One of many key properties that’s normally hunted for in a cryptoeconomic algorithm, whether or not a blockchain consensus algorithm such a proof of labor or proof of stake, a fame system or a buying and selling course of for one thing like information transmission or file storage, is the best of incentive-compatibility – the concept that it ought to be in everybody’s financial curiosity to actually comply with the protocol. The important thing underlying assumption on this aim is the concept that folks (or extra exactly on this case nodes) are “rational” – that’s to say, that individuals have a comparatively easy outlined set of goals and comply with the optimum technique to maximise their achievement of these goals. In game-theoretic protocol design, that is normally simplified to saying that individuals like cash, since cash is the one factor that can be utilized to assist additional one’s success in nearly any goal. In actuality, nevertheless, this isn’t exactly the case.
People, and even the de-facto human-machine hybrids which might be the members of protocols like Bitcoin and Ethereum, aren’t completely rational, and there are particular deviations from rationality which might be so prevalent amongst customers that they can’t be merely categorized as “noise”. Within the social sciences, economics has responded to this concern with the subfield of behavioral economics, which mixes experimental research with a set of latest theoretical ideas together with prospect principle, bounded rationality, defaults and heuristics, and has succeeded in making a mannequin which in some instances significantly extra precisely fashions human conduct.
Within the context of cryptographic protocols, rationality-based analyses are arguably equally suboptimal, and there are explicit parallels between a few of the ideas; for instance, as we are going to later see, “software program” and “heuristic” are basically synonyms. One other focal point is the truth that we arguably don’t even have an correct mannequin of what constitutes an “agent”, an perception that has explicit significance to protocols that attempt to be “trust-free” or have “no single level of failure”.
Conventional fashions
In conventional fault-tolerance principle, there are three sorts of fashions which might be used for figuring out how properly a decentralized system can survive elements of it deviating from the protocol, whether or not as a consequence of malice or easy failure. The primary of those is easy fault tolerance. In a easy fault tolerant system, the concept is that every one elements of the system will be trusted to do both of two issues: precisely comply with the protocol, or fail. The system ought to be designed to detect failures and get better and route round them in some vogue. Easy fault tolerance is normally the most effective mannequin for evaluating methods which might be politically centralized, however architecturally decentralized; for instance, Amazon or Google’s cloud internet hosting. The system ought to undoubtedly be capable of deal with one server going offline, however the designers don’t want to consider one of many servers changing into evil (if that does occur, then an outage is suitable till the Amazon or Google group manually work out what’s going on and shut that server down).
Nonetheless, easy fault tolerance just isn’t helpful for describing methods that aren’t simply architecturally, but in addition politically, decentralized. What if we have now a system the place we need to be fault-tolerant towards some elements of the system misacting, however the elements of the system is likely to be managed by totally different organizations or people, and you don’t belief all of them to not be malicious (though you do belief that at the least, say, two thirds of them will act actually)? On this case, the mannequin we wish is Byzantine fault tolerance (named after the Byzantine Generals Drawback) – most nodes will actually comply with the protocol, however some will deviate, they usually can deviate in any means; the idea is that every one deviating nodes are colluding to screw you over. A Byzantine-fault-tolerant protocol ought to survive towards a restricted variety of such deviations.
For an instance of straightforward and Byzantine fault-tolerance in motion, a great use case is decentralized file storage.
Past these two situations, there’s additionally one other much more refined mannequin: the Byzantine/Altruistic/Rational mannequin. The BAR mannequin improves upon the Byzantine mannequin by including a easy realization: in actual life, there isn’t any sharp distinction between “trustworthy” and “dishonest” folks; everyone seems to be motivated by incentives, and if the incentives are excessive sufficient then even nearly all of members could properly act dishonestly – notably if the protocol in query weights folks’s affect by financial energy, as just about all protocols do within the blockchain area. Thus, the BAR mannequin assumes three sorts of actors:
- Altruistic – altruistic actors all the time comply with the protocol
- Rational – rational actors comply with the protocol if it fits them, and don’t comply with the protocol if it doesn’t
- Byzantine – Byzantine actors are all conspiring to screw you over
In apply, protocol builders are typically uncomfortable assuming any particular nonzero amount of altruism, so the mannequin that many protocols are judged by is the even harsher “BR” mannequin; protocols that survive below BR are mentioned to be incentive-compatible (something that survives below BR survives below BAR, since an altruist is assured to be at the least nearly as good for the well being of the protocol as anybody else as benefitting the protocol is their specific goal).
