Fashionable AI chatbots usually depend on Retrieval-Augmented Era (RAG), a method the place the chatbot pulls in exterior knowledge to floor its solutions in actual information. When you’ve used a “Chat along with your” device, you’ve seen RAG in motion: the system finds related snippets from a doc and feeds them right into a Massive Language Mannequin (LLM) so it could actually reply your query with correct info.
RAG has drastically improved the factual accuracy of LLM solutions. Nonetheless, conventional RAG methods principally deal with information as disconnected textual content passages. The LLM is given a handful of related paragraphs and left to piece them collectively throughout its response. This works for easy questions, nevertheless it struggles with advanced queries that require connecting the dots throughout a number of sources.
This text will demystify two ideas that may take chatbots to the following stage, specifically, ontologies and information graphs, and present how they mix with RAG to type a GraphRAG (Graph-based Retrieval-Augmented Era). We’ll clarify what they imply and why they matter in easy phrases.
Why does this matter, you may ask? As a result of GraphRAG guarantees to make chatbot solutions extra correct, context-aware, and insightful than what you get with a standard RAG. Companies exploring AI options worth these qualities — an AI that may actually perceive context, keep away from errors, and motive by means of advanced questions could be a game-changer. (Though this wants an ideal implementation, which frequently is just not the case in follow.)
By combining unstructured textual content with a structured information graph, GraphRAG methods can present solutions that really feel way more knowledgeable. Bridging information graphs with LLMs is a key step towards AI that doesn’t simply retrieve info, however truly understands it.
What’s RAG?
Retrieval-Augmented Era, or RAG, is a method for enhancing language mannequin responses by grounding them in exterior information. As an alternative of replying primarily based solely on what’s in its mannequin reminiscence, which may be outdated or incomplete, a RAG-based system will fetch related info from an outdoor supply (e.g., paperwork, databases and the net) and feed that into the mannequin to assist formulate the reply.
In easy phrases, RAG = LLM + Search Engine: the mannequin first retrieves supporting knowledge, augments its understanding of the subject after which generates a response utilizing each its built-in information and the retrieved data.
