In recent times, many corporations have rushed to develop AI options or merchandise, but most initiatives fail to progress past the proof-of-concept stage.
The primary cause behind the failure to productize these functions is usually a scarcity of analysis and correct knowledge science. The so-called “vibe” growth paradigm can solely get you to date earlier than issues begin to collapse and you start to really feel like you’re constructing one thing on prime of a quicksand.
On this article, I describe methods to deal with these issues by discussing the correct analysis of functions that make the most of LLMs and methods to leverage this data to provide dependable options.
Lifecycle Of AI Utility Growth
There’s nothing fallacious with writing customized prompts with none analysis when beginning a brand new product or function. Quite the opposite, I might argue that it’s a most well-liked strategy when that you must create a proof-of-concept as rapidly as doable. Nonetheless, after some time, you will see that that it’s inadequate, particularly while you start to transition to the manufacturing section. With out correct analysis, you’ll find yourself entering into circles from one regression to a different.
Furthermore, you do not need any knowledge to assist the reliability of your resolution.Due to this fact, after the preliminary section of prototyping your thought, it’s best to transfer to implementing the analysis of your AI utility. With the analysis in place, you will get confidence in how your resolution performs and enhance it iteratively with out reintroducing bugs or undesired conduct.
Moreover, you’ll be able to transfer on to a different step in AI app growth and use immediate optimizers comparable to DSPy and discard guide immediate tuning utterly. You’ll be able to see this lifecycle visualized under:

Analysis of AI Purposes
Evaluating AI functions differs considerably from conventional software program testing or knowledge science validation. These methods, sometimes called Software program 3.0, mix conventional software program engineering with knowledge science. Because of this, the analysis doesn’t concentrate on the underlying LLM, nor does it resemble normal unit testing. As an alternative, it assesses the conduct of an utility constructed on prime of assorted AI fashions, comparable to LLMs, embedding fashions, and rerankers.
The first goal is to judge the configuration of the entire AI system. This would possibly embrace RAG pipelines (retrieval and reranking phases), immediate templates (e.g., structured directions, few-shot examples, prompting methods), and any surrounding pre-/post-processing logic. This text focuses particularly on the analysis of the LLM elements (i.e., immediate templates) of such functions. The analysis of RAG pipelines falls beneath the area of knowledge retrieval and deserves a separate article.
To conduct a significant analysis, three core parts are wanted:
-
A
dataset
with floor fact outputs, if accessible,
-
Acceptable
analysis metrics
that mirror desired conduct
An analysis infrastructure to run and monitor the analysis course of.
Datasets
To judge an AI utility, you want a dataset with anticipated outputs, additionally known as floor fact. The toughest half is usually getting the preliminary dataset. Happily, even a tiny dataset will help you meaningfully tune your utility and test if it behaves as anticipated.
There are three essential methods to acquire a dataset. First, you’ll be able to manually write just a few input-output pairs. This helps make clear precisely what you count on from the applying, moderately than counting on obscure specs. Second, if your organization coverage permits and the applying is already operating, you need to use consumer interactions with optimistic suggestions to increase the dataset. Lastly, you need to use an LLM to generate artificial examples from crafted prompts or present dataset gadgets, however at all times evaluate these rigorously earlier than utilizing them.
Analysis Metrics
Selecting the best metrics is essential when performing an analysis to find out whether or not your AI utility behaves as you count on. Metrics can assess the output on their very own (e.g., politeness, toxicity, contextual relevance) or measure how intently it aligns with the anticipated end result. Broadly, these analysis metrics fall into three classes: analytical metrics (generally utilized in conventional ML), deterministic assertions (akin to unit assessments), and LLM-as-a-judge (a more recent strategy utilizing LLM for analysis).
A typical mistake is to begin with LLM-as-a-Decide and use it for each side of the analysis. Whereas the LLM-as-a-judge is chosen for its ease of use, this strategy comes with important drawbacks. These embrace the price and latency of calling the choose itself, in addition to the uncertainty it introduces into the analysis.
