Key Findings
- On common, within the Organisation for Co-operation and Improvement (OECD) and choose European Union nations, long-term capital beneficial properties from the sale of shares are taxed at a high price of 18.78 p.c, and dividends are taxed at a high price of 23.85 p.c.
- There are two layers of taxA tax is a compulsory cost or cost collected by native, state, and nationwide governments from people or companies to cowl the prices of common authorities companies, items, and actions.
on funding earnings. First, companies pay the company earnings taxA company earnings tax (CIT) is levied by federal and state governments on enterprise income. Many firms usually are not topic to the CIT as a result of they’re taxed as pass-through companies, with earnings reportable beneath the particular person earnings tax.
on their income. Second, shareholders pay an earnings tax on each the dividends and capital beneficial properties they obtain. - Since company earnings is taxed twice, on common, the OECD and choose EU nations tax company earnings distributed as dividends at 41.16 p.c and capital beneficial properties derived from company earnings at 37.38 p.c.
- To encourage long-term retirement financial savings, nations generally present tax preferences for personal retirement accounts. These normally present a tax exemptionA tax exemption excludes sure earnings, income, and even taxpayers from tax altogether. For instance, nonprofits that fulfill sure necessities are granted tax-exempt standing by the Inner Income Service (IRS), stopping them from having to pay earnings tax.
for the preliminary principal funding quantity and/or for the funding returns. - Tax-preferred non-public retirement accounts typically have complicated guidelines and limitations. Common financial savings accounts could possibly be a less complicated different—or addition—to many nations’ present system of personal retirement financial savings accounts.
Introduction
Lengthy-term financial savings and funding play an vital function in people’ monetary stability and the economic system general. Taxes typically influence whether or not, and the way a lot, people set earnings apart for financial savings and investments. Varied elements decide the quantity of taxes one is required to pay on these financial savings and investments, akin to the kind of asset, the person’s earnings stage, the interval over which the asset has been held, and the financial savings function.
Whereas long-term financial savings and funding can are available many types, this paper usually focuses on the tax remedy of shares in publicly traded firms.[1] Every nation approaches the taxation of shares in another way, however most nations levy some type of capital beneficial properties and dividend taxes on people’ earnings from proudly owning shares. Capital beneficial properties and dividend taxes are levied after company earnings taxes are paid on income on the entity stage, and thus represent a second layer of taxation.
Nevertheless, lawmakers have acknowledged the necessity to incentivize long-term financial savings—significantly relating to non-public retirement financial savings. Thus, nations generally present tax preferences for people who save and make investments inside devoted non-public retirement accounts—normally by exempting the preliminary principal funding quantity or the funding returns from tax. These tax-preferred non-public retirement accounts play a major function when taking a look at an economic system’s whole financial savings and investments. For instance, within the United States, about 30 p.c of whole U.S. fairness is held in tax-preferred retirement accounts. Foreigners maintain 40 p.c of U.S. fairness, and solely about 25 p.c is estimated to be in taxable accounts.[2]
This paper will first clarify how dividends and capital beneficial properties taxes influence one’s funding earnings, and the way tax-preferred non-public retirement accounts decrease the tax burden on such investments. Second, a survey of capital beneficial properties taxes, dividends taxes, and the tax remedy of personal retirement accounts exhibits how the taxation of financial savings and investments differs throughout nations. Lastly, we briefly spotlight the significance of simplicity relating to retirement financial savings and clarify how common financial savings accounts could possibly be a step in that route.
Understanding the Tax Remedy of Financial savings and Funding
Financial savings and funding can are available many types. This paper focuses on saving within the type of proudly owning shares in publicly traded firms. Shares present two methods for buyers to get earnings.
The primary is by shopping for a inventory and promoting it later at the next worth. This ends in a capital achieve. An investor who buys a inventory for €100 and later sells it for €110 has earned a €10 capital achieve.
The second option to get earnings from shares is to buy shares in firms that often pay out dividends to shareholders. An organization that pays out annual dividends at €1 per share would offer a person that owned 10 shares of that firm €10 annually.