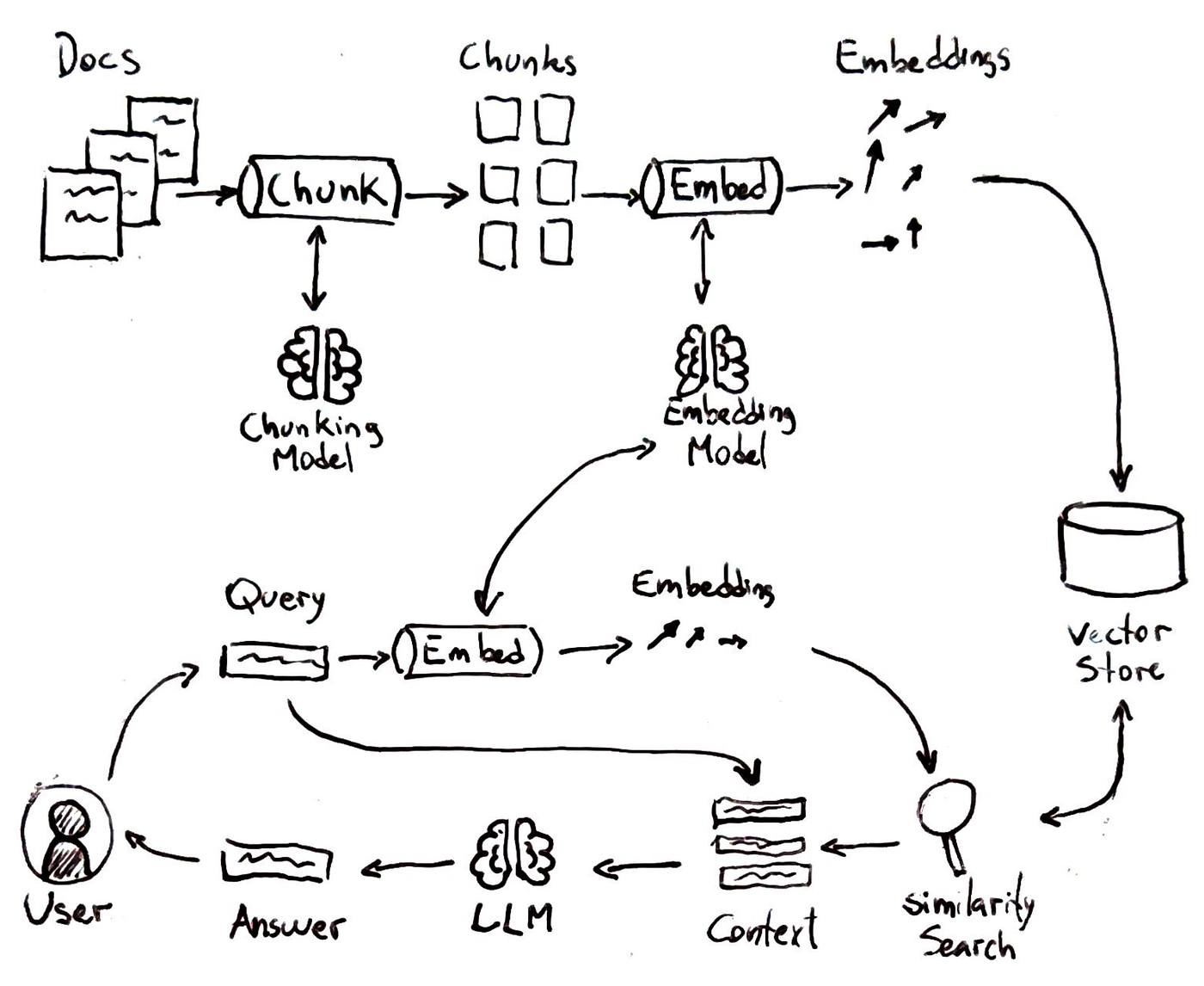
As proven within the determine above the everyday RAG pipeline includes a number of steps that mirror a sensible lookup course of:
-
Indexing Data:
First, the system breaks the information supply (say a group of paperwork) into chunks of textual content and creates vector embeddings for every chunk. These embeddings are numerical representations of the textual content which means. All these vectors are saved in a vector database or index.
-
Question Embedding:
When a person asks a query, the question can also be transformed right into a vector embedding utilizing the identical method.
-
Similarity Search:
The system compares the question vector to all of the saved vectors to seek out which textual content chunks are most “comparable” or related to the query.
-
Era with Context:
Lastly, the language mannequin is given the person’s query plus the retrieved snippets as context. It then generates a solution that includes the offered info.
RAG has been an enormous step ahead for making LLMs helpful in real-world eventualities. It’s how instruments like Bing Chat or varied doc QA bots can present present, particular solutions with references. By grounding solutions in retrieved textual content, RAG reduces hallucinations (the mannequin may be pointed to the information) and permits entry to info past the AI’s coaching cutoff date. Nonetheless, conventional RAG additionally has some well-known limitations:
- It treats the retrieved paperwork basically as separate, unstructured blobs. If a solution requires synthesising data throughout a number of paperwork or understanding relationships, the mannequin has to do this heavy lifting itself throughout era.
- RAG retrieval is often primarily based on semantic similarity. It finds related passages however doesn’t inherently perceive the which means of the content material or how one truth may relate to a different.
- There is no such thing as a built-in mechanism for reasoning or implementing consistency throughout the retrieved knowledge; the LLM simply will get a dump of textual content and tries its greatest to weave it collectively.
In follow, for easy factual queries, e.g., “When was this firm based?”, conventional RAG is nice. For extra advanced questions, e.g., “Evaluate the traits in Q1 gross sales and Q1 advertising spend and determine any correlations.”, conventional RAG may falter. It might return one chunk about gross sales, one other about advertising, however depart the logical integration to the LLM, which can or might not succeed coherently.
