The approaching 2025 taxA tax is a compulsory fee or cost collected by native, state, and nationwide governments from people or companies to cowl the prices of normal authorities companies, items, and actions.
debate is riddled with trillion-dollar questions. The income price ticket of extending present tax insurance policies for people and reversing some base broadeners for corporations will exceed $3 trillion {dollars}.
Over the previous yr, Tax Basis economists have evaluated a number of choices for altering the trajectory of federal tax insurance policies.
Utilizing our Taxes and Progress Mannequin, we will measure the income impression of tax insurance policies conventionally (with out financial suggestions) and dynamically (with financial suggestions).
Not all coverage adjustments are created equal. A coverage change that grows the financial system can elevate extra (or lose much less) income on a dynamic foundation than it does on a standard foundation. However, coverage adjustments that shrink the financial system will often elevate extra (or lose much less) income on a standard foundation than on a dynamic foundation.
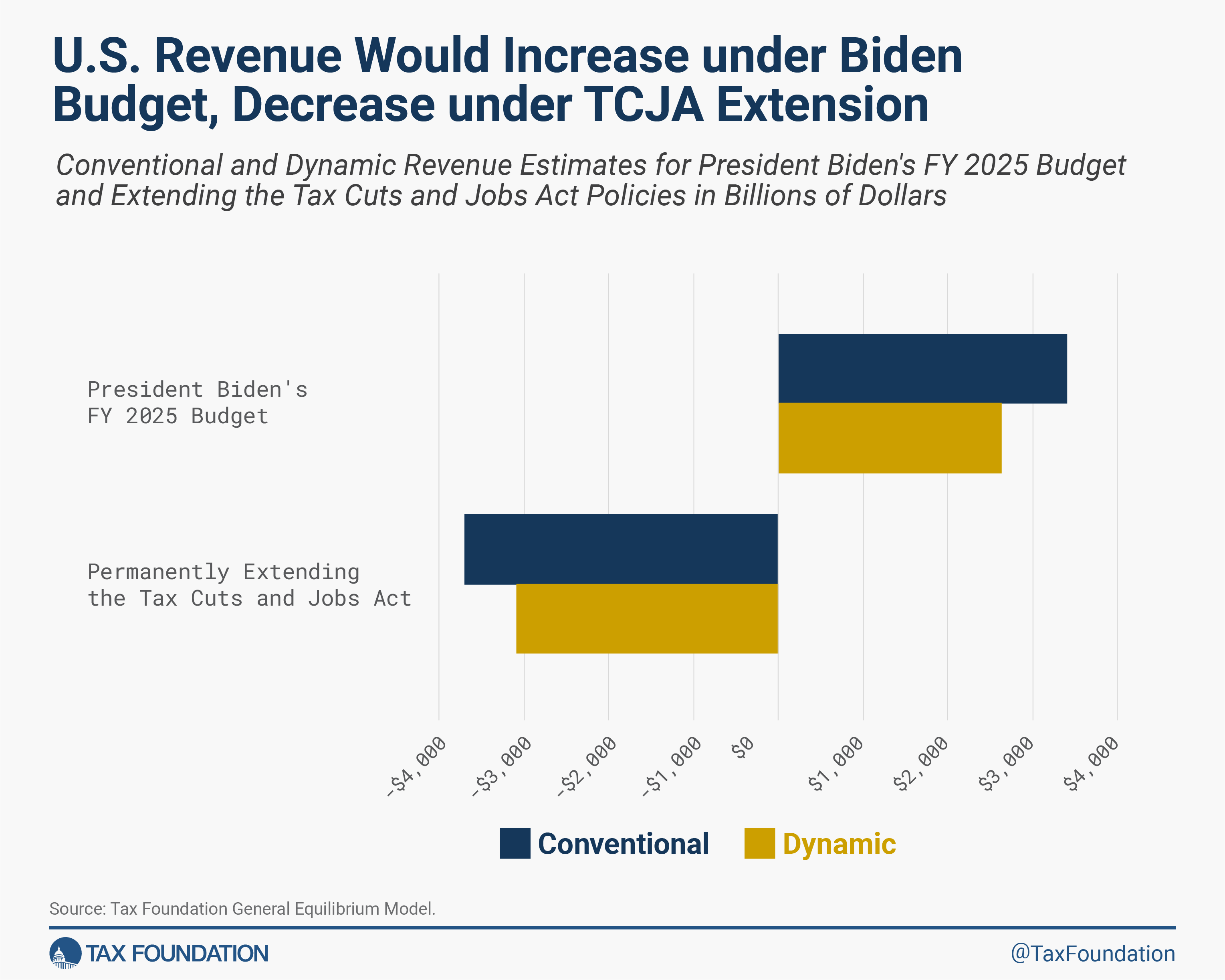
Two coverage eventualities present bookends to the upcoming tax debate. The primary is extending the insurance policies within the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) and reversing a few of the enterprise provisions that have been designed to part out over time.
