On 14 December, the European Council agreed to open accession negotiations with Ukraine. Negotiators from the European Union and Ukraine will now resolve what reforms should conditionally happen beneath the chapters of acquis earlier than the nation turns into an EU Member State. TaxA tax is a compulsory cost or cost collected by native, state, and nationwide governments from people or companies to cowl the prices of common authorities providers, items, and actions.
coverage reforms and insurance policies that have an effect on Ukraine’s influence on the EU funds can be basic to the result of the negotiations.
Regardless of current EU enlargement concepts in Brussels, the chapters are targeted on what reforms Ukraine should implement earlier than accession, not what reforms the EU must implement earlier than accepting a brand new Member State.
There are additionally many inside components driving tax and funds coverage reforms, along with making ready for membership, comparable to a historical past of corruption, the necessity for presidency income, and the promotion of innovation and funding. Ukraine should finance the continuing warfare effort and wishes roughly €45.8 billion per yr ($50 billion) in support to shut its present funds hole. Absolutely, this quantity will improve for reconstruction after the warfare, so Ukraine should take steps to create a secure, wholesome financial system that wants as few EU transfers as potential.
On the opposite facet of the negotiation, the EU should resolve how finest to financially assist Ukraine with out burdening it with debt or permitting it to develop into a everlasting drain on EU coffers. Some Member States fear in regards to the home political fallout of Ukraine’s membership on their very own distribution of EU funds. Sarcastically, different Member States may worry that Ukraine’s tax system is just too aggressive and will tempt firms to shift funding additional east.
So, how aggressive is Ukraine’s tax system relative to present EU Member States, and what tax reforms ought to the EU mandate to ease Member States’ fears?
And not using a widespread understanding, Ukraine’s membership bid might face pushback throughout the continent.
Ukraine’s Tax Code Is Aggressive, however the Tax BaseThe tax base is the whole quantity of revenue, property, property, consumption, transactions, or different financial exercise topic to taxation by a tax authority. A slim tax base is non-neutral and inefficient. A broad tax base reduces tax administration prices and permits extra income to be raised at decrease charges.
