Notice: The next is the written testimony of Sean Bray, Director of European Coverage on the TaxA tax is a compulsory fee or cost collected by native, state, and nationwide governments from people or companies to cowl the prices of common authorities providers, items, and actions.
Basis, ready for a listening to earlier than the European Parliament Subcommittee on Tax Issues (FISC) on January 23, 2024, titled, “Capital Positive aspects Taxation within the EU.”
Pricey Chair Tang and Distinguished Members of the FISC Committee,
Thanks for the chance to supply testimony on capital positive aspects taxation within the EU.
Throughout EU Member States, tax charges on capital positive aspects common 18.6 p.c, although they differ extensively. Denmark costs the very best prime fee of 42 p.c fee. Finland and France cost 34 p.c, whereas Bulgaria and Romania cost 10 p.c. In the meantime, 5 Member States, together with Belgium, Czechia, Luxembourg, Slovakia, and Slovenia, have a zero p.c fee below numerous situations.
The theme of this listening to is the hurt that non-harmonized capital positive aspects charges may cause within the EU. Presumably, some will argue that the hurt is coming from these 5 Member States with zero p.c charges. Others may argue that it’s unfair to have decrease tax charges on capital positive aspects than on labor earnings and supply doubtful political motivations for why such variations exist within the first place. These arguments don’t inform the entire story.
Frankly, I agree that disparate capital positive aspects charges may cause hurt to the European economic system, and there’s a query of equity to debate. Nevertheless, it’s nations with greater charges, not decrease charges, which can be inflicting probably the most hurt. Moreover, capital positive aspects ought to be thought of alongside the company earnings taxA company earnings tax (CIT) is levied by federal and state governments on enterprise earnings. Many corporations usually are not topic to the CIT as a result of they’re taxed as pass-through companies, with earnings reportable below the particular person earnings tax.
. With out the broader image, it’s deceptive to focus solely on the capital positive aspects charges in these 5 Member States.
A Double Tax on Company Earnings
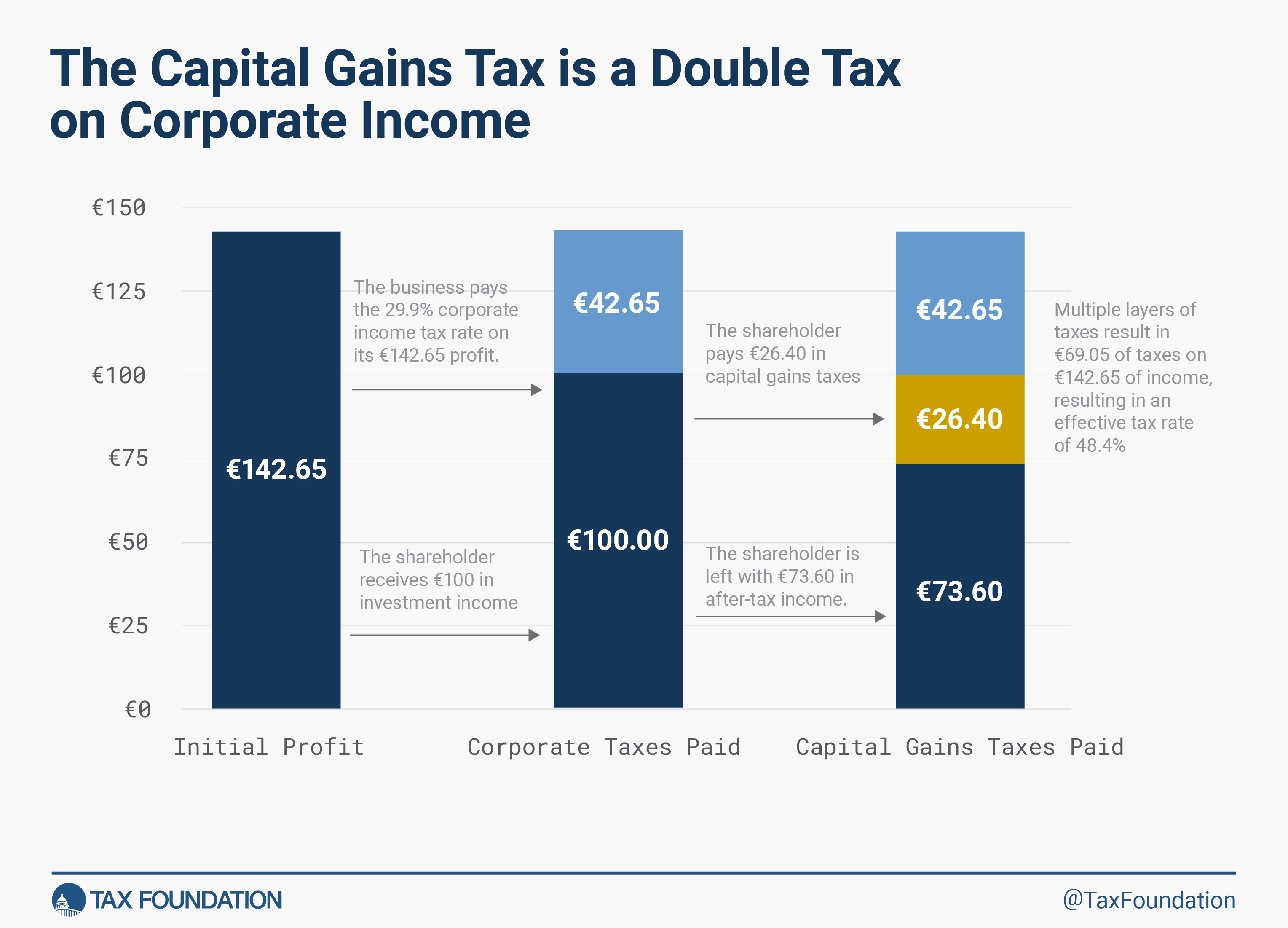
To start out, it’s important to grasp that the taxation of capital positive aspects locations a double tax on company earnings. Ideally, below a impartial tax system, every euro of earnings would solely be taxed as soon as. Nevertheless, this isn’t the case, as capital positive aspects face a number of layers of tax.