Be aware that these are worst-case situations that the system should survive, not correct descriptions of actuality always
To see how this mannequin works, allow us to study an argument for why Bitcoin is incentive-compatible. The a part of Bitcoin that we care most about is the mining protocol, with miners being the customers. The “appropriate” technique outlined within the protocol is to all the time mine on the block with the best “rating”, the place rating is roughly outlined as follows:
- If a block is the genesis block, rating(B) = 0
- If a block is invalid, rating(B) = -infinity
- In any other case, rating(B) = rating(B.mum or dad) + 1
In apply, the contribution that every block makes to the full rating varies with problem, however we are able to ignore such subtleties in our easy evaluation. If a block is efficiently mined, then the miner receives a reward of fifty BTC. On this case, we are able to see that there are precisely three Byzantine methods:
- Not mining in any respect
- Mining on a block apart from the block with highest rating
- Making an attempt to provide an invalid block
The argument towards (1) is easy: in case you do not mine, you do not get the reward. Now, let’s take a look at (2) and (3). When you comply with the right technique, you have got a chance p of manufacturing a sound block with rating s + 1 for some s. When you comply with a Byzantine technique, you have got a chance p of manufacturing a sound block with rating q + 1 with q < s (and in case you attempt to produce an invalid block, you have got a chance of manufacturing some block with rating destructive infinity). Thus, your block just isn’t going to be the block with the best rating, so different miners aren’t going to mine on it, so your mining reward is not going to be a part of the eventual longest chain. Be aware that this argument doesn’t rely upon altruism; it solely is dependent upon the concept that you have got an incentive to maintain in line if everybody else does – a traditional Schelling level argument.
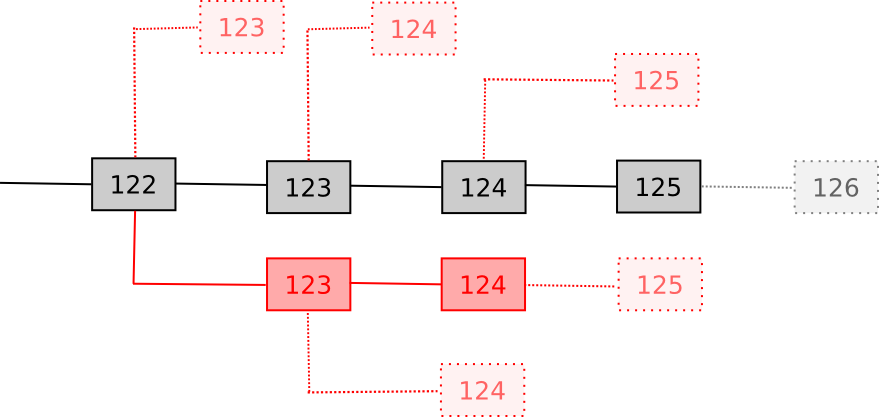
The very best technique to maximise the possibility that your block will get included within the eventual successful blockchain is to mine on the block that has the best rating.
Belief-Free Programs
One other necessary class of cryptoeconomic protocols is the set of so-called “trust-free” centralized protocols. Of those, there are a number of main classes:
Provably honest playing
One of many massive issues in on-line lotteries and playing websites is the opportunity of operator fraud, the place the operator of the location would barely and imperceptibly “load the cube” of their favor. A significant advantage of cryptocurrency is its potential to take away this downside by setting up a playing protocol that’s auditable, so any such deviation will be in a short time detected. A tough define of a provably honest playing protocol is as follows:
- At first of every day, the location generates a seed s and publishes H(s) the place H is a few normal hash operate (eg. SHA3)
- When a person sends a transaction to make a wager, the “cube roll” is calculated utilizing H(s + TX) mod n the place TX is the transaction used to pay for the wager and n is the variety of doable outcomes (eg. if it is a 6-sided die, n = 6, for a lottery with a 1 in 927 likelihood of successful, n = 927 and successful video games are video games the place H(s + TX) mod 927 = 0).
