Coverage and financial variations amongst OECD nations have created variances in how they increase taxA tax is a compulsory cost or cost collected by native, state, and nationwide governments from people or companies to cowl the prices of common authorities companies, items, and actions.
income, with the United States deviating considerably from the OECD common on some sources of income.
Totally different taxes have completely different financial results, so policymakers ought to all the time take into account how tax income is raised and never simply how a lot is raised. That is particularly vital because the financial restoration from the pandemic continues.
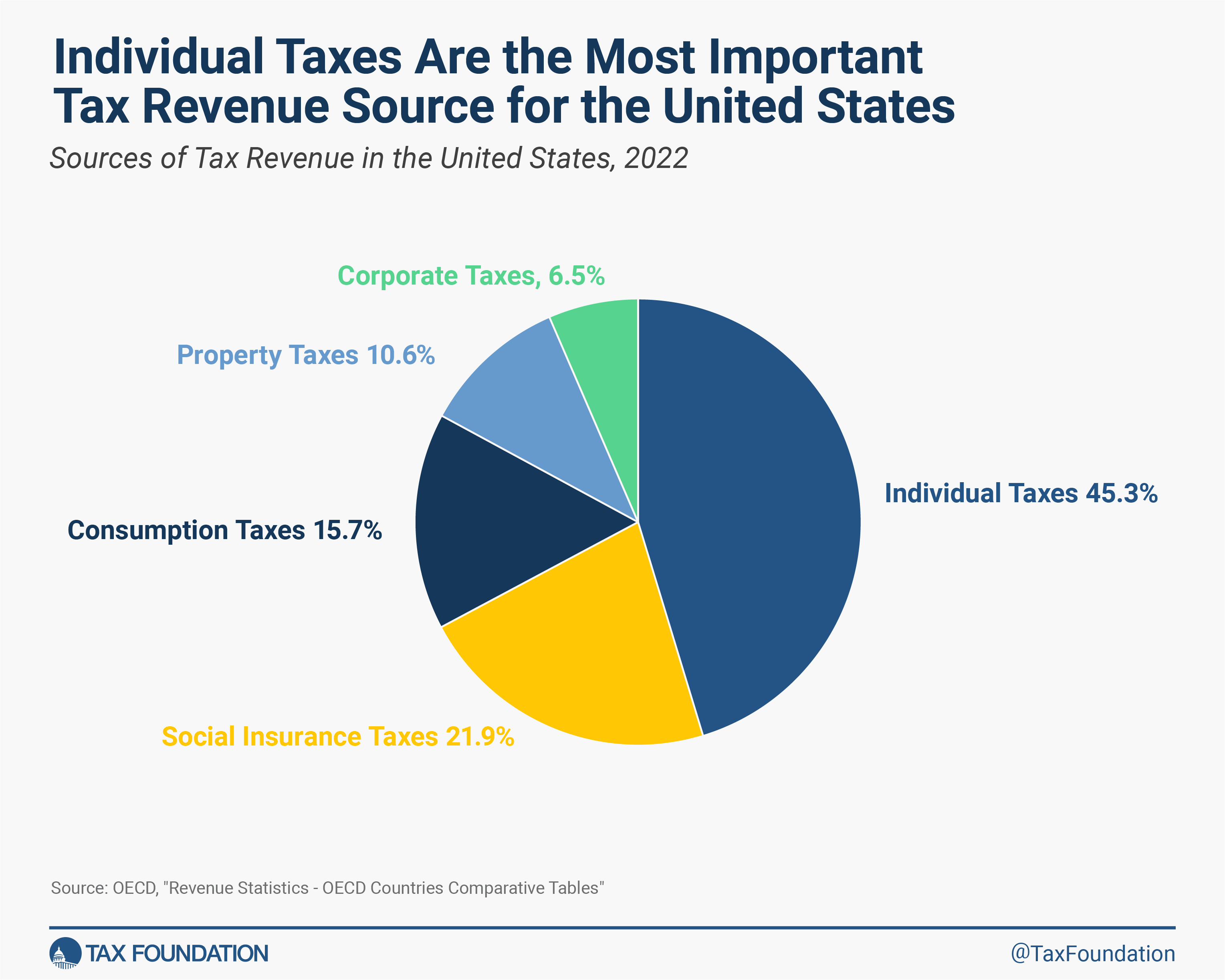
Within the United States, particular person earnings taxes (federal, state, and native) have been the first supply of tax income in 2022, at 45.3 p.c of complete tax income. Social insurance coverage taxes (together with payroll taxes for Social Safety and Medicare) made up the second-largest share at 21.9 p.c, adopted by consumption taxes at 15.7 p.c, and property taxes at 10.6 p.c. Company earnings taxes accounted for six.5 p.c of complete U.S. tax income in 2022.
