Greater than 170 nations worldwide—together with all main European nations —levy a value-added taxA tax is a compulsory fee or cost collected by native, state, and nationwide governments from people or companies to cowl the prices of basic authorities providers, items, and actions.
(VAT) on items and providers. As right this moment’s tax map reveals, EU Member States’ VAT charges differ throughout nations, although they’re considerably harmonized by the EU.
The VAT is a consumption taxA consumption tax is often levied on the acquisition of products or providers and is paid straight or not directly by the patron within the type of retail gross sales taxes, excise taxes, tariffs, value-added taxes (VAT), or an revenue tax the place all financial savings is tax-deductible.
assessed on the worth added in every manufacturing stage of or service. Each enterprise alongside the worth chain receives a tax credit scoreA tax credit score is a provision that reduces a taxpayer’s ultimate tax invoice, dollar-for-dollar. A tax credit score differs from deductions and exemptions, which cut back taxable revenue, relatively than the taxpayer’s tax invoice straight.
for the VAT already paid. The tip client doesn’t, making it a tax on ultimate consumption.
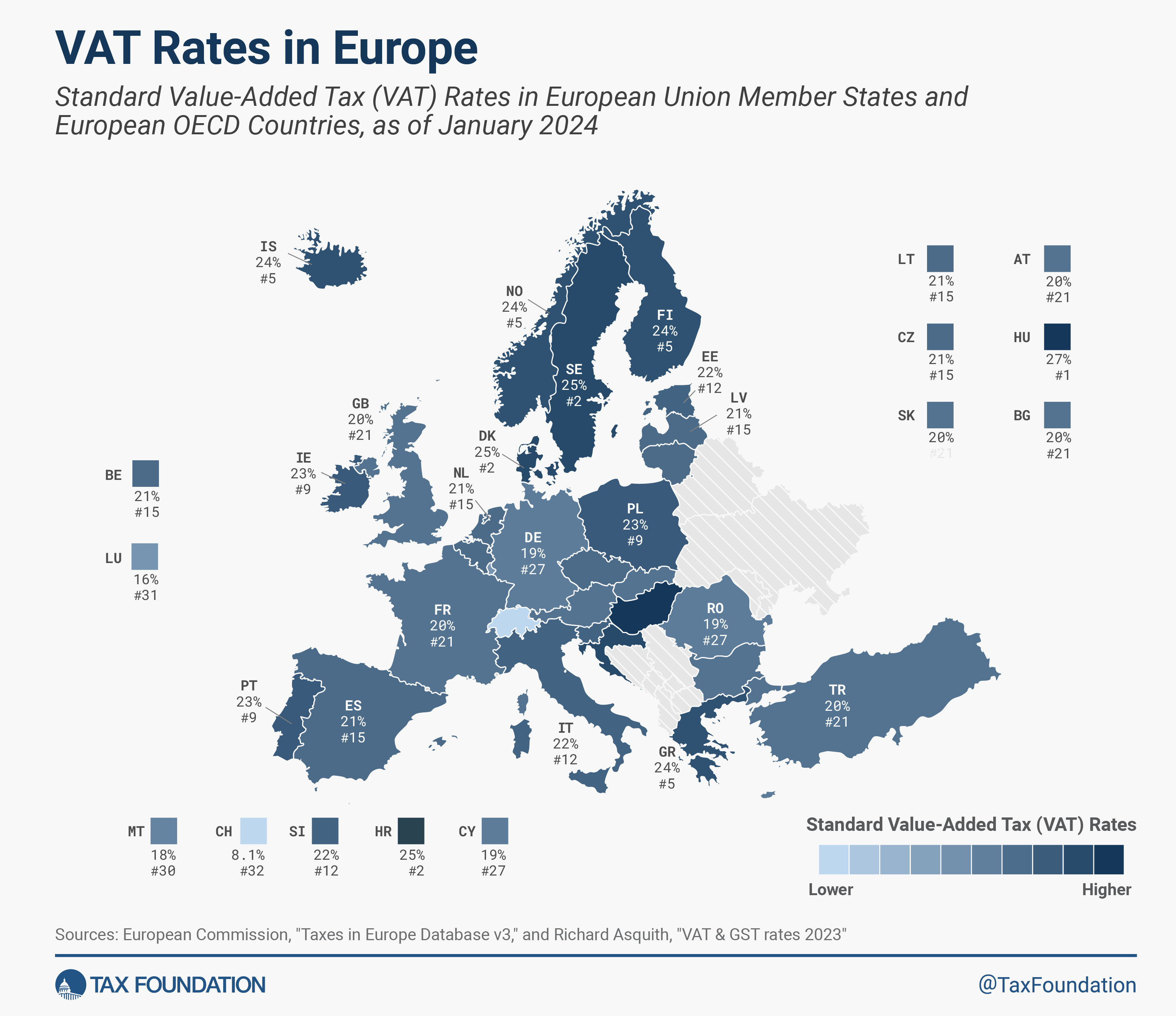
The EU nations with the very best customary VAT charges are Hungary (27 p.c), Croatia, Denmark, and Sweden (all at 25 p.c). Luxembourg levies the bottom customary VAT price at 16 p.c, adopted by Malta (18 p.c), Cyprus, Germany, and Romania (all at 19 p.c). The EU’s common customary VAT price is 21.6 p.c, greater than six share factors greater than the minimal customary VAT price required by EU regulation.
Among the many 5 European OECD nations that aren’t a part of the European Union—Iceland, Norway, Switzerland, Turkey, and the United Kingdom—solely Switzerland levies a regular VAT price beneath the EU minimal at a price of 8.1 p.c. Compared, within the United States, mixed state and native gross sales taxA gross sales tax is levied on retail gross sales of products and providers and, ideally, ought to apply to all ultimate consumption with few exemptions. Many governments exempt items like groceries; base broadening, comparable to together with groceries, may hold charges decrease. A gross sales tax ought to exempt business-to-business transactions which, when taxed, trigger tax pyramiding.
