French President Emmanuel Macron promised to rein within the nation’s finances deficit inside the subsequent 4 years. Newly launched knowledge reveals France is transferring within the incorrect course.
On 26 March, the French Nationwide Institute of Statistics and Financial Research (INSEE) discovered that France’s 2023 finances deficit was a shocking 5.5 p.c of GDP—0.6 p.c over the federal government’s 4.9 p.c goal. The €154 billion hole places into doubt President Macron’s aim of slicing France’s deficit to lower than 3 p.c of GDP—in step with the EU’s Stability & Development Pact guidelines—by 2027.
Essentially, French society is engaged in a debate in regards to the guarantees of financial development, the standard of public spending, and general fiscal equity. Many are questioning what position development and taxA tax is a compulsory cost or cost collected by native, state, and nationwide governments from people or companies to cowl the prices of basic authorities companies, items, and actions.
coverage ought to play in stabilizing public funds over the long run.
This isn’t to say the general public protests, such because the Yellow Vests, which have made it clear to all political events that tax coverage’s results on their lifestyle is a essential difficulty. Companions taken with joint financial reforms on the EU degree, together with joint debt proposals to finance a extra geopolitically bold agenda, are additionally watching with a skeptical eye.
Total, France’s downside just isn’t the shortage of worthwhile financial exercise to tax; it’s the tax system’s inefficiency. To make systematic and aggressive reforms, policymakers ought to deal with principled tax coverage.
Reform Proposals So Far
Finance Minister Bruno Le Maire has known as for cuts to public spending to cut back the finances hole and has dominated out rising taxes. The latter is in keeping with President Macron’s place since he was elected in 2017 to revive competitiveness, develop the French economic system, and enhance income. In spite of everything, France already has one of many highest mixed tax and obligatory contribution charges on this planet and an above-average 110.6 p.c debt-to-GDP ratio.
Nevertheless, opponents have recommended that elevated development and cuts to present public spending won’t generate sufficient income to stabilize public funds after considering rising rates of interest, public funding for the inexperienced transition, and elevated protection prices. Due to this fact, they argue that tax will increase should be a part of the long-term answer.
However French tax reform is extra difficult than whether or not the wealthy ought to pay extra or the poor ought to pay their very own manner. Proposing insurance policies that sound good politically however don’t clear up the issue—like extending momentary windfall earnings taxes on vitality corporations—fail to boost enough income and additional erode public belief in policymakers to search out significant options.
Development Issues for Income
Lowering public spending is one technique to shut the finances deficit within the quick time period. Nevertheless, given that the entire charge of tax and social contributions in France is near 50 p.c of financial manufacturing, policymakers ought to keep away from slicing public spending too quickly as a result of it might probably scale back long-term financial development. For each one p.c of GDP misplaced, a 0.5 share level enhance within the deficit may be anticipated.
Equally essential for development is to know that there’s a hierarchy of higher and worse methods to boost a euro of income as a result of several types of taxes influence the economic system in several magnitudes.
For instance, taxes on essentially the most cell components within the economic system, reminiscent of capital, trigger essentially the most distortions and have essentially the most destructive influence. Taxes on components that may’t simply be moved, reminiscent of land, are essentially the most steady and least distortive. Moreover, consumption taxes, such because the value-added tax (VAT), are comparatively impartial, minimally distortive, and a extra economically environment friendly technique to increase income. Understanding the distortive results of sure tax insurance policies in comparison with others would enable policymakers to realize their development and income objectives extra simply.
Does France Have a Aggressive and Impartial Tax System?
Typically, a aggressive tax system retains marginal tax charges low as a result of mobility of capital whereas a impartial system goals to boost essentially the most income with the fewest financial distortions. There are various components that contribute to a rustic’s financial efficiency, however a aggressive and impartial tax system promotes sustainable financial development and funding whereas elevating enough income for presidency priorities.