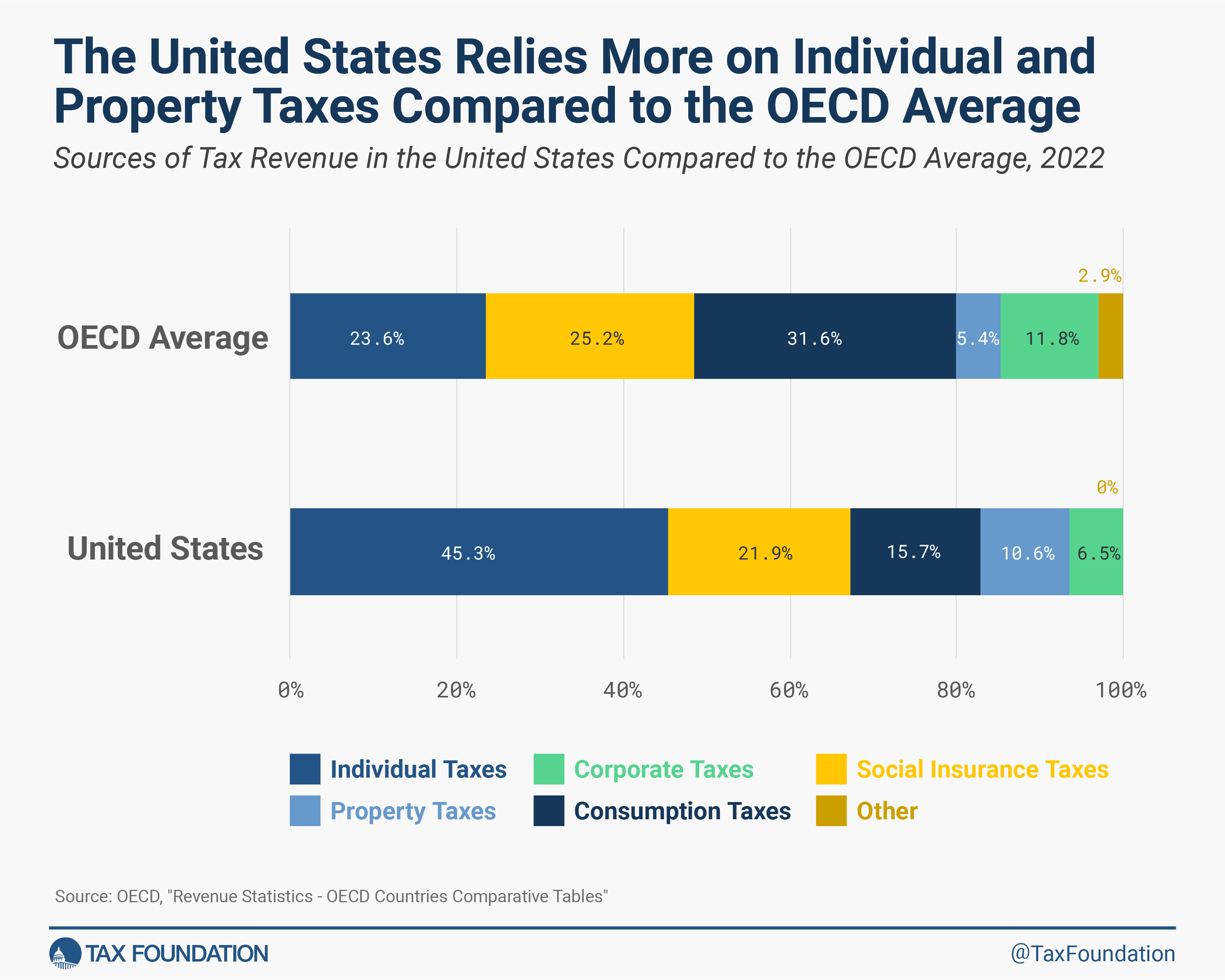
In comparison with the OECD common, america depends considerably extra on particular person earnings taxes and property taxes. Whereas OECD nations on common raised 23.6 p.c of complete tax income from particular person earnings taxes, the share in america was 45.3 p.c, a distinction of 21.7 share factors.
That is partially as a result of greater than half of enterprise earnings in america is reported on particular person tax returns. Relative to different OECD nations, the U.S. strategy to taxing enterprise earnings boosts the share of tax income from particular person earnings taxes within the U.S. and reduces the share of company tax income.
The OECD on common raised 5.4 p.c of complete tax income from property taxes, in comparison with 10.4 p.c in america.
The USA depends a lot much less on consumption taxes than different OECD nations. Taxes on items and companies accounted for less than 15.7 p.c of complete U.S. tax income, in comparison with 31.6 p.c within the OECD.
It’s because all OECD nations, besides america, levy value-added taxes (VAT), often at comparatively excessive charges. State and native gross sales taxA gross sales tax is levied on retail gross sales of products and companies and, ideally, ought to apply to all ultimate consumption with few exemptions. Many governments exempt items like groceries; base broadening, reminiscent of together with groceries, may hold charges decrease. A gross sales tax ought to exempt business-to-business transactions which, when taxed, trigger tax pyramiding.
charges in america are comparatively low by comparability, however they’re on a completely different tax base.