Earlier than shareholders pay taxes, the enterprise pays the company earnings tax on its earnings. Due to this fact, when the shareholder pays their layer of tax on the private stage, they’re doing so on capital positive aspects distributed from after-tax earnings.[1]
For instance, Determine 1 under reveals the double tax burden on earnings in Germany, which faces a 29.9 p.c statutory company earnings tax fee and a 26.4 p.c capital positive aspects fee.
Because of this, even in Member States with a zero p.c capital positive aspects fee, this earnings remains to be being taxed by the company earnings tax. To compensate for this double layer of taxation, governments usually cost a decrease tax fee on capital positive aspects than extraordinary earnings.
The tax fee that comes with the capital positive aspects fee plus the company earnings fee is named the built-in tax fee on company earnings. This fee is extra indicative of the real-world financial affect of capital positive aspects taxation than the straightforward capital positive aspects fee.
Desk 1 reveals that the typical built-in tax fee is way greater than the typical capital positive aspects fee. Satirically, it additionally reveals that company earnings in Belgium (a rustic with a zero p.c capital positive aspects fee), faces a better built-in fee than a number of Member States with non-zero capital positive aspects charges.
One other financial rationale for charging a decrease fee is that the majority Member States don’t regulate positive aspects for inflationInflation is when the overall worth of products and providers will increase throughout the economic system, lowering the buying energy of a forex and the worth of sure property. The identical paycheck covers much less items, providers, and payments. It’s generally known as a “hidden tax,” because it leaves taxpayers much less well-off because of greater prices and “bracket creep,” whereas growing the federal government’s spending energy.
. Because of this traders may be taxed on capital positive aspects that accrue because of price-level will increase fairly than actual positive aspects.[2]
Significance of Saving and EU Capital Markets Union
Typically, greater capital positive aspects taxes create a bias in opposition to saving and funding, scale back capital formation, and sluggish financial development.[3] Capital positive aspects taxes distort the choice to instantly eat or save over time as a result of there’s a further tax burden on saving.
These taxes may be particularly dangerous to entrepreneurship and small companies that require capital. The EU can’t afford this given its ageing demographic and declining long-term development initiatives.
Moreover, if the built-in fee on company earnings is excessive and curiosity is deductible, then the steadiness towards debt financing might be comparatively robust.[4] Companies might be extra more likely to finance their investments by way of debt fairly than fairness, with fewer IPOs and personal choices.[5] This might be one more hindrance to reaching a vibrant EU Capital Markets Union.
Conclusion
Some could argue that capital positive aspects charges within the EU ought to be harmonized to a fee as much as 40 p.c greater than the established order. This might hurt the European economic system.
As an alternative, policymakers ought to search for principled methods to extend saving, funding, and financial development. If a harmonized EU capital positive aspects fee of zero p.c makes politicians uncomfortable, then the second-best coverage choice could be to a minimum of encourage long-term funding and saving with a zero p.c long-term capital positive aspects fee.
Thanks once more for the chance to testify right here right this moment, and I sit up for your questions.
Keep knowledgeable on the tax insurance policies impacting you.
Subscribe to get insights from our trusted consultants delivered straight to your inbox.
[1] Erica York, “An Overview of Capital Positive aspects Taxes,” Tax Basis, Apr. 16, 2019, https://taxfoundation.org/analysis/all/federal/capital-gains-taxes/.
[2] Kyle Pomerleau, “How One Can Face an Infinite Efficient Tax Charge on Capital Positive aspects,” Tax Basis, Jan. 7, 2015, https://taxfoundation.org/weblog/how-one-can-face-infinite-effective-tax-rate-capital-gains/.
[3] Daniel Bunn and Elke Asen, “Financial savings and Funding: The Tax Remedy of Inventory and Retirement Accounts within the OECD,” Tax Basis, Might 26, 2021, https://taxfoundation.org/savings-and-investment-oecd/.
[4] Elke Asen, “Double TaxationDouble taxation is when taxes are paid twice on the identical greenback of earnings, no matter whether or not that’s company or particular person earnings.
of Company Earnings within the United States and the OECD,” Tax Basis, Jan. 13, 2021, https://taxfoundation.org/information/all/federal/double-taxation-of-corporate-income/#Distortions.
[5] Rudd A. de Mooij, “Tax Biases to Debt Finance: Assessing the Downside, Discovering Options,” IMF, Might 3, 2011, https://www.imf.org/exterior/pubs/ft/sdn/2011/sdn1111.pdf.
Share