- On the finish of the day, the location publishes s.
Customers can then confirm that (1) the hash supplied in the beginning of the day really is H(s), and (2) that the outcomes of the bets really match the formulation. Thus, a playing website following this protocol has no means of dishonest with out getting caught inside 24 hours; as quickly because it generates s and must publish a worth H(s) it’s principally certain to comply with the exact protocol accurately.
Proof of Solvency
One other utility of cryptography is the idea of making auditable monetary companies (technically, playing is a monetary service, however right here we’re serious about companies that maintain your cash, not simply briefly manipulate it). There are robust theoretical arguments and empirical proof that monetary companies of that kind are more likely to attempt to cheat their customers; maybe probably the most parcticularly jarring instance is the case of MtGox, a Bitcoin alternate which shut down with over 600,000 BTC of buyer funds lacking.
The concept behind proof of solvency is as follows. Suppose there’s an alternate with customers U[1] … U[n] the place person U[i] has steadiness b[i]. The sum of all balances is B. The alternate needs to show that it really has the bitcoins to cowl everybody’s balances. It is a two-part downside: the alternate should concurrently show that for some B it’s true that (1) the sum of customers’ balances is B, and (ii) the alternate is in possession of at the least B BTC. The second is simple to show; simply signal a message with the personal key that holds the bitcoins on the time. The best option to show the primary is to only publish everybody’s balances, and let folks examine that their balances match the general public values, however this compromises privateness; therefore, a greater technique is required.
The answer includes, as standard, a Merkle tree – besides on this case it is a funky enhanced kind of Merkle tree referred to as a “Merkle sum tree”. As a substitute of every node merely being the hash of its youngsters, each node incorporates the hash of its youngsters and the sum of the values of its youngsters:
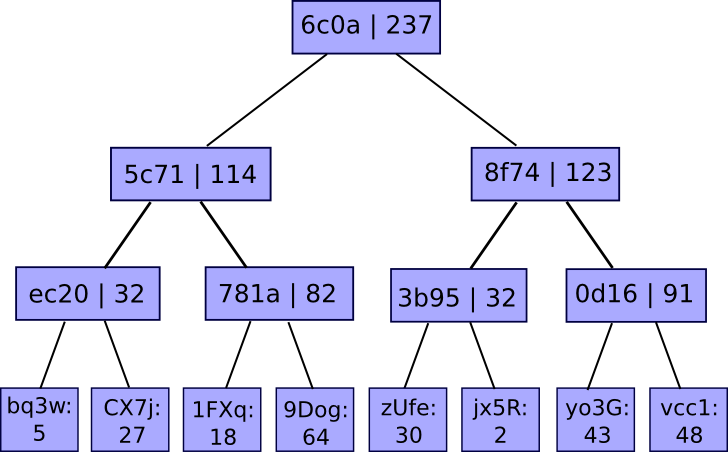
The values on the backside are mappings of account IDs to balances. The service publishes the basis of the tree, and if a person needs a proof that their account is accurately included within the tree, the service can merely give them the department of the tree similar to their account:
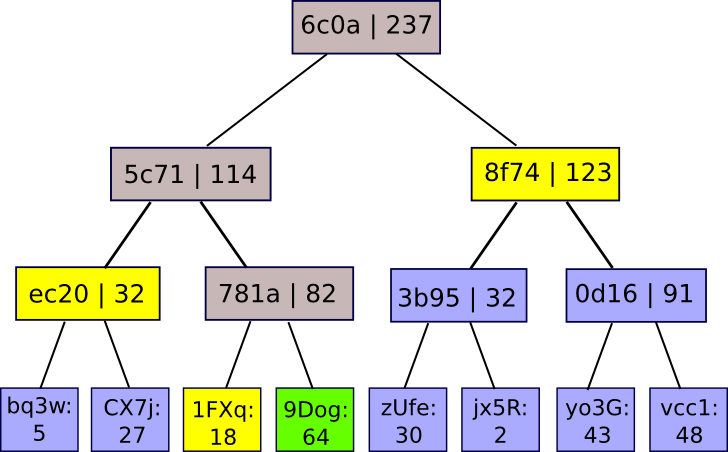
There are two ways in which the location can cheat, and attempt to get away with having a fractional reserve. First, it could attempt to have one of many nodes within the Merkle tree incorrectly sum the values of its youngsters. On this case, as quickly as a person requests a department containing that node they are going to know that one thing is flawed. Second, it could attempt to insert destructive values into the leaves of the tree. Nonetheless, if it does this, then until the location offers pretend optimistic and destructive nodes that cancel one another out (thus defeating the entire level), then there might be at the least one authentic person whose Merkle department will comprise the destructive worth; typically, getting away with having X % lower than the required reserve requires relying on a selected X % of customers by no means performing the audit process – a outcome that’s really the most effective that any protocol can do, provided that an alternate can all the time merely zero out some proportion of its customers’ account balances if it is aware of that they are going to by no means uncover the fraud.