Nations even have completely different ranges of presidency at which taxes are collected. The U.S. and 9 different OECD nations have a decentralized political construction the place state or regional governments play an vital function in tax assortment.
Practically half of U.S. tax income is raised on the state and native ranges.
Each nation’s mixture of taxes is completely different, relying on elements reminiscent of its financial state of affairs and coverage objectives. Nonetheless, every sort of tax impacts the economic system in another way, with some taxes being extra dangerous than others.
Typically, consumption-based taxes are a extra environment friendly income as a result of they create much less financial injury and distortionary results than taxes on earnings. Because the U.S. economic system recovers from the pandemic, policymakers ought to keep away from enacting dangerous tax will increase that place pointless burdens on U.S. employees and companies.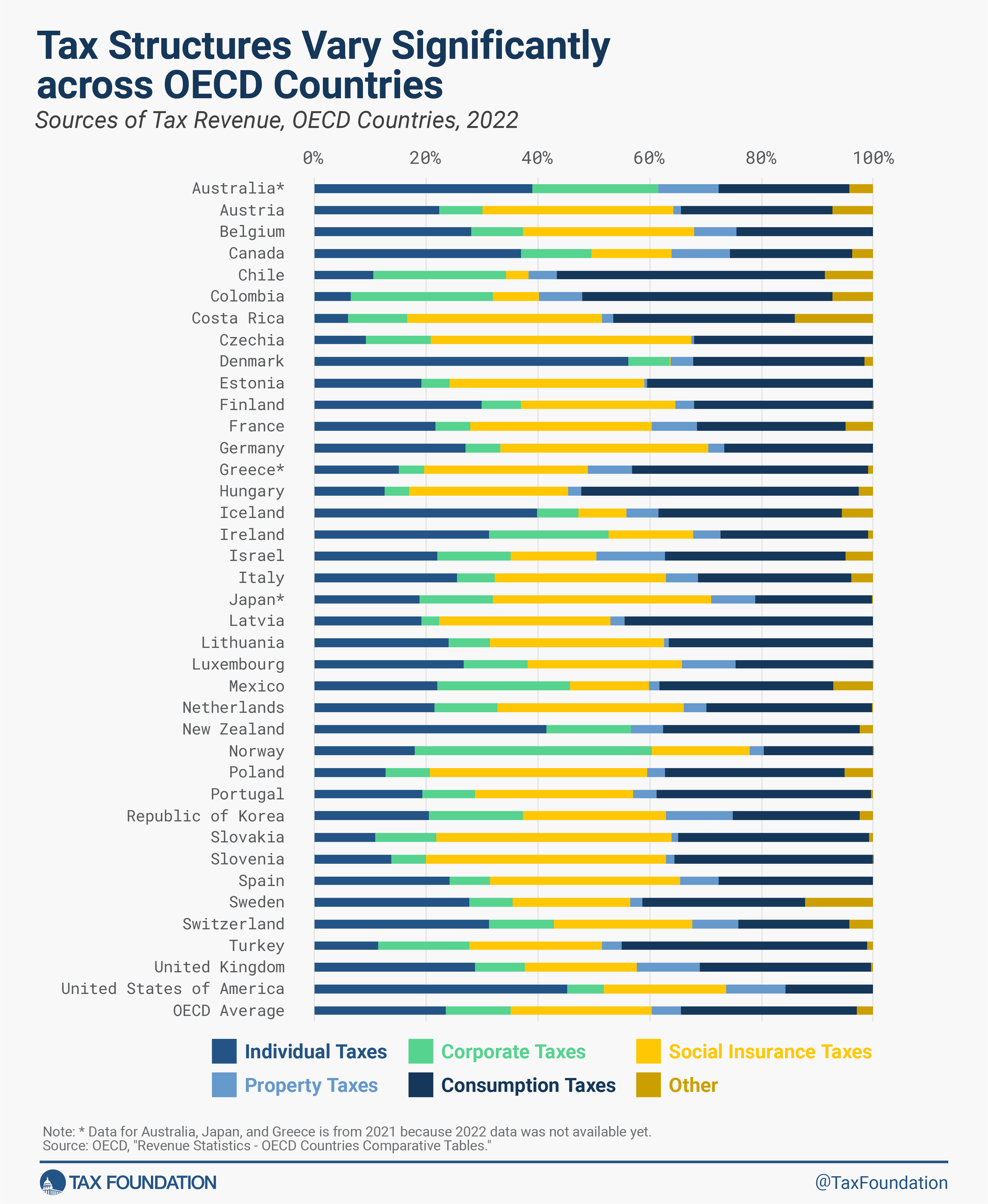

Keep knowledgeable on the tax insurance policies impacting you.
Subscribe to get insights from our trusted consultants delivered straight to your inbox.
Share