These limitations level to a possibility. What if, as a substitute of giving the AI system only a pile of paperwork, we additionally gave it a information graph (i.e. a community of entities and their relationships) as a scaffold for reasoning? If RAG retrieval might return not simply textual content primarily based on similarity search, however a set of interconnected information, the AI system might observe these connections to supply a extra insightful reply.
GraphRAG is about integrating this graph-based information into the RAG pipeline. By doing so, we purpose to beat the multi-source, ambiguity, and reasoning points highlighted above.
Earlier than we get into how GraphRAG works, although, let’s make clear what we imply by information graphs and ontologies — the constructing blocks of this method.
Data Graphs
A information graph is a networked illustration of real-world information, the place every node represents an entity and every edge represents a relationship between entities.
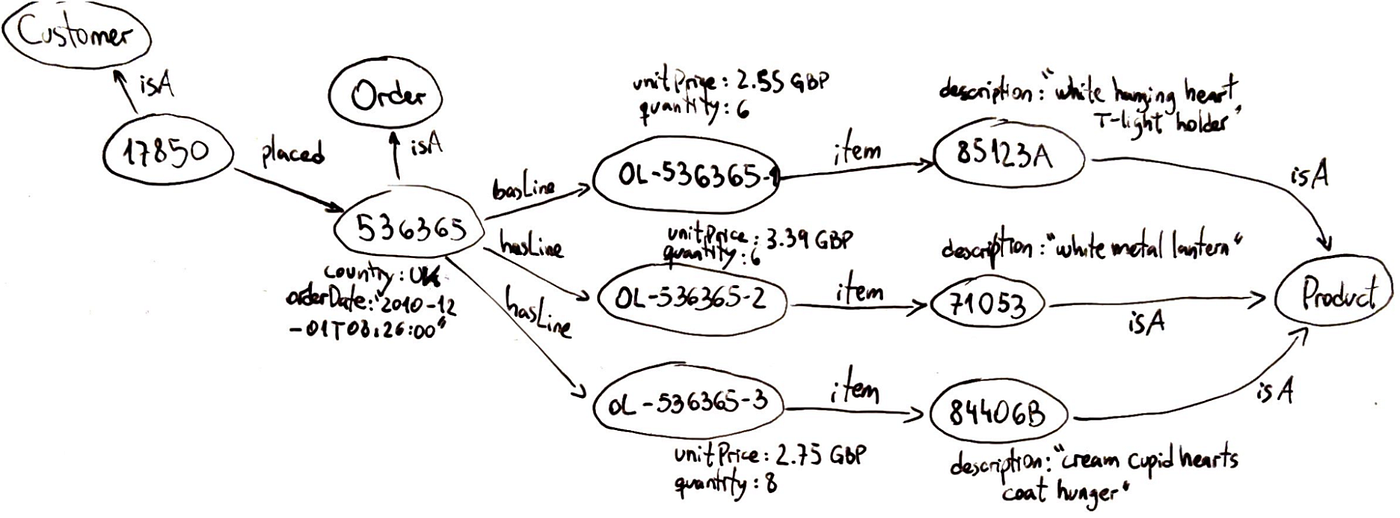
Within the determine above, we see a graphical illustration of what a information graph appears to be like like. It buildings knowledge as a graph, not as tables or remoted paperwork. This implies info is saved in a method that inherently captures connections. Some key traits:
- They’re versatile: You’ll be able to add a brand new kind of relationship or a brand new property to an entity with out upending the entire system. Graphs can simply evolve to accommodate new information.
- They’re semantic: Every edge has which means, which makes it doable to traverse the graph and retrieve significant chains of reasoning. The graph can signify context together with content material.
- They naturally assist multi-hop queries: If you wish to discover how two entities are linked, a graph database can traverse neighbors, then neighbors-of-neighbors, and so forth.
- Data graphs are often saved in specialised graph databases or triplestores. These methods are optimised for storing nodes and edges and operating graph queries.
The construction of data graphs is a boon for AI methods, particularly within the RAG context. As a result of information are linked, an LLM can get a net of associated info moderately than remoted snippets. This implies:
- AI methods can higher disambiguate context. For instance, if a query mentions “Jaguar,” the graph can make clear whether or not it refers back to the automotive or the animal by means of relationships, offering context that textual content alone usually lacks.