Is Shrinking
Other than wartime tax coverage measures, Ukraine’s present tax code is pretty typical by EU requirements and its charges are in step with different EU nations. The non-public revenue tax charge is eighteen %, the company charge is eighteen %, and the value-added tax (VAT) charge is 20 %. The social contribution charge is 22 % with an extra 1.5 % army surcharge.
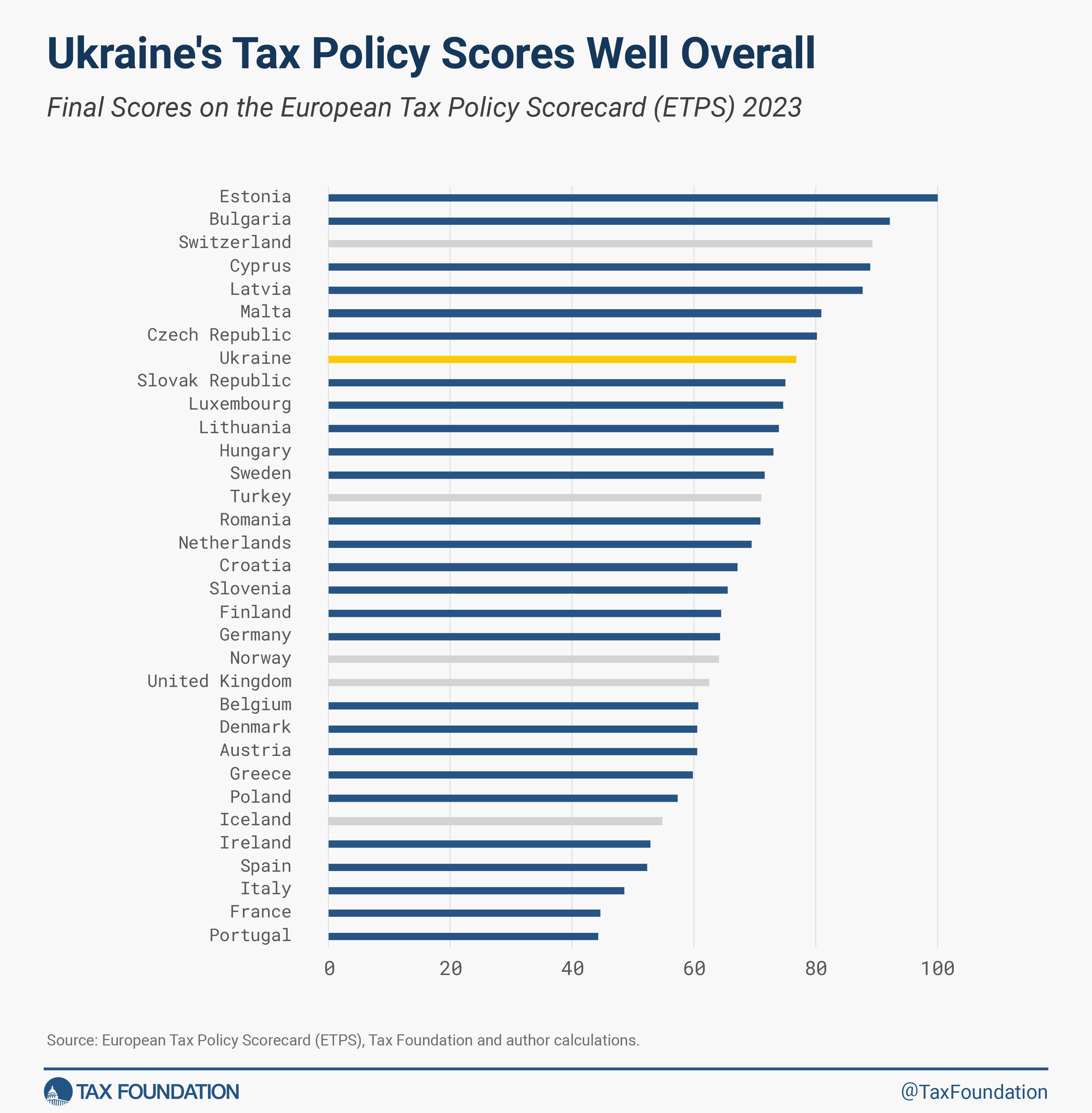
Utilizing Tax Basis’s European Tax Coverage Scorecard, Ukraine would rank because the 7th-most aggressive tax system within the EU (and the 8th amongst ETPS nations) if it joined right this moment.
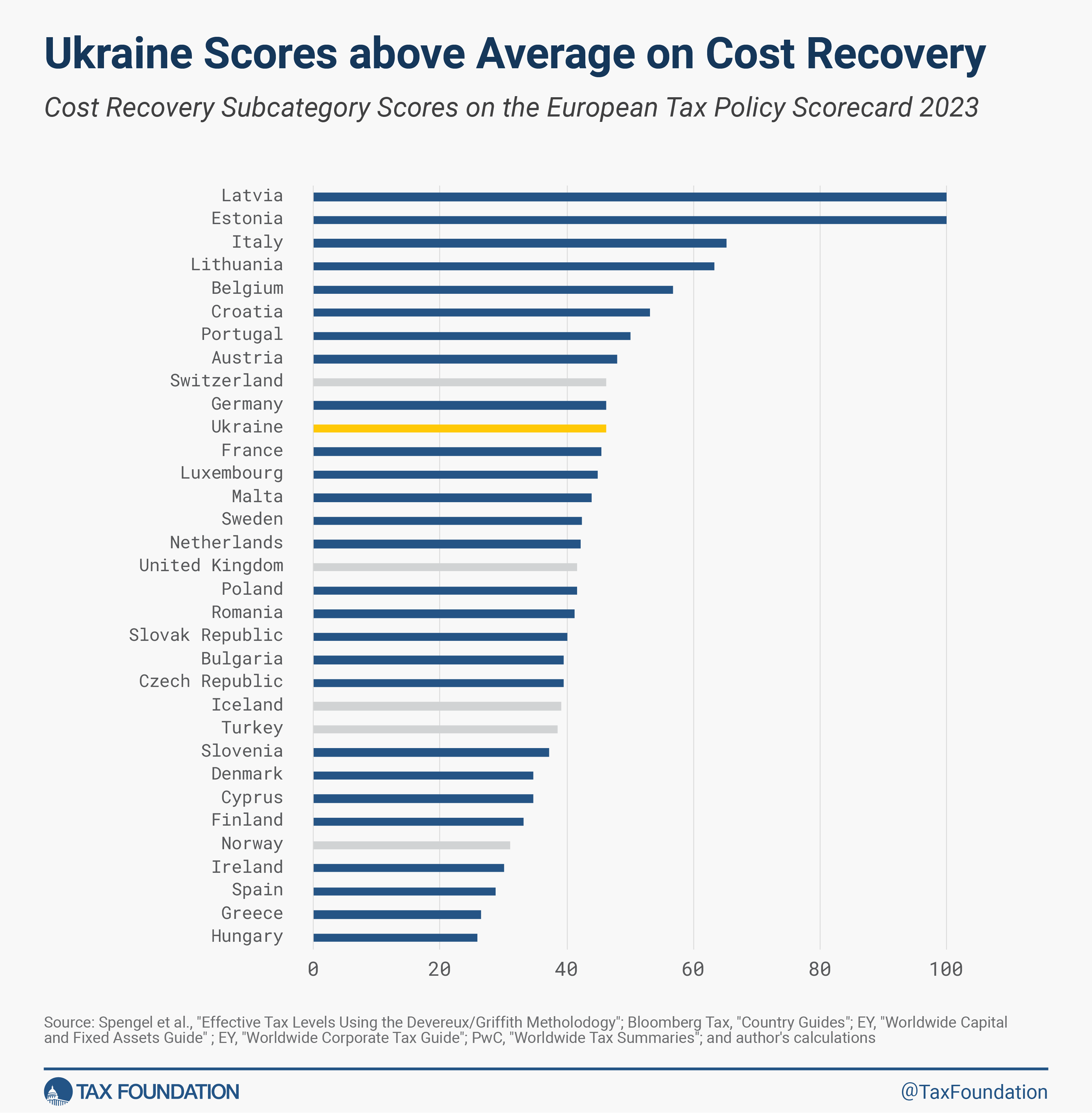
Moreover, Ukraine would rank 10th within the EU (11th amongst ETPS nations) on capital value restorationPrice restoration is the power of companies to get better (deduct) the prices of their investments. It performs an vital function in defining a enterprise’ tax base and may influence funding selections. When companies can’t absolutely deduct capital expenditures, they spend much less on capital, which reduces employee’s productiveness and wages.
. That is notably vital for reconstruction funding and financial progress after the warfare.
Ukraine’s financial system, nevertheless, isn’t typical. In 2022, each the financial system and the tax base contracted by about one-third. As many as 5 million residents fled to different nations to flee the warfare, additional shrinking the tax base.
The World Financial institution has estimated that as a lot as 46 % of the Ukrainian financial system is taken into account “casual,” which suggests practically half of the financial system is successfully untaxed.
Weak Enforcement and Corruption Plague Ukraine’s Tax System
The Centre for Financial Coverage Analysis (CEPR) reviews, “The federal government has had weak institutional capability to implement tax assortment.” Corruption amongst tax collectors is a complicating issue and it’s well-known that better-connected corporations pay much less.
The grievance from small and medium-sized companies (SMEs) is that the tax system is unpredictable, unfair, and burdensome to adjust to.