The dynamic and standard income impacts are proven in Determine 1. Extending the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act would scale back federal revenues considerably, even after accounting for the bigger financial system. The bigger financial system would help about $600 billion in further income, however this isn’t sufficient to cowl the price of a multi-trillion greenback tax minimize.
The second coverage state of affairs is President Biden’s price range for fiscal yr 2025, which proposes greater than $3.4 trillion in web tax will increase that can cut back funding and general financial exercise. The smaller financial system signifies that, realistically, tax revenues is not going to hit that $3 trillion mark. Roughly $770 billion will probably be shaved off as a result of smaller financial system, leading to our estimated web income improve of $2.6 trillion.
These are usually not the one choices, in fact. Policymakers will possible contemplate a variety of coverage adjustments between renewing the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act and placing the Biden price range into regulation.
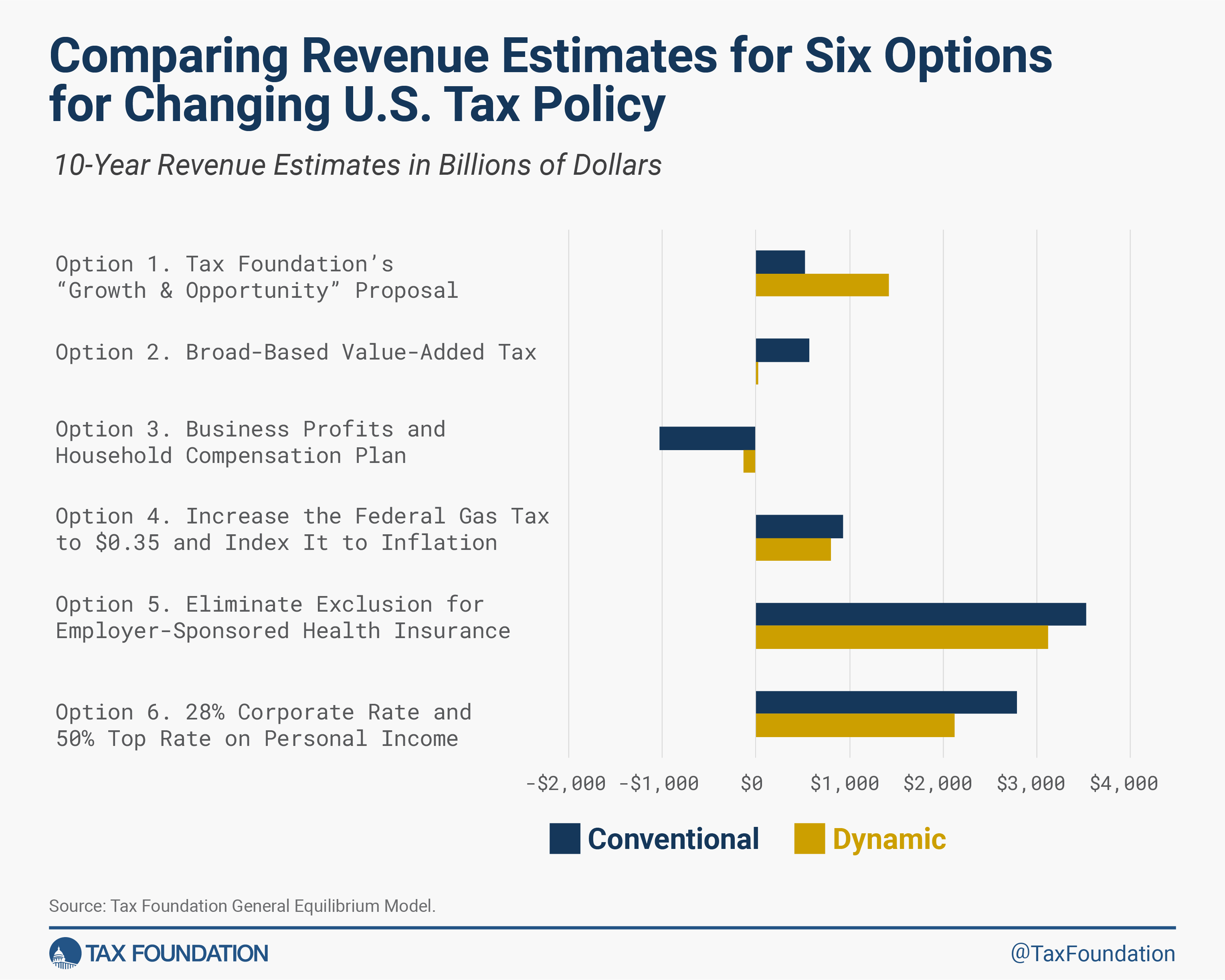
Six examples from Tax Basis’s current work, summarized under, present policymakers different choices to think about, together with their income and financial impacts. Within the coming weeks, we are going to launch but another choice for a revenue-neutral, pro-growth reform that might maintain many Tax Cuts and Jobs Act insurance policies in place whereas constructing on a few of its successes and avoiding a few of its pitfalls.
Choice 1: A Tax Reform for Progress and Alternative
The first reform is transformative and would help a bigger financial system whereas additionally rising tax income. It features a flat taxAn earnings tax is known as a “flat tax” when all taxable earnings is topic to the identical tax charge, no matter earnings degree or belongings.