- An AI system can use “joins” or traversals to gather associated information. As an alternative of separate passages, a graph question can present a linked subgraph of all related info, providing the mannequin a pre-connected puzzle moderately than particular person items.
- Data graphs guarantee consistency. For instance, if a graph is aware of Product X has Half A and Half B, it could actually reliably record solely these elements, in contrast to textual content fashions which may hallucinate or miss info. The structured nature of graphs permits full and proper aggregation of information.
- Graphs provide explainability by tracing the nodes and edges used to derive a solution, permitting for a transparent chain of reasoning and elevated belief by means of cited information.
To sum up, a information graph injects which means into the AI’s context. Somewhat than treating your knowledge as a bag of phrases, it treats it as a community of data. That is precisely what we wish for an AI system tasked with answering advanced questions: a wealthy, linked context it could actually navigate, as a substitute of a heap of paperwork it has to brute-force parse each time.
Now that we all know what information graphs are, and the way they’ll profit AI methods, let’s see what ontologies are and the way they could assist to construct higher information graphs.
Ontologies
Within the context of data methods, an ontology is a proper specification of data for a selected area. It defines the entities (or ideas) that exist within the area and the relationships between these entities.
Press enter or click on to view picture in full measurement
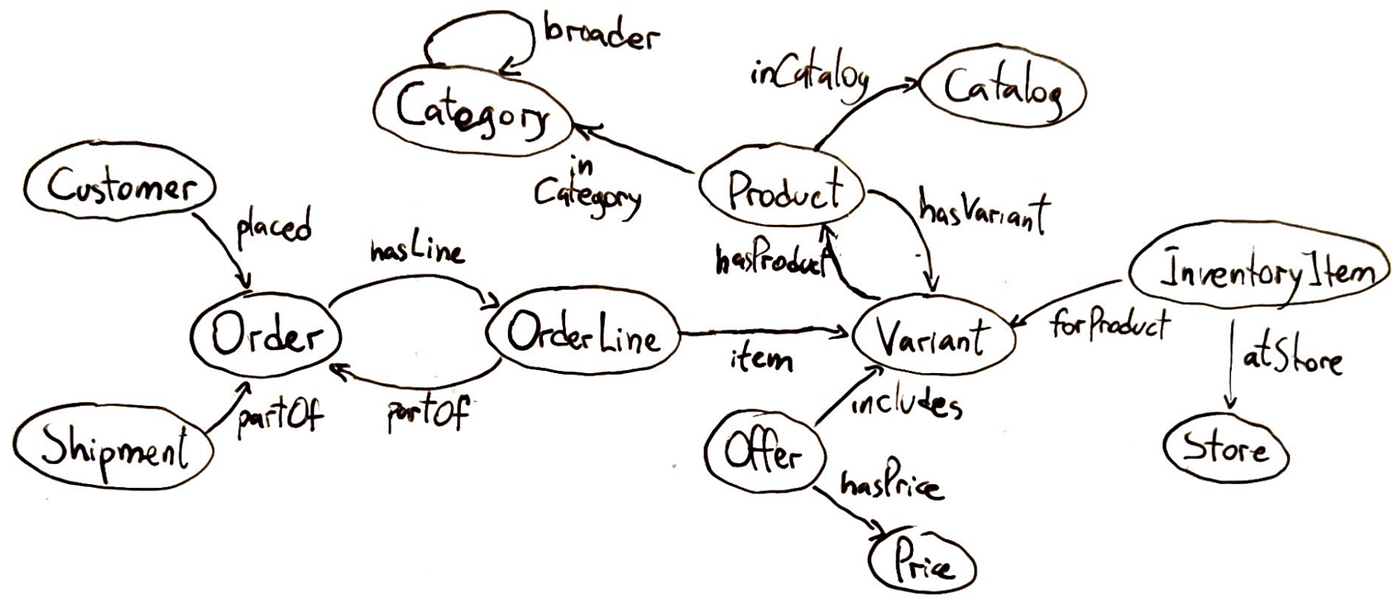
Ontologies usually organise ideas into hierarchies or taxonomies. However can even embrace logical constraints or guidelines: for instance, one might declare “Each Order should have at the least one Product merchandise.”