Two kinds of taxes apply to these totally different earnings: capital beneficial properties taxes and dividends taxes, respectively. A capital beneficial properties taxA capital beneficial properties tax is levied on the revenue created from promoting an asset and is commonly along with company earnings taxes, often leading to double taxation. These taxes create a bias in opposition to saving, resulting in a decrease stage of nationwide earnings by encouraging current consumption over funding.
applies to the €10 in beneficial properties the investor made, and a dividends tax applies to the €10 in dividends that have been paid out.
Each taxes create a burden on financial savings. If a person has a financial savings purpose and wishes a 5 p.c whole return on funding to achieve that purpose, a capital beneficial properties tax would require that particular person’s precise return on funding to be greater than 5 p.c to fulfill the purpose. If the capital beneficial properties tax is 20 p.c, then the person’s before-tax return on funding would have to be 6.25 p.c.
Equally, taxes on dividends scale back earnings for buyers.
For employees who’re investing their cash after paying particular person earnings taxes, taxes on capital beneficial properties and dividends characterize an extra layer of tax on their earnings.
Nevertheless, relating to retirement financial savings, governments often present tax exemptions for both the wages used to contribute to a financial savings account or an exemption on the beneficial properties.
Desk 1 exhibits there are 4 fundamental tax regimes for buyers. The 2 dimensions of taxation concern the principal, or the preliminary deposit, and the returns to funding. Techniques usually fall into one of many 4 classes within the desk.
Some investments are taxed each on the preliminary principal and on the return. These embrace investments in brokerage accounts. For the sort of funding, there may be normally no exemption or deduction for the preliminary value of buying shares, and the earnings from the funding (whether or not a capital achieve or a dividend) is taxable.
Personal retirement financial savings, however, normally face an exemption from tax on the preliminary principal funding quantity or on the returns to that funding. Within the U.S., that is referred to both as “conventional” or “Roth” remedy for particular person retirement preparations (IRAs). With conventional remedy, there isn’t any tax on the preliminary funding principal, however there’s a tax on the overall quantity (principal plus beneficial properties) upon withdrawal. Roth remedy contains taxable principal investments and no tax upon withdrawal.
Within the U.S., well being financial savings accounts present an exemption from tax each on the principal and the returns upon contribution in addition to withdrawal, representing the fourth sort of tax remedy on funding the place neither the principal nor the returns are taxed at any level.
The A number of Layers of Taxes on Funding