Due to this fact, it is suggested to make use of LLM-as-a-Decide at all times as a final resort when conventional approaches comparable to analytical metrics or deterministic assertions aren’t sufficient. It’s helpful to contemplate these metrics in an analogous method to unit, integration, and E2E assessments, the place E2E assessments are akin to LLM-as-a-judge since they’ve the best price. Right here is the view of those metric varieties visualized :
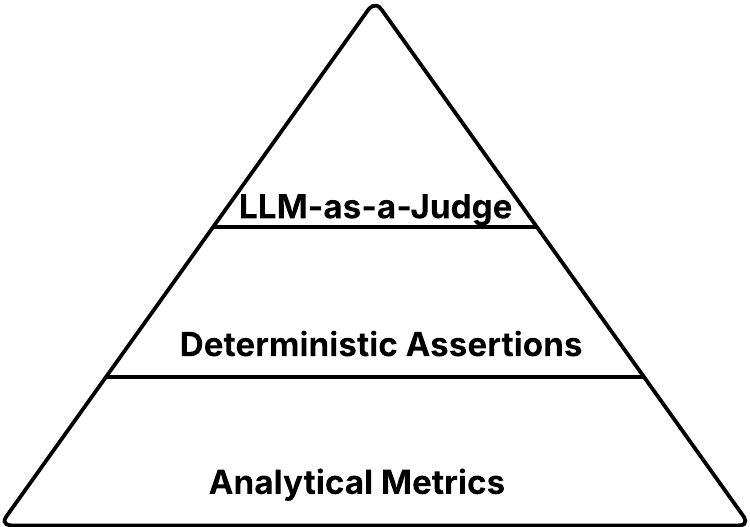
Analytical Metrics
Analytical metrics are quantitative capabilities that assign a numerical rating to the output of the AI utility. These metrics are current on the backside of our pyramid since they’re broadly relevant to all check instances with minimal implementation or actual price. Let’s describe these metrics, clarify methods to use them, and talk about their interpretation. Be aware that the choice of a metric at all times is dependent upon the particular use case you’re evaluating.
Let’s checklist generally used analytical metrics:
Perplexity
-
Clarification:
Perplexity measures how properly the mannequin predicts the sequence of tokens. It’s outlined because the exponentiated common detrimental log-likelihood of a token sequence.
-
Interpretation:
The decrease the perplexity, the extra assured the LLM is in its prediction.
-
Use Case
: It’s a good follow to trace Perplexity each time you could have entry to the token output possibilities.
Cosine Similarity
-
Clarification:
Cosine similarity measures how comparable two embedding vectors are. These vectors are produced by encoder fashions (e.g., BERT) educated to seize the semantic which means of sentences. The similarity corresponds to the cosine of the angle between the vectors.
-
Interpretation:
The cosine similarity rating will be difficult to interpret as a result of it relies upon considerably on the underlying embedding fashions and the distribution of scores they produce.
-
Use Case:
Because of the issue of interpretation, I might not suggest counting on this measure when doing iterative growth, however it may be leveraged in computerized immediate optimization frameworks.
NLP Metrics (BLUE, ROUGE, METEOR)
-
Clarification:
Conventional NLP metrics that examine variations between two texts use token-level overlaps, n-grams, or the variety of edits to get the identical textual content.
-
Interpretation:
The results of these metrics is often normalized between zero and one, the place one is the absolute best rating.
-
Use Case:
A lot of these metrics are perfect for comparatively quick texts with decrease variability.
Different
- Aside from the aforementioned metrics, you’ll be able to observe a number of different elements of the technology, such because the variety of tokens, the variety of reasoning tokens, latency, price, and many others.