After years of being the least aggressive tax system within the Organisation for Financial Co-operation and Improvement (OECD), France has made its tax system extra aggressive underneath President Macron by progressively lowering the statutory company earnings taxA company earnings tax (CIT) is levied by federal and state governments on enterprise earnings. Many corporations should not topic to the CIT as a result of they’re taxed as pass-through companies, with earnings reportable underneath the particular person earnings tax.
charge from 33.3 p.c to 25.83 p.c, slicing private earnings taxes, simplifying contributions to the social safety system, and implementing numerous property taxA property tax is primarily levied on immovable property like land and buildings, in addition to on tangible private property that’s movable, like autos and tools. Property taxes are the one largest supply of state and native income within the U.S. and assist fund colleges, roads, police, and different companies.
reforms.
Nevertheless, too typically a aggressive tax system is mistaken within the public debate to imply a low company tax charge. Whereas the company tax charge can sway funding choices, having a aggressive tax system goes nicely past the speed charged on company earnings.
Based on Tax Basis’s 2023 Worldwide Tax Competitiveness Index, which seeks to measure the extent to which a rustic’s tax system is aggressive and impartial, France nonetheless ranks 36th out of 38 OECD international locations. Broadly, this is because of vital complexity all through the tax system, tax baseThe tax base is the entire quantity of earnings, property, property, consumption, transactions, or different financial exercise topic to taxation by a tax authority. A slim tax base is non-neutral and inefficient. A broad tax base reduces tax administration prices and permits extra income to be raised at decrease charges.
points, and economically distortive insurance policies.
For instance, France ranks 32nd general within the OECD on consumption taxes. This isn’t essentially because of a excessive charge (which ranks 16th) however reasonably to the consumption base’s design (ranked 36th).
Ideally, the VAT ought to be levied at a typical charge on all closing consumption, however French policymakers have carried out charge reductions on some merchandise and exempted sure items from the VAT base. The C-efficiency ratio (which measures how a lot of ultimate consumption the VAT covers) is just at 53 p.c, revealing each coverage and enforcement gaps. The OECD common is 58 p.c.
On prime of that, France’s VAT threshold (€91.900) is the third-highest within the OECD relative to buying energy, solely behind Italy (€85.000) and the Czech Republic (€79.000) and greater than twice the OECD common of round €34.000 (when it comes to French buying energy).
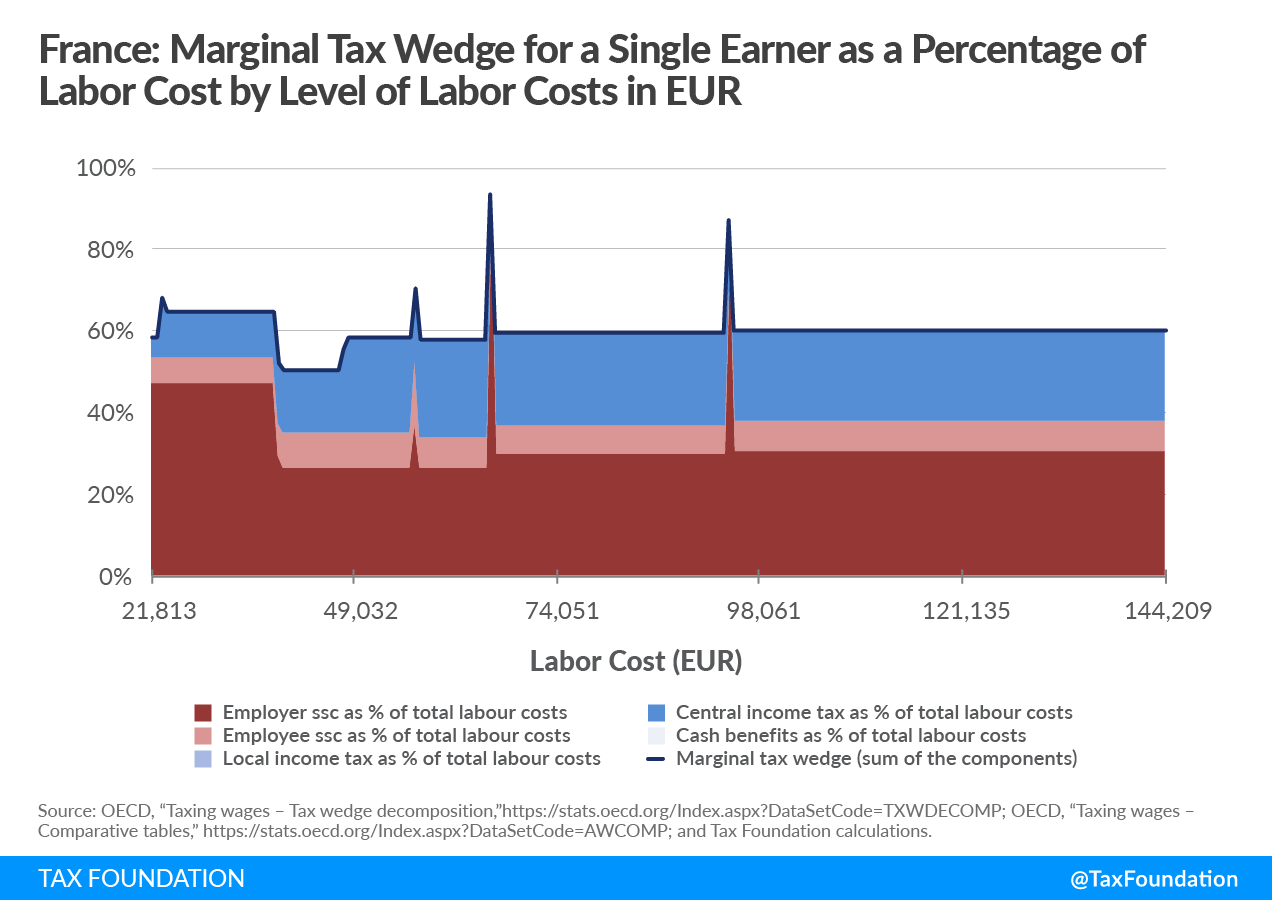
Moreover, the French earnings tax construction discourages employee mobility. Given the complexity of the social safety contribution system, a number of unintended spikes happen throughout the marginal tax wedgeA tax wedge is the distinction between whole labor prices to the employer and the corresponding internet take-home pay of the worker. It is usually an financial time period that refers back to the financial inefficiency ensuing from taxes.