Multisig
A 3rd utility, and a vital one, is multisig, or extra usually the idea of multi-key authorization. As a substitute of your account being managed by one personal key which can get hacked, there are three keys, of which two are wanted to entry the account (or another configuration, maybe involving withdrawal limits or time-locked withdrawals; Bitcoin doesn’t help such options however extra superior methods do). The way in which multisig is normally carried out to this point is as a 2-of-3: you have got one key, the server has one key, and you’ve got a 3rd backup key in a secure place. In the middle of regular exercise, once you signal a transaction you usually signal it along with your key regionally, then ship it to the server. The server performs some second verification course of – maybe consisting of sending a affirmation code to your cellphone, and if it confirms that you just meant to ship the transaction then it indicators it as properly.
The concept is that such a system is tolerant towards any single fault, together with any single Byzantine fault. When you lose your password, you have got a backup, which along with the server can get better your funds, and in case your password is hacked, the attacker solely has one password; likewise for loss or theft of the backup. If the service disappears, you have got two keys. If the service is hacked or seems to be evil, it solely has one. The chance of two failures taking place on the similar time could be very small; arguably, you usually tend to die.
Basic Models
The entire above arguments make one key assumption that appears trivial, however really must be challenged way more carefully: that the elemental unit of the system is the pc. Every node has the motivation to mine on the block with the best rating and never comply with some deviant technique. If the server will get hacked in a multisig then your laptop and your backup nonetheless have 2 out of three keys, so you might be nonetheless secure. The issue with the strategy is that it implicitly assumes that customers have full management over their computer systems, and that the customers absolutely perceive cryptography and are manually verifying the Merkle tree branches. In actuality, this isn’t the case; actually, the very necessity of multisig in any incarnation in any respect is proof of this, because it acknowledges that customers’ computer systems can get hacked – a duplicate of the behavioral-economics concept that people will be considered as not being in full management of themselves.
A extra correct mannequin is to view a node as a mixture of two classes of brokers: a person, and a number of software program suppliers. Customers in almost all instances don’t confirm their software program; even in my very own case, though I confirm each transaction that comes out of the Ethereum exodus handle, utilizing the pybitcointools toolkit that I wrote from scratch myself (others have supplied patches, however even these I reviewed personally), I’m nonetheless trusting that (1) the implementations of Python and Ubuntu that I downloaded are authentic, and (2) that the {hardware} just isn’t someway bugged. Therefore, these software program suppliers ought to be handled as separate entities, and their targets and incentives ought to be analyzed as actors in their very own proper. In the meantime, customers also needs to be considered as brokers, however as brokers who’ve restricted technical functionality, and whose selection set usually merely consists of which software program packages to put in, and never exactly which protocol guidelines to comply with.
The primary, and most necessary, remark is that the ideas of “Byzantine fault tolerance” and “single level of failure” ought to be considered in gentle of such a distinction. In principle, multisig removes all single factors of failure from the cryptographic token administration course of. In apply, nevertheless, that isn’t the way in which that multisig is normally offered. Proper now, most mainstream multisig wallets are net functions, and the entity offering the online utility is similar entity that manages the backup signing key. What this implies is that, if the pockets supplier does get hacked or does turn into evil, they really have management over two out of three keys – they have already got the primary one, and might simply seize the second just by making a small change to the client-side browser utility they ship to you each time you load the webpage.