Why ontologies matter? Chances are you’ll ask. Effectively, an ontology supplies a shared understanding of a site, which is extremely helpful when integrating knowledge from a number of sources or when constructing AI methods that have to motive in regards to the area. By defining a typical set of entity varieties and relationships, an ontology ensures that totally different groups or methods check with issues persistently. For instance, if one dataset calls an individual a “Shopper” and one other calls them “Buyer,” mapping each to the identical ontology class (say Buyer as a subclass of Individual) allows you to merge that knowledge seamlessly.
Within the context of AI and GraphRAG, an ontology is the blueprint for the information graph — it dictates what sorts of nodes and hyperlinks your graph can have. That is essential for advanced reasoning. In case your chatbot is aware of that “Amazon” within the context of your utility is a Firm (not a river) and that Firm is outlined in your ontology (with attributes like headquarters, CEO, and so on., and relationships like hasSubsidiary), it could actually floor its solutions way more exactly.
Now that we learn about information graphs and ontologies, let’s see how we put all of it collectively in a RAG-alike pipeline.
GraphRAG
GraphRAG is an evolution of the standard RAG method that explicitly incorporates a information graph into the retrieval course of. In GraphRAG, when a person asks a query, the system doesn’t simply do a vector similarity search over textual content; it additionally queries the information graph for related entities and relationships.
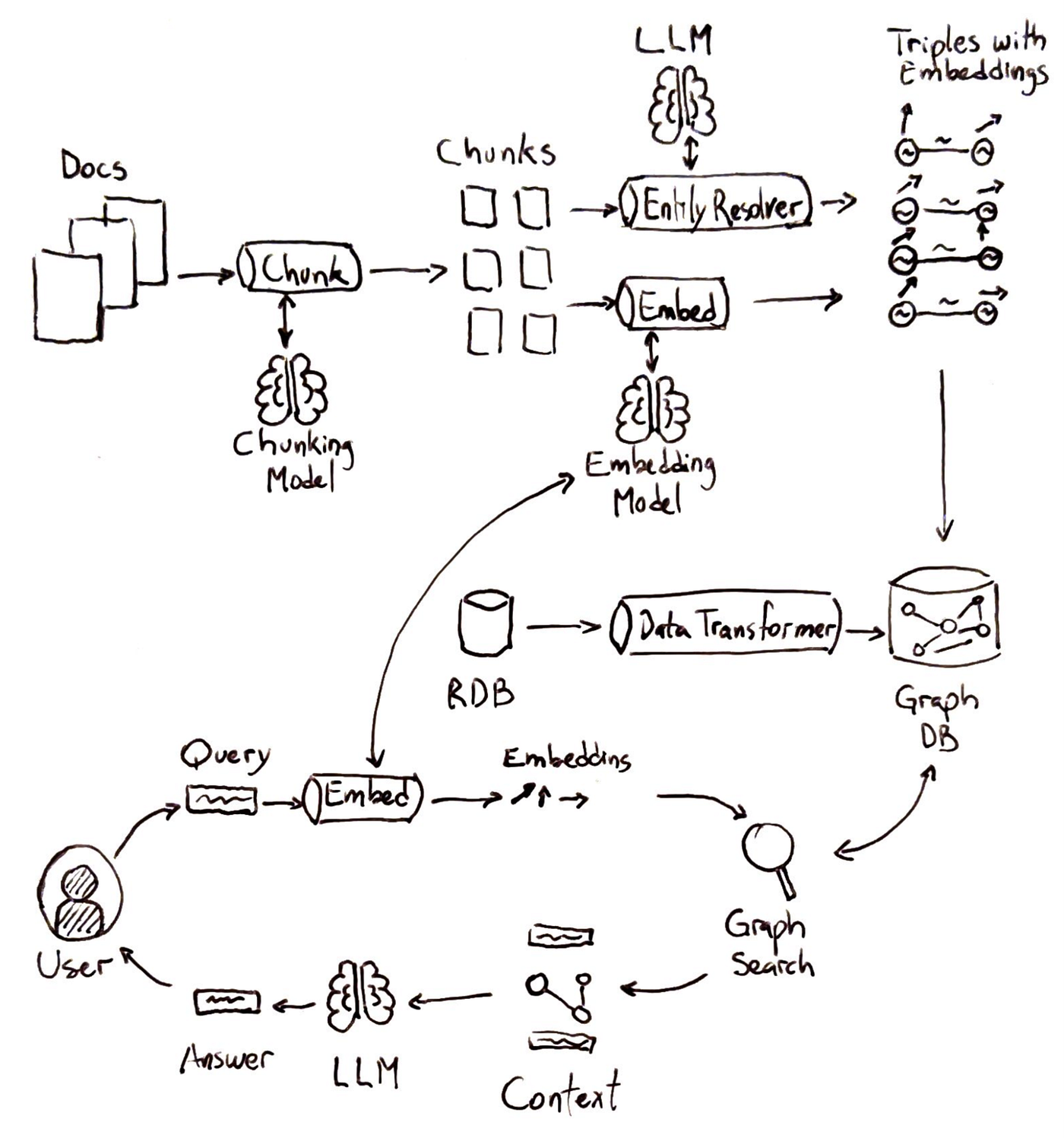
Let’s stroll by means of a typical GraphRAG pipeline at a excessive stage:
-
Indexing information:
Each structured knowledge (e.g., databases, CSV recordsdata) and unstructured knowledge (e.g., paperwork) are taken as enter. Structured knowledge goes by means of knowledge transformation, changing desk rows to triples. Unstructured knowledge is damaged down into manageable textual content chunks. Entities and relationships are extracted from these chunks and concurrently embeddings are calculated to create triples with embeddings.
-
Query Evaluation and Embedding:
The person’s question is analyzed to determine key phrases or entities. These components are embedded with the identical embedding mannequin used for indexing.