of 20 p.c on particular person earnings and a distributed income taxA distributed income tax is a business-level tax levied on corporations after they distribute income to shareholders, together with via dividends and web share repurchases (inventory buybacks).
of 20 p.c (changing present enterprise tax guidelines), whereas additionally eliminating taxes at dying and simplifying the remedy of capital positive aspects.
Along with supporting a bigger financial system, it might dramatically simplify the tax system.
Over 10 years, this reform would improve federal revenues by $523 billion on a standard foundation and by $1.4 trillion on a dynamic foundation. Learn extra
Choice 2: Broad-Based mostly Worth-Added Tax
This reform is equally transformative. It replaces the company earnings taxA company earnings tax (CIT) is levied by federal and state governments on enterprise income. Many corporations are usually not topic to the CIT as a result of they’re taxed as pass-through companies, with earnings reportable beneath the particular person earnings tax.
with a value-added tax (VAT), whereas additionally changing present tax credit for employees and households (youngster tax credit scoreA tax credit score is a provision that reduces a taxpayer’s ultimate tax invoice, dollar-for-dollar. A tax credit score differs from deductions and exemptions, which cut back taxable earnings, relatively than the taxpayer’s tax invoice straight.
, earned earnings tax credit score, and youngster and dependent care tax credit score) with a rebate.
The VAT is far much less dangerous to funding and a rising financial system, so the reform would result in a bigger financial system than present tax insurance policies. Over 10 years, it might improve federal revenues by $569 billion on a standard foundation and by $24 billion on a dynamic foundation.