In multisig pockets suppliers’ protection, companies like BitGo and GreenAddress do provide an API, permitting builders to make use of their key administration performance with out their interface in order that the 2 suppliers will be separate entities. Nonetheless, the significance of this type of separation is at the moment drastically underemphasized.
This perception applies equally properly to provably honest playing and proof of solvency. Explicit, such provably honest protocols ought to have normal implementations, with open-source functions that may confirm proofs in an ordinary format and in a means that’s simple to make use of. Providers like exchanges ought to then comply with these protocols, and ship proofs which will be verifies by these exterior instruments. If a service releases a proof that may solely be verified by its personal inner instruments, that isn’t a lot better than no proof in any respect – barely higher, since there’s a likelihood that dishonest will nonetheless be detected, however not by a lot.
Software program, Customers and Protocols
If we really do have two lessons of entities, it is going to be useful to supply at the least a tough mannequin of their incentives, in order that we could higher perceive how they’re more likely to act. On the whole, from software program suppliers we are able to roughly count on the next targets:
- Maximize revenue – within the heyday of proprietary software program licensing, this aim was really simple to know: software program firms maximize their earnings by having as many customers as doable. The drive towards open-source and free-to-use software program extra lately has very many benefits, however one drawback is that it now makes the profit-maximization evaluation way more tough. Now, software program firms usually earn money by way of industrial value-adds, the defensibility of which generally includes creating proprietary walled-garden ecosystems. Even nonetheless, nevertheless, making one’s software program as helpful as doable normally helps, at the least when it does not intrude with a proprietary value-add.
- Altruism – altruists write software program to assist folks, or to assist notice some imaginative and prescient of the world.
- Maximize fame – lately, writing open-source software program is commonly used as a means of build up one’s resume, in order to (1) seem extra engaging to employers and (2) achieve the social connections to maximise potential future alternatives. Firms may do that, writing free instruments to drive folks to their web site to be able to promote different instruments.
- Laziness – software program suppliers is not going to write code in the event that they may also help it. The primary consequence of this might be an underinvestment in options that don’t profit their customers, however profit the ecosystem – like responding to requests for information – until the software program ecosystem is an oligopoly.
- Not going to jail – this entails compliance with legal guidelines, which generally includes anti-features similar to requiring identification verification, however the dominant impact of this motive is a disincentive towards screwing one’s clients over too blatantly (eg. stealing their funds).
Customers we is not going to analyze when it comes to targets however reasonably when it comes to a behavioral mannequin: customers choose software program packages from an accessible set, obtain the software program, and select choices from inside that software program. Guiding components in software program choice embody:
- Performance – what’s the utility (that is the economics jargon “utility”) can they derive from the choices that the software program offers?
- Ease of use – of explicit significance is the query of how shortly they will stand up and working doing what they should do.
- Perceived legitimacy – customers usually tend to obtain software program from reliable or at the least trustworthy-seeming entities.
- Salience – if a software program package deal is talked about extra usually, customers might be extra more likely to go for it. A direct consequence is that the “official” model of a software program package deal has a big benefit over any forks.
- Ethical and ideological issues – customers may desire open supply software program for its personal sake, reject purely parasitic forks, and so on.
As soon as customers obtain a chunk of software program, the primary bias that we are able to depend on is that customers will stick with defaults even when it may not profit them to; past that, we have now extra conventional biases similar to loss aversion, which we are going to focus on briefly later.
Now, allow us to present an instance of how this course of works in motion: BitTorrent. Within the BitTorrent protocol, customers can obtain recordsdata from one another a packet at a time in a decentralized vogue, however to ensure that one person to obtain a file there have to be somebody importing (“seeding”) it – and that exercise just isn’t incentivized. Actually, it carries non-negligible prices: bandwidth consumption, CPU useful resource consumption, copyright-related authorized danger (together with danger of getting one’s web connection shut down by one’s ISP, or maybe even a risk of lawsuit). And but folks nonetheless seed – vastly insufficiently, however they do.