-
Graph Search:
The system queries the information graph for any nodes associated to these key phrases. As an alternative of retrieving solely semantically comparable gadgets, the system additionally leverages relationships.
-
Era with Graph Context:
A generative mannequin makes use of the person’s question and the retrieved graph-enriched context to supply a solution.
Underneath the hood, GraphRAG can use varied methods to combine the graph question. The system may first do a semantic seek for top-Okay textual content chunks as common, then traverse the graph neighborhood of these chunks to assemble further context, earlier than producing the reply. This ensures that if related data is unfold throughout paperwork, the graph will assist pull within the connecting items. In follow, GraphRAG may contain additional steps like entity disambiguation (to verify the “Apple” within the query is linked to the correct node, both Firm or Fruit) and graph traversal algorithms to broaden the context. However the high-level image is as described: search + graph lookup as a substitute of search alone.
Total, for non-technical readers, you possibly can consider GraphRAG as giving the AI a “brain-like” information community along with the library of paperwork. As an alternative of studying every guide (doc) in isolation, the AI additionally has an encyclopedia of information and the way these information relate. For technical readers, you may think an structure the place we now have each a vector index and a graph database working in tandem — one retrieving uncooked passages, the opposite retrieving structured information, each feeding into the LLM’s context window.
Constructing a Data Graph for RAG: Approaches
There are two broad methods to construct the information graph that powers a GraphRAG system: a Prime-Down method or a Backside-Up method. They’re not mutually unique (usually you may use a little bit of each), nevertheless it’s useful to tell apart them.
Method 1: Prime-Down (Ontology First)
The highest-down method to ontology begins by defining the area’s ontology earlier than including knowledge. This includes area consultants or business requirements to determine lessons, relationships, and guidelines. This schema, loaded right into a graph database as empty scaffolding, guides knowledge extraction and group, performing as a blueprint.