The federal government’s effort to simplify the tax code in the course of the warfare by making a “small entrepreneurs cost” has created alternatives for evasion. Entrepreneurs and the self-employed pays a 2 % flat charge on turnover as an alternative of an revenue tax and social contribution tax. In response to CEPR, roughly 2 million employees are working as “personal entrepreneurs,” which permits them to attenuate their tax legal responsibility and the tax legal responsibility of their employers. A everlasting turnover tax could be notably dangerous to enterprise funding and restoration efforts if the tax is to proceed after the warfare.
Regardless of Every part, the World Financial institution Says that Ukraine Stays Resilient
Companies are working beneath capability however are adapting their product combine, innovating, and growing their use of knowledge know-how. Multinational corporations haven’t pulled again their investments and operations in Ukraine, though Ukraine has one of many lowest ranges of international direct funding per capita of any European nation.
What Ought to the EU Do?
EU negotiators ought to contemplate historic classes on wartime financing (specified by a earlier weblog) instructive for his or her mission and never pressure Ukraine to implement reforms that can harm progress sooner or later. Specifically, quite a few chapters of the acquis might have important tax coverage and funds ramifications, particularly Chapters 15-17 (Vitality, Taxation, and Financial and Financial Coverage), Chapter 20 (Enterprise and Industrial Coverage), Chapter 27 (Setting), and Chapter 33 (Monetary and Budgetary Provisions).
It’s financial liberalization, not burdensome laws, or conditional loans, that can flip Ukraine right into a contributing Member State in the long term. The EU ought to encourage Ukraine to enhance upon its personal model of the varied flat taxAn revenue tax is known as a “flat tax” when all taxable revenue is topic to the identical tax charge, no matter revenue stage or property.
reforms championed by fellow former communist nations comparable to Bulgaria, Estonia, Latvia, and Slovakia. A flat tax, or money circulation tax, higher fits Ukraine’s financial and governance wants than a Western-style tax system.
Some within the EU might fear {that a} low-rate flat tax or money circulation system might make Ukraine extra aggressive than many EU nations, however that ought to be seen as a welcome trade-off in comparison with years of economic assist.
Ultimately, one of the best ways for the EU to assist Ukraine’s post-war restoration is to ensure its tax sovereignty, not simply its territorial sovereignty.
Keep knowledgeable on the tax insurance policies impacting you.
Subscribe to get insights from our trusted consultants delivered straight to your inbox.
Share