Why? The state of affairs is defined completely by the two-layer mannequin: software program suppliers need to make their software program extra helpful, in order that they embody the seeding performance by default, and customers are too lazy to show it off (and a few customers are intentionally altruistic, although the order-of-magnitude mismatch between willingness to torrent copyrighted content material and willingness to donate to artists does counsel that almost all members do not actually care). Message-sending in Bitcoin (ie. to information requests like getblockheader and getrawtransaction) can also be altruistic but in addition equally explainable, as is the inconsistency between transaction charges and what the economics counsel transaction charges at the moment ought to be.
One other instance is proof of stake algorithms. Proof of stake algorithms have the (principally) widespread vulnerability that there’s “nothing at stake” – that’s to say, that the default conduct within the occasion of a fork is to attempt to vote on all chains, so an attacker want solely overpower all altruists that vote on one chain solely, and never all altruists plus all rational actors as within the case of proof of labor. Right here, as soon as once more we are able to see that this doesn’t imply that proof of stake is totally damaged. If the stake is essentially managed by a smaller variety of refined events, then these events can have their possession within the foreign money as the motivation to not take part in forks, and if the stake is managed by very many extra abnormal folks then there would should be some intentionally evil software program supplier who would take an effort to incorporate a multi-voting function, and promote it in order that probably customers really know in regards to the function.
Nonetheless, if the stake is held in custodial wallets (eg. Coinbase, Xapo, and so on) which don’t legally personal the cash, however are specialised skilled entities, then this argument breaks down: they’ve the technical potential to multi-vote, and low incentive to not, notably if their companies aren’t “Bitcoin-centric” (or Ethereum-centric, or Ripple-cetric) and help many protocols. There’s even a probabilistic multi-voting technique which such custodial entities can use to get 99% of the advantages of multi-voting with out the danger of getting caught. Therefore, efficient proof of stake to a average extent is dependent upon applied sciences that enable customers to soundly hold management of their very own cash.
Darker Penalties
What we get out of the default impact is actually a sure degree of centralization, having a useful function by setting customers’ default conduct towards a socially useful motion and thereby correcting for what would in any other case be a market failure. Now, if software program introduces some advantages of centralization, we are able to additionally count on a few of the destructive results of centralization as properly. One explicit instance is fragility. Theoretically, Bitcoin mining is an M-of-N protocol the place N is within the 1000’s; in case you do the combinatoric math, the chance that even 5% of the nodes will deviate from the protocol is infinitesimally small, so Bitcoin ought to have just about excellent reliability. In actuality, in fact, that is incorrect; Bitcoin has had at least two outages within the final six years.
For many who don’t keep in mind, the 2 instances have been as follows:

Driver of 43-year-old automobile exploits integer overflow vulnerability, sells it for 91% of unique buy worth passing it off as new
- In 2010, an unknown person created a transaction with two outputs, every containing barely greater than 263 satoshis. The 2 outputs mixed have been barely over 264, and integer overflow led to the full wrapping round to near-zero, inflicting the Bitcoin consumer to assume that the transaction really launched solely the identical small amount of BTC that it consumed as an enter, and so was authentic. The bug was fastened, and the blockchain reverted, after 9 hours.
- In 2013, a brand new model of the Bitcoin consumer unknowingly fastened a bug during which a block that revamped 5000 accesses to a sure database useful resource would trigger a BerkeleyDB error, resulting in the consumer rejecting the block. Such a block quickly appeared, and new shoppers accepted it and outdated shoppers rejected it, resulting in a fork. The fork was fastened in six hours, however within the meantime $10000 of BTC was stolen from a cost service supplier in a double-spend assault.
In each instances, the community was solely capable of fail as a result of, though there have been 1000’s of nodes, there was just one software program implementation working all of them – maybe the final word fragility in a community that’s usually touted for being antifragile. Different implementations similar to btcd at the moment are more and more getting used, however it is going to be years earlier than Bitcoin Core’s monopoly is something near damaged; and even then fragility will nonetheless be pretty excessive.
