The Joint Committee on Taxation’s (JCT) December 2023 tax expenditureTax expenditures are a departure from the “regular” tax code that decrease the tax burden of people or companies, by means of an exemption, deduction, credit score, or preferential fee. Expenditures may end up in important income losses to the federal government and embody provisions such because the earned revenue tax credit score, baby tax credit score, deduction for employer health-care contributions, and tax-advantaged financial savings plans.
report reveals a regarding development in company taxA tax is a compulsory fee or cost collected by native, state, and nationwide governments from people or companies to cowl the prices of basic authorities companies, items, and actions.
coverage. The report reveals the influence of the 2017 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) and the 2022 InflationInflation is when the overall worth of products and companies will increase throughout the economic system, lowering the buying energy of a foreign money and the worth of sure belongings. The identical paycheck covers much less items, companies, and payments. It’s generally known as a “hidden tax,” because it leaves taxpayers much less well-off as a consequence of increased prices and “bracket creep,” whereas growing the federal government’s spending energy.
Discount Act (IRA), with one impact significantly clear: company tax breaks have shifted away from deductions for basic funding towards subsidies for particular forms of funding.
Tax expenditures are insurance policies that diverge from “regular” revenue taxation. Nonetheless, what constitutes a standard revenue tax is controversial. The JCT report depends on the Haig-Simons definition of revenue, which defines revenue as consumption plus change in web value. Think about how this impacts the “regular” tax remedy of funding. When an organization buys a brand new manufacturing facility, its web value doesn’t instantly change. Nonetheless, its web value does decline as a manufacturing facility depreciates (i.e., loses worth over time), so below Haig-Simons, corporations ought to take deductions for investments as an asset depreciates. Accordingly, deductions for investments in extra of financial depreciationDepreciation is a measurement of the “helpful life” of a enterprise asset, resembling equipment or a manufacturing facility, to find out the multiyear interval over which the price of that asset might be deducted from taxable revenue. As a substitute of permitting companies to deduct the price of investments instantly (i.e., full expensing), depreciation requires deductions to be taken over time, lowering their worth and discouraging funding.
rely as tax expenditures below the JCT’s definitions.
The depreciation strategy, nonetheless, shouldn’t be economically sound. Spreading deductions for investments out over time means they lose worth in actual phrases, due to inflation and alternative price. Consequently, utilizing financial depreciation within the tax system creates penalties for capital funding, which reduces funding and financial progress. The choice to the Haig-Simons-style company revenue taxA company revenue tax (CIT) is levied by federal and state governments on enterprise income. Many corporations usually are not topic to the CIT as a result of they’re taxed as pass-through companies, with revenue reportable below the particular person revenue tax.
is a money flow-based company revenue tax, the place corporations deduct all prices (whether or not recurring operational bills or main capital investments) instantly.