charges averaged solely 6.6 p.c in 2023.
Typically, consumption taxes are an economically environment friendly manner of elevating tax income. To attenuate financial distortions, there may be ideally just one customary price that’s levied on all ultimate consumption, with as few exemptions as attainable. Nevertheless, EU nations levy diminished charges and exempt sure items and providers from the VAT.
One of many primary causes for diminished VAT charges and VAT-exempted items/providers is the promotion of fairness, as lower-income households are likely to spend a bigger share of their incomes on items and providers comparable to meals and public transportation. Different causes embrace encouraging the consumption of “benefit items” (e.g., books), selling native providers (e.g., tourism), and correcting externalities (e.g., clear energy).
Nevertheless, proof reveals that diminished VAT charges and VAT exemptions aren’t essentially efficient in attaining these coverage targets and may even be regressive in some cases. Such diminished charges and exemptions can result in greater administrative and compliance prices and may create financial distortions. A current research reveals that scrapping VAT-reduced charges in EU nations will permit customary charges to drop beneath 15 p.c. To handle fairness issues, the OECD as a substitute recommends measures that straight improve poorer households’ actual incomes.
A number of European nations have made modifications to their VAT charges from final yr. Estonia elevated its customary price from 20 p.c to 22 p.c. Switzerland elevated its customary price from 7.7 p.c to eight.1 p.c and its diminished price from 3.7 to three.8 p.c. Turkey elevated its customary VAT price from 18 to twenty p.c and its diminished price from 8 to 10 p.c. The Czech Republic has taken a step to cut back the complexity of its VAT system by consolidating its diminished charges of 10 and 15 p.c into one diminished price of 12 p.c.
Keep knowledgeable on the tax insurance policies impacting you.
Subscribe to get insights from our trusted consultants delivered straight to your inbox.
Share