Endowment results and Defaults
An necessary set of biases to remember on the person facet are the ideas of the endowment impact, loss aversion, and the default impact. The three usually go hand in hand, however are considerably totally different from one another. The default impact is usually most precisely modeled as an inclination to proceed following one’s present technique until there’s a substantial profit to switching – in essence, a synthetic psychological switching value of some worth ε. The endowment impact is the tendency to see issues as being extra precious if one already has them, and loss aversion is the tendency to care extra about avoiding losses than searching for positive factors – experimentally, the scaling issue appears to be constantly round 2x.
The results of those results pronounce themselves most strongly within the context of multi-currency environments. As one instance, think about the case of staff being paid in BTC. We will see that when persons are paid in BTC, they’re much extra more likely to maintain on to these BTC than they might have been possible to purchase the BTC had they been paid USD; the reason being partially the default impact, and partially the truth that if somebody is paid in BTC they “assume in BTC” so in the event that they promote to USD then if the worth of BTC goes up after that they’ve a danger of struggling a loss, whereas if somebody is paid in USD it’s the USD-value of their BTC that they’re extra involved with. This is applicable additionally to smaller token methods; in case you pay somebody in Zetacoin, they’re more likely to money out into BTC or another coin, however the chance is far lower than 100%.
The loss aversion and default results are a few of the strongest arguments in favor of the thesis {that a} extremely polycentric foreign money system is more likely to proceed to outlive, contra Daniel Krawisz’s viewpoint that BTC is the one token to rule all of them. There’s clearly an incentive for software program builders to create their very own coin even when the protocol might work simply as properly on prime of an present foreign money: you are able to do a token sale. StorJ is the most recent instance of this. Nonetheless, as Daniel Krawisz argues, one might merely fork such an “app-coin” and launch a model on prime of Bitcoin, which might theoretically be superior as a result of Bitcoin is a extra liquid asset to retailer one’s funds in. The explanation why such an consequence has a big likelihood of not taking place is solely the truth that customers comply with defaults, and by default customers will use StorJ with StorJcoin since that’s what the consumer will promote, and the unique StorJ consumer and web site and ecosystem is the one that can get all the eye.
Now, this argument breaks down considerably in a single case: if the fork is itself backed by a robust entity. The newest instance of that is the case of Ripple and Stellar; though Stellar is a fork of Ripple, it’s backed by a big firm, Stripe, so the truth that the unique model of a software program package deal has the benefit of a lot higher salience doesn’t apply fairly as strongly. In such instances, we don’t actually know what is going to occur; maybe, as is commonly the case within the social sciences, we are going to merely have to attend for empirical proof to seek out out.
The Approach Ahead
Counting on particular psychological options of people in cryptographic protocol design is a harmful sport. The explanation why it’s good in economics to maintain one’s mannequin easy, and in cryptoeconomics much more so, is that even when needs like the need to accumulate extra foreign money models don’t precisely describe the entire of human motivation, they describe an evidently very highly effective element of it, and a few could argue the one highly effective element we are able to depend on. Sooner or later, training could start to intentionally assault what we all know as psychological irregularities (actually, it already does), altering tradition could result in altering morals and beliefs, and notably on this case the brokers we’re coping with are “fyborgs” – practical cyborgs, or people who’ve all of their actions mediated by machines just like the one which sits between them and the web.
Nonetheless, there are particular basic options of this mannequin – the idea of cryptoeconomic methods as two-layer methods that includes software program and customers as brokers, the desire for simplicity, and so on, that maybe will be counted on, and on the very least we must always strive to concentrate on circumstances the place our protocol is safe below the BAR mannequin, however insecure below the mannequin the place a number of centralized events are in apply mediating everybody’s entry to the system. The mannequin additionally highlights the significance of “software program politics” – having an understanding of the pressures that drive software program improvement, and making an attempt to give you approaches to improvement that software program builders have the very best incentives (or, in the end, write software program that’s most favorable to the protocol’s profitable execution). These are issues that Bitcoin has not solved, and that Ethereum has not solved; maybe some future system will do at the least considerably higher.