Due to a reliance on the Haig-Simons definition, the bottom-line totals of the JCT tax expenditures report don’t distinguish between true subsidies (insurance policies that present extra help to companies [e.g., an investment tax creditA tax credit is a provision that reduces a taxpayer’s final tax bill, dollar-for-dollar. A tax credit differs from deductions and exemptions, which reduce taxable income, rather than the taxpayer’s tax bill directly.
]) and deductions for funding prices incurred that will be regular below a money move tax. However, when digging deeper into the report, one can see how the 2 forms of insurance policies have moved in several instructions.
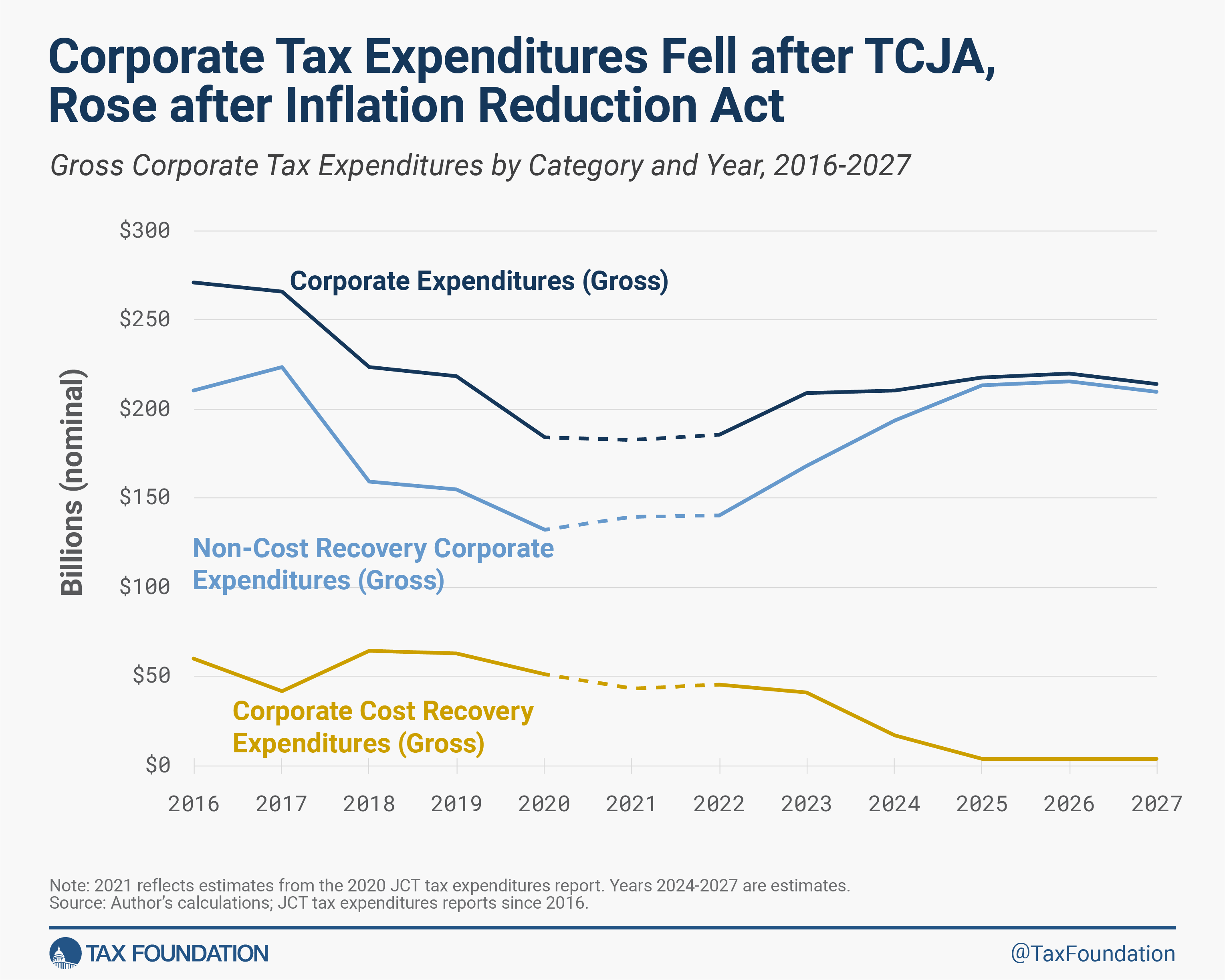
General, company tax expenditures fell considerably following the passage of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act in 2017. The drop principally displays the legislation’s discount of the company tax fee—tax deductions are extra priceless towards a 35 % company tax fee than they’re towards a 21 % tax fee. Nonetheless, the legislation did eradicate a significant company tax expenditure, the 9 % deduction for home manufacturing actions. On the identical time, the TCJA launched 100% bonus depreciationBonus depreciation permits companies to deduct a bigger portion of sure “short-lived” investments in new or improved know-how, gear, or buildings, within the first yr. Permitting companies to write down off extra investments partially alleviates a bias within the tax code and incentivizes corporations to speculate extra, which, in the long term, raises employee productiveness, boosts wages, and creates extra jobs.
for gear and equipment, rising price restorationPrice restoration is the power of companies to get better (deduct) the prices of their investments. It performs an vital position in defining a enterprise’ tax base and might influence funding choices. When companies can’t totally deduct capital expenditures, they spend much less on capital, which reduces employee’s productiveness and wages.
tax expenditures.
The development of upper price restoration deductions and total decrease company tax expenditures—which typically displays a transfer towards higher tax coverage—has begun to reverse. The TCJA changed expensing for analysis and improvement (R&D) funding with amortization of R&D bills initially of 2022, and 100% bonus depreciation started phasing out initially of 2023 (first to 80 %, then it is going to drop by 20 share factors every subsequent yr). The TCJA phaseouts clarify the decline in price restoration tax expenditures since 2022.
The decline in complete company tax expenditures has reversed in recent times due to the IRA and the CHIPS and Science Act, each enacted in 2022. Whereas price restoration expenditures have shrunk, expanded tax credit for renewable vitality manufacturing, renewable vitality funding, and superior manufacturing have elevated non-cost restoration expenditures sufficient to push up complete expenditures. This reversal factors to a troubling development of shifting away from the impartial tax remedy of funding towards focused, industry-specific tax subsidies.
Whereas the CHIPS Act and the IRA are aimed toward professional coverage objectives—resembling strategic competitors with China and lowering greenhouse gasoline emissions, respectively—lawmakers ought to prioritize making a tax system that helps funding extra broadly relatively than subsidizing particular industries and permitting broad, impartial pro-investment provisions to run out.
Keep knowledgeable on the tax insurance policies impacting you.
Subscribe to get insights from our trusted specialists delivered straight to your inbox.
Share