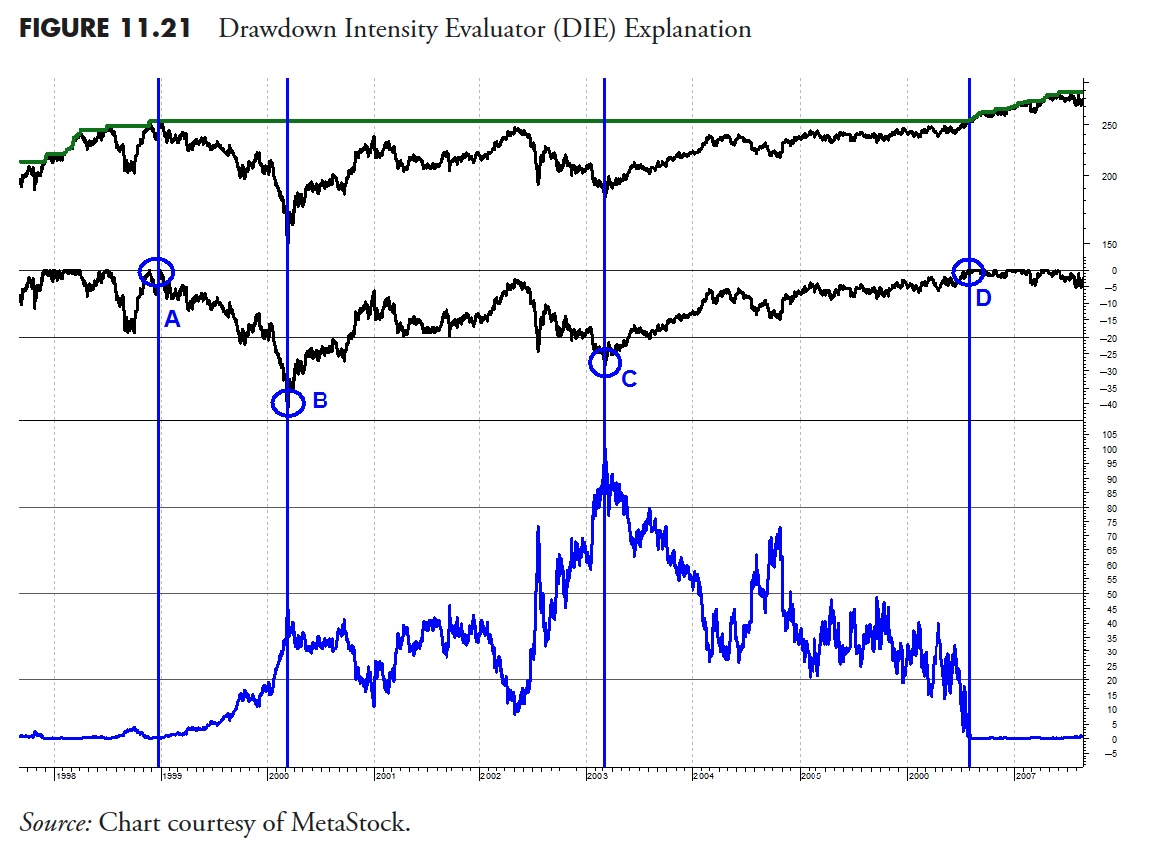
The DIE in Determine 11.21 makes use of the information for your entire interval to find out the ache. The subsequent instance, Determine 11.22 , is an try to normalize the data utilizing a four-year look-back. Normalizing information on this case resets the drawdown numbers and provides us a greater image of present circumstances relative to a current time period and is especially helpful for lengthy period drawdowns. Which means that it’s measuring DIE over a shifting four-year window.