As soon as the ontology (schema) is in place, the following step is to instantiate it with actual knowledge. There are a number of sub-approaches right here:
-
Utilizing Structured Sources:
If in case you have current structured databases or CSV recordsdata, you map these to the ontology. This will generally be performed through automated ETL instruments that convert SQL tables to graph knowledge if the mapping is easy.
-
Extracting from Textual content through Ontology:
For unstructured knowledge (like paperwork, PDFs, and so on.), you’ll use NLP strategies however guided by the ontology. This usually includes writing extraction guidelines or utilizing an LLM with prompts that reference the ontology’s phrases.
-
Handbook or Semi-Handbook Curation:
In important domains, a human may confirm every extracted triple or manually enter some knowledge into the graph, particularly if it’s a one-time setup of key information. For instance, an organization may manually enter its org chart or product hierarchy into the graph in accordance with the ontology, as a result of that knowledge is comparatively static and essential.
The secret is that with a top-down method, the ontology acts as a information at each step. It tells your extraction algorithms what to search for and ensures the info coming in suits a coherent mannequin.
One huge benefit of utilizing a proper ontology is that you would be able to leverage reasoners and validators to maintain the information graph constant. Ontology reasoners can robotically infer new information or examine for logical inconsistencies, whereas instruments like SHACL implement knowledge form guidelines (just like richer database schemas). These checks forestall contradictory information and enrich the graph by robotically deriving relationships. In GraphRAG, this implies solutions may be discovered even when multi-hop connections aren’t express, because the ontology helps derive them.
Method 2: Backside-Up (Knowledge First)
The underside-up method seeks to generate information graphs immediately from knowledge, with out counting on a predefined schema. Advances in NLP and LLMs allow the extraction of structured triples from unstructured textual content, which may then be ingested right into a graph database the place entities type nodes and relationships type edges.
Underneath the hood, bottom-up extraction can mix classical NLP and fashionable LLMs:
-
Named Entity Recognition (NER):
Determine names of individuals, organizations, locations, and so on., in textual content.
-
Relation Extraction (RE):
Determine if any of these entities have a relationship talked about.
-
Coreference Decision:
Determine the referent of a pronoun in a passage, so the triple can use the complete identify.
There are libraries like spaCy or Aptitude for the standard method, and newer libraries that combine LLM requires IE (Data Extraction). Additionally, strategies like ChatGPT plugins or LangChain brokers may be set as much as populate a graph: the agent might iteratively learn paperwork and name a “graph insert” device because it finds information. One other attention-grabbing technique is utilizing LLMs to recommend the schema by studying a pattern of paperwork (this edges in the direction of ontology era, however bottom-up).
A giant warning with bottom-up extraction is that LLMs may be imperfect and even “inventive” in what they output. They may hallucinate a relationship that wasn’t truly acknowledged, or they may mis-label an entity. Subsequently, an necessary step is validation:
- Cross-check important information in opposition to the supply textual content.
- Use a number of passes: e.g., first move for entities, second move simply to confirm and fill relations.
- Human spot-checking: Have people evaluate a pattern of the extracted triples, particularly these which can be going to be excessive affect.
The method is often iterative. You run the extraction, discover errors or gaps, modify your prompts or filters, and run once more. Over time, this may dramatically refine the information graph high quality. The excellent news is that even with some errors, the information graph can nonetheless be helpful for a lot of queries — and you may prioritize cleansing the elements of the graph that matter most to your use circumstances.
Lastly, take into account that sending textual content for extraction exposes your knowledge to the LLM/service, so it’s best to guarantee compliance with privateness and retention necessities.
Constructing a GraphRAG system may sound daunting, you must handle a vector database, a graph database, run LLM extraction pipelines, and so on. The excellent news is that the group is growing instruments to make this simpler. Let’s briefly point out among the instruments and frameworks that may assist, and what position they play.
Graph Storage
First, you’ll want a spot to retailer and question your information graph. Conventional graph databases like Neo4j, Amazon Neptune, TigerGraph, or RDF triplestores (like GraphDB or Stardog) are frequent decisions.