Over the longer run (past the ten yr time-frame), this selection retains a optimistic financial impact and is roughly income impartial even on a standard foundation. Learn extra
Choice 3: Enterprise Earnings and Family Compensation Reform
This reform would change the present company and particular person earnings taxes with a tax on enterprise money flows and a progressive taxA progressive tax is one the place the common tax burden will increase with earnings. Excessive-income households pay a disproportionate share of the tax burden, whereas low- and middle-income taxpayers shoulder a comparatively small tax burden.
on family compensation with a per particular person credit score (in lieu of the identical credit changed in Choice 2).
This reform additionally helps a a lot bigger financial system, however it might cut back revenues, even after accounting for the bigger financial system. Over 10 years, this reform would lower federal revenues by $1 trillion on a standard foundation and by $130 billion on a dynamic foundation. Learn extra
Choice 4: Enhance the Federal Gasoline TaxA gasoline tax is often used to explain the number of taxes levied on gasoline at each the federal and state ranges, to supply funds for freeway restore and upkeep, in addition to for different authorities infrastructure initiatives. These taxes are levied in a couple of methods, together with per-gallon excise taxes, excise taxes imposed on wholesalers, and normal gross sales taxes that apply to the acquisition of gasoline.
by $0.35 and Index It for InflationInflation is when the final worth of products and companies will increase throughout the financial system, lowering the buying energy of a forex and the worth of sure belongings. The identical paycheck covers much less items, companies, and payments. It’s generally known as a “hidden tax,” because it leaves taxpayers much less well-off attributable to greater prices and “bracket creep,” whereas rising the federal government’s spending energy.
This feature might not be politically standard, however it’s simple. The federal gasoline tax has not been elevated since 1993 and is at present nonetheless 18.4 cents per gallon. The gasoline tax is a tax on consumption, and elevating it might have comparatively little impact on the long-term trajectory of the financial system.
Over 10 years, this reform would improve federal revenues by $931 billion on a standard foundation and by $797 billion on a dynamic foundation. Learn extra
Choice 5: Eradicate Exclusion for Employer-Sponsored Well being Insurance coverage
This subsequent reform merely broadens the tax baseThe tax base is the overall quantity of earnings, property, belongings, consumption, transactions, or different financial exercise topic to taxation by a tax authority. A slim tax base is non-neutral and inefficient. A broad tax base reduces tax administration prices and permits extra income to be raised at decrease charges.
. The biggest exclusion from the U.S. tax base is the exclusion for employer-sponsored medical health insurance. The associated fee is a deductible expense for employers, and it’s not taxed as earnings for workers. Nevertheless, the advantages are actually “earnings” within the financial sense. Even after accounting for a smaller financial system, this reform would elevate substantial income.
Over 10 years, this growth of the tax base would improve federal revenues by $3.5 trillion on a standard foundation and by $3.1 trillion on a dynamic foundation. Learn extra
Choice 6: 28 P.c Company Tax Charge and 50 P.c High Private Revenue Tax Charge
As a distinction to the opposite revenue-raising choices, this reform would improve each the company earnings tax charge and the highest private earnings tax charge. At the moment, these charges are 21 p.c for corporations and 37 p.c for top earners.
These reforms would distort financial selections and result in a smaller financial system.
Over 10 years, the upper tax charges would improve federal revenues by $2.8 trillion on a standard foundation and by $2.1 trillion on a dynamic foundation. Learn extra
Provided that U.S. debt is roughly the scale of our annual financial output, policymakers will face many robust fiscal decisions within the coming years. The excellent news is there are insurance policies that each help a bigger financial system and keep away from including to the debt. By selecting these choices, Congress can set the U.S. on the trail to fiscal sustainability.
Keep knowledgeable on the tax insurance policies impacting you.
Subscribe to get insights from our trusted consultants delivered straight to your inbox.
Share