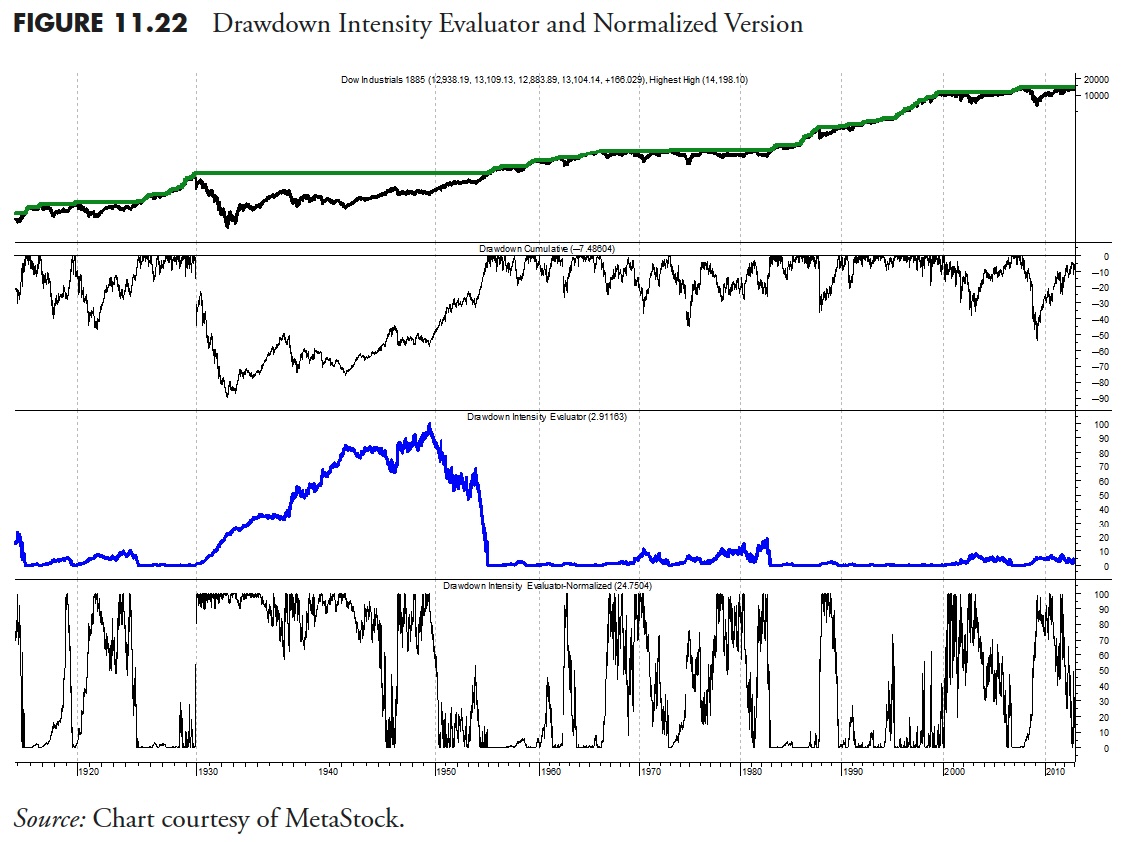
Determine 11.22 is a chart of the Dow Industrial Common within the prime plot, with the cumulative drawdown within the second plot. The third plot is the Drawdown Depth Evaluator, or DIE. The underside plot is the DIE that has been normalized over a four-year interval. The info begins in 1969.
The DIE is a comparatively easy course of, because it merely calculates the share of drawdown and multiplies it by the variety of cumulative days it’s in drawdown. An instance right here is in 1987, when there was a big drawdown nevertheless it didn’t final very lengthy; in reality, the market fully recovered in solely two years
The world of finance, with its insufficient arithmetic, inappropriate statistics, and defective assumptions, needs buyers to consider that danger is volatility as represented by Commonplace Deviation (sigma). Though volatility is a contributor to drawdown, it’s also a contributor to cost features. Threat is lack of capital, and that’s finest measured by drawdown. An funding technique that makes an attempt to sort out and restrict drawdowns will likely be a extra comfy “Funding Trip” for many buyers.
This wraps up Half II: Market Analysis and Evaluation. Let’s now transfer to why we wish to perceive all this — constructing a trend-following rules-based mannequin designed to take part as a lot as doable within the good occasions, attempting to keep away from the dangerous occasions, and most of all, hold the subjectivity out of the method.
Thanks for studying this far. I intend to publish one article on this sequence each week. Cannot wait? The guide is on the market right here.