These databases are optimized for precisely the sort of operations we mentioned:
- traversing relationships
- discovering neighbors
- executing graph queries
In a GraphRAG setup, the retrieval pipeline can use such queries to fetch related subgraphs. Some vector databases (like Milvus or Elasticsearch with Graph plugin) are additionally beginning to combine graph-like querying, however typically, a specialised graph DB affords the richest capabilities. The necessary factor is that your graph retailer ought to enable environment friendly retrieval of each direct neighbors and multi-hop neighborhoods, since a posh query may require grabbing a complete community of information.
Rising Instruments
New instruments are rising to mix graphs with LLMs:
- Cognee — An open-source “AI reminiscence engine” that builds and makes use of information graphs for LLMs. It acts as a semantic reminiscence layer for brokers or chatbots, turning unstructured knowledge into structured graphs of ideas and relationships. LLMs can then question these graphs for exact solutions. Cognee hides graph complexity: builders solely want to offer knowledge, and it produces a graph prepared for queries. It integrates with graph databases and affords a pipeline for ingesting knowledge, constructing graphs, and querying them with LLMs.
- Graphiti (by Zep AI) — A framework for AI brokers needing real-time, evolving reminiscence. In contrast to many RAG methods with static knowledge, Graphiti updates information graphs incrementally as new info arrives. It shops each information and their temporal context, utilizing Neo4j for storage and providing an agent-facing API. In contrast to earlier batch-based GraphRAG methods, Graphiti handles streams effectively with incremental updates, making it suited to long-running brokers that study constantly. This ensures solutions at all times replicate the most recent knowledge.
- Different frameworks — Instruments like LlamaIndex and Haystack add graph modules with out being graph-first. LlamaIndex can extract triplets from paperwork and assist graph-based queries. Haystack experimented with integrating graph databases to increase query answering past vector search. Cloud suppliers are additionally including graph options: AWS Bedrock Data Bases helps GraphRAG with managed ingestion into Neptune, whereas Azure Cognitive Search integrates with graphs. The ecosystem is evolving shortly.
No Have to Reinvent the Wheel
The takeaway is that if you wish to experiment with GraphRAG, you don’t should construct every little thing from scratch. You’ll be able to:
- Use Cognee to deal with information extraction and graph building out of your textual content (as a substitute of writing all of the prompts and parsing logic your self).
- Use Graphiti for those who want a plug-and-play reminiscence graph particularly for an agent that has conversations or time-based knowledge.
- Use LlamaIndex or others to get fundamental KG extraction capabilities with only a few traces of code.
- Depend on confirmed graph databases so that you don’t have to fret about writing a customized graph traversal engine.
In abstract, whereas GraphRAG is on the leading edge, the encompassing ecosystem is quickly rising. You’ll be able to leverage these libraries and providers to face up a prototype shortly, then iteratively refine your information graph and prompts.
Conclusion
Conventional RAG works properly for easy truth lookups, however struggles when queries demand deeper reasoning, accuracy, or multi-step solutions. That is the place GraphRAG excels. By combining paperwork with a information graph, it grounds responses in structured information, reduces hallucinations, and helps multi-hop reasoning. Thus enabling AI to attach and synthesize info in methods commonplace RAG can not.
After all, this energy comes with trade-offs. Constructing and sustaining a information graph requires schema design, extraction, updates, and infrastructure overhead. For easy use circumstances, conventional RAG stays the easier and extra environment friendly alternative. However when richer solutions, consistency, or explainability matter, GraphRAG delivers clear advantages.
Trying forward, knowledge-enhanced AI is evolving quickly. Future platforms might generate graphs robotically from paperwork, with LLMs reasoning immediately over them. For corporations like GoodData, GraphRAG bridges AI with analytics, enabling insights that transcend “what occurred” to “why it occurred.”
In the end, GraphRAG strikes us nearer to AI that doesn’t simply retrieve information, however actually understands and causes about them, like a human analyst, however at scale and pace. Whereas the journey includes complexity, the vacation spot (extra correct, explainable, and insightful AI) is properly definitely worth the funding. The important thing lies in not simply accumulating information, however connecting them.