. This could particularly harm average-income employees that events throughout the political spectrum declare to wish to assist.
Lastly, France is among the final remaining international locations in Europe to depend on enterprise turnover taxes. These manufacturing taxes—generally known as the cotisation sur la valeur ajoutée des entreprises (CVAE), cotisation foncière des entreprises (CFE), and cotisation économique territoriale (CET)—are regressive, as a result of they tax earnings reasonably than earnings, and are disconnected from a enterprise’s financial efficiency. The federal government has appropriately recognized these insurance policies as problematic however has continued to delay their correction. That is along with the digital companies tax that produces an identical regressive outcome.
That is removed from an exhaustive listing of flaws within the French tax system, however these examples assist illustrate the broader uncompetitive and non-neutral themes.
Effectivity Reforms
The excellent news for French policymakers trying to effectively increase extra income whereas sustaining financial development is that there are profitable choices out there.
At €73 billion, France has the biggest VAT actionable coverage hole within the EU, which is a measure of misplaced income because of policymakers coverage decisions, reminiscent of decreased charges on sure items or exempting sure gadgets from the VAT base altogether. As a result of this foregone income is because of decisions, policymakers can change these decisions to a extra environment friendly combine whereas supporting financial development.
Moreover, smoothing marginal tax chargeThe marginal tax charge is the quantity of extra tax paid for each extra greenback earned as earnings. The typical tax charge is the entire tax paid divided by whole earnings earned. A ten p.c marginal tax charge signifies that 10 cents of each subsequent greenback earned can be taken as tax.
variation over earnings ranges would doubtless increase labor provide and encourage the upward mobility of employees. That is particularly true for average-income employees. Lastly, eliminating regressive manufacturing taxes on companies would enhance their competitiveness and development potential.
By way of fairness, all of those coverage modifications would assist scale back France’s tax burden on labor, which is among the highest within the OECD at 47 p.c.
Relatively than pushing unsound tax coverage options as a result of they’re politically handy, French policymakers ought to undertake structural tax system reform. Specializing in competitiveness, neutrality, and environment friendly insurance policies to boost income would go a great distance in rising financial development and stabilizing public funds over the long run.
Keep knowledgeable on the tax insurance policies impacting you.
Subscribe to get insights from our trusted specialists delivered straight to your inbox.
Share