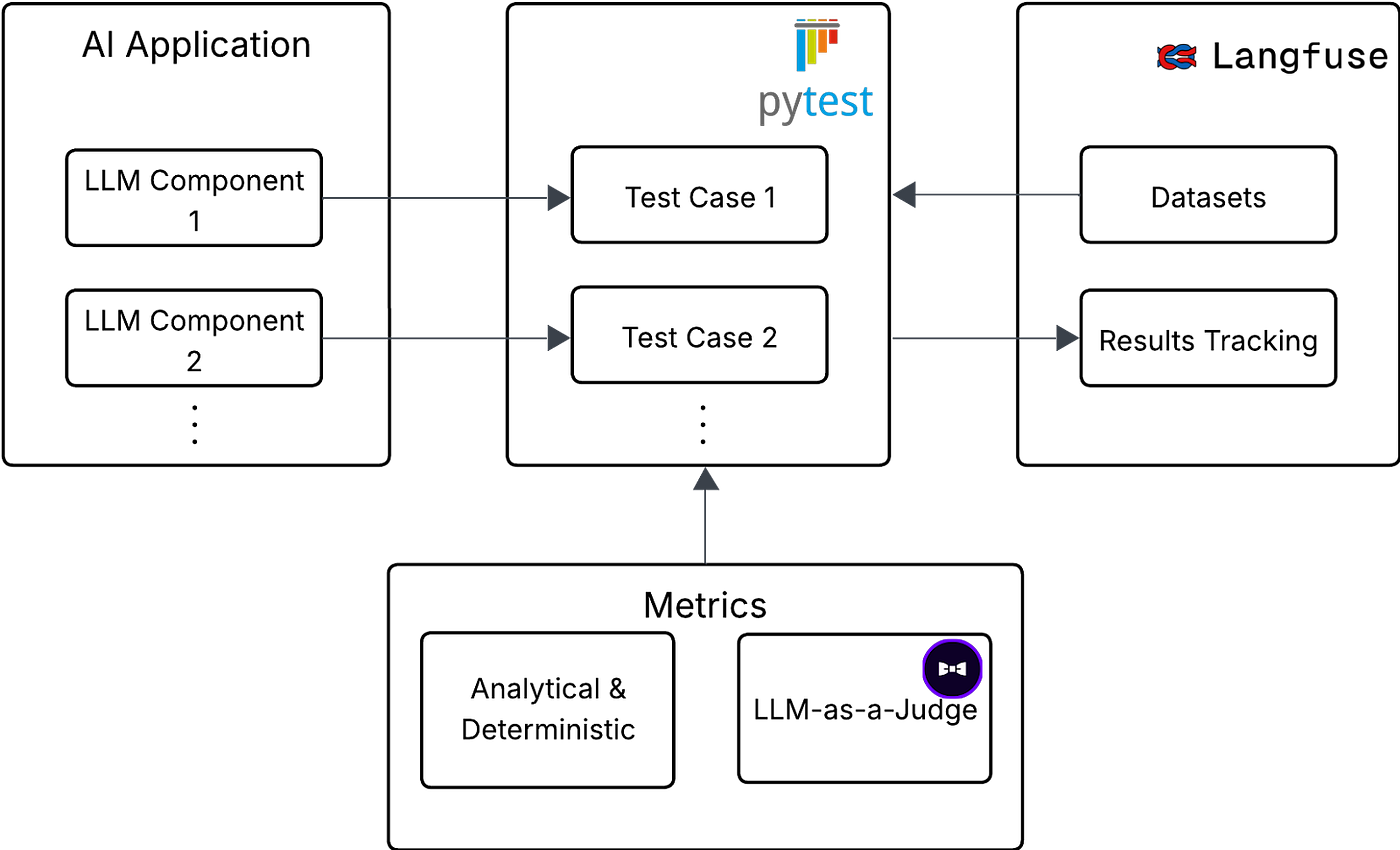
Our Analysis Infrastructure
To attain correct analysis within the compound AI system with a number of elements that depend upon one another and reap the benefits of LLM, it’s important to have these LLM elements encapsulated to allow them to be simply examined and evaluated.
This strategy was impressed by the chapter “Design Your Analysis Pipeline” from the e book AI Engineering by Chip Huyen.
In our analysis infrastructure, every LLM element has its personal dataset and analysis pipeline. You’ll be able to consider the LLM element as an arbitrary machine studying mannequin that’s being evaluated. This separation of elements is critical in a posh utility like ours, which focuses on an AI-assisted analytics use case, as a result of evaluating such a system end-to-end will be extraordinarily difficult.
To judge every of those elements, we use the next instruments:
Langfuse
- An LLM observability framework that’s used primarily to trace and log consumer interplay with an AI utility
- Moreover, it helps dataset and experiment monitoring, which we make use of in our infrastructure.
Pytest
- It’s a minimalistic framework for operating unit assessments
- We use it as our script runner when evaluating totally different LLM elements
DeepEval
For every element, we’ve exactly one check. Every check is parametrized utilizing the pytest_generate_tests operate, so it runs for every merchandise of the dataset for every component. The entire infrastructure setup with using these instruments visualized:
The outcomes of the analysis of the particular LLM element are logged to the Langfuse, proven within the subsequent picture. As you’ll be able to see, we’re utilizing G-Eval LLM-as-a-Decide. We’re thresholding scores from the G-Eval to find out if the output is appropriate. On prime of that, we’re monitoring the perplexity of the mannequin. If perplexity values begin to spike, it may be a sign that one thing is likely to be fallacious within the configuration of the LLM element.
Conclusion
Analysis is crucial for constructing dependable and production-ready AI functions. In comparison with conventional unit testing or mannequin analysis, evaluating AI methods presents its distinctive challenges. Step one is at all times creating or gathering a dataset that matches your corporation objectives and helps information enhancements. Then, deciding on the correct metrics is essential to understanding how successfully your system performs. With these foundations in place, you’ll be able to apply the concepts by a sensible analysis setup, as described on this article. I hope it helps you’re taking the subsequent step in evaluating your AI utility.