Particular person buyers who save exterior of a retirement account will face a number of layers of taxation. If an investor buys inventory in a company, that firm will owe the company earnings tax, and the investor will owe dividends tax on any dividend earnings or capital beneficial properties tax if the investor sells the inventory at the next worth.
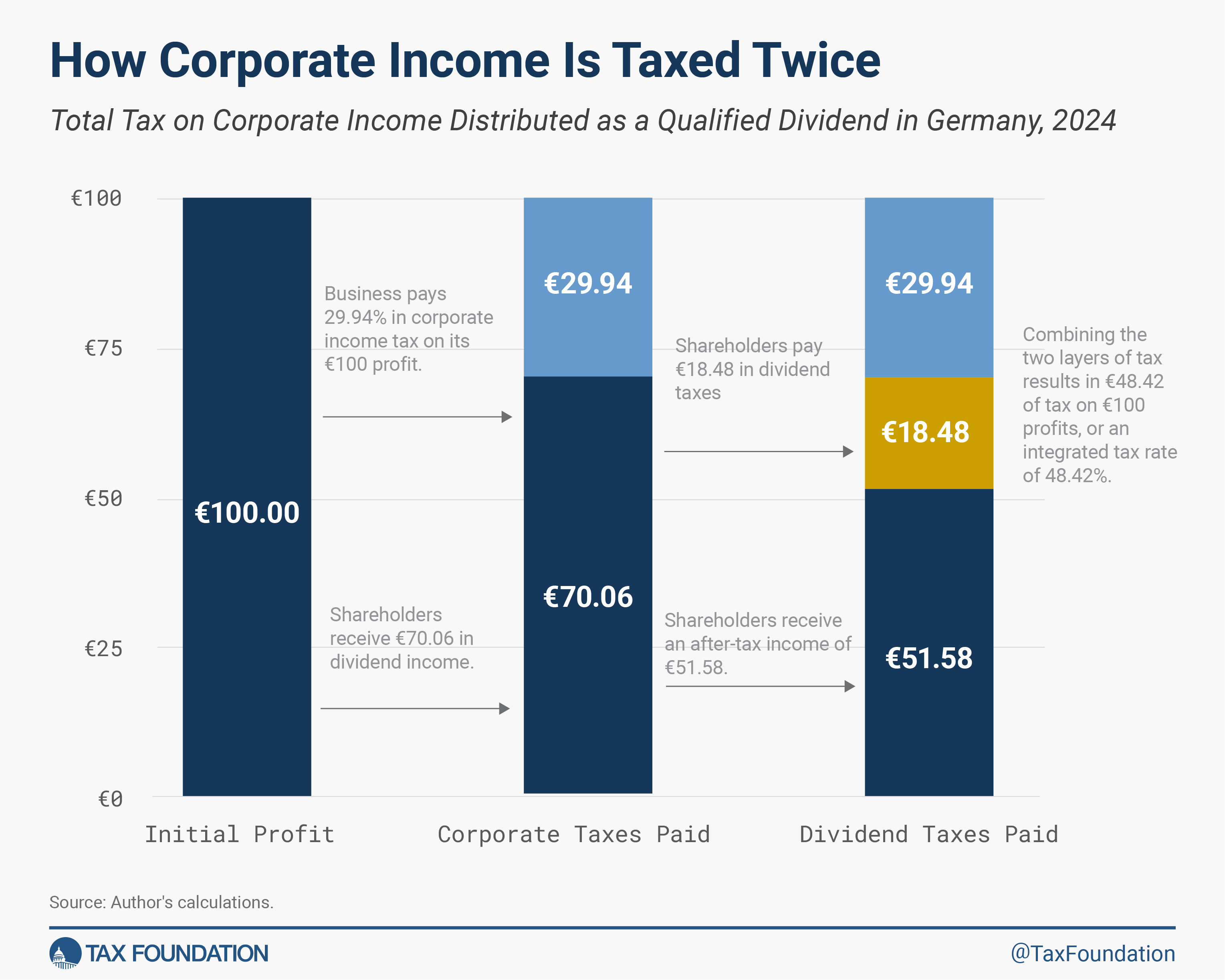
The next instance exhibits how €48.42 in tax would apply to €100 in company income when accounting for each company taxes and taxes on dividends. First, the company earns €100 in income. If it’s a German firm and faces the company earnings tax price, it might pay €29.94 in company taxes on that earnings.
This leaves €70.06 out there for a dividend. The shareholder would owe an extra €18.48 in dividend taxes.
From the €100 in income, simply €51.58 in after-tax income stay for the shareholder within the type of a dividend.
Nevertheless, some nations have built-in tax programs. Which means that if an organization pays company taxes on its income, an investor can declare a (partial or full) credit score in opposition to taxes on capital beneficial properties and dividends. This ends in buyers solely paying taxes to the extent that capital beneficial properties or dividends tax liabilities are greater than the (partial or full) credit score for company taxes paid.
Tax Remedy of Personal Retirement Accounts
Most people in OECD nations can make the most of a tax-preferred financial savings account to construct up particular person retirement financial savings—typically along with public pensions. Two common types of tax remedy are the commonest and fall into the classes mentioned earlier.
One method permits people to contribute to retirement accounts utilizing cash that has already been taxed as wages. Nevertheless, returns on the funding and withdrawals from the account are tax-exempt. That is what is named a taxed, exempt, exempt (or TEE) method, referring to the coverage’s remedy of contributions, returns on funding, and withdrawals from a retirement account. Within the U.S., that is known as the “Roth” remedy for retirement financial savings.[3]
The opposite method permits people to contribute to accounts with both pre-tax earnings or present a tax deductionA tax deduction is a provision that reduces taxable earnings. An ordinary deduction is a single deduction at a set quantity. Itemized deductions are in style amongst higher-income taxpayers who typically have important deductible bills, akin to state/native taxes paid, mortgage curiosity, and charitable contributions.
for contributions. Returns on the funding don’t face tax, however withdrawals from the account (principal plus earnings) are taxed. That is known as an exempt, exempt, taxed (EET) method. Within the U.S., “conventional” retirement autos observe this method.
Determine 2 compares how these two preferences for retirement financial savings influence an investor and compares them to an investor who’s saving exterior a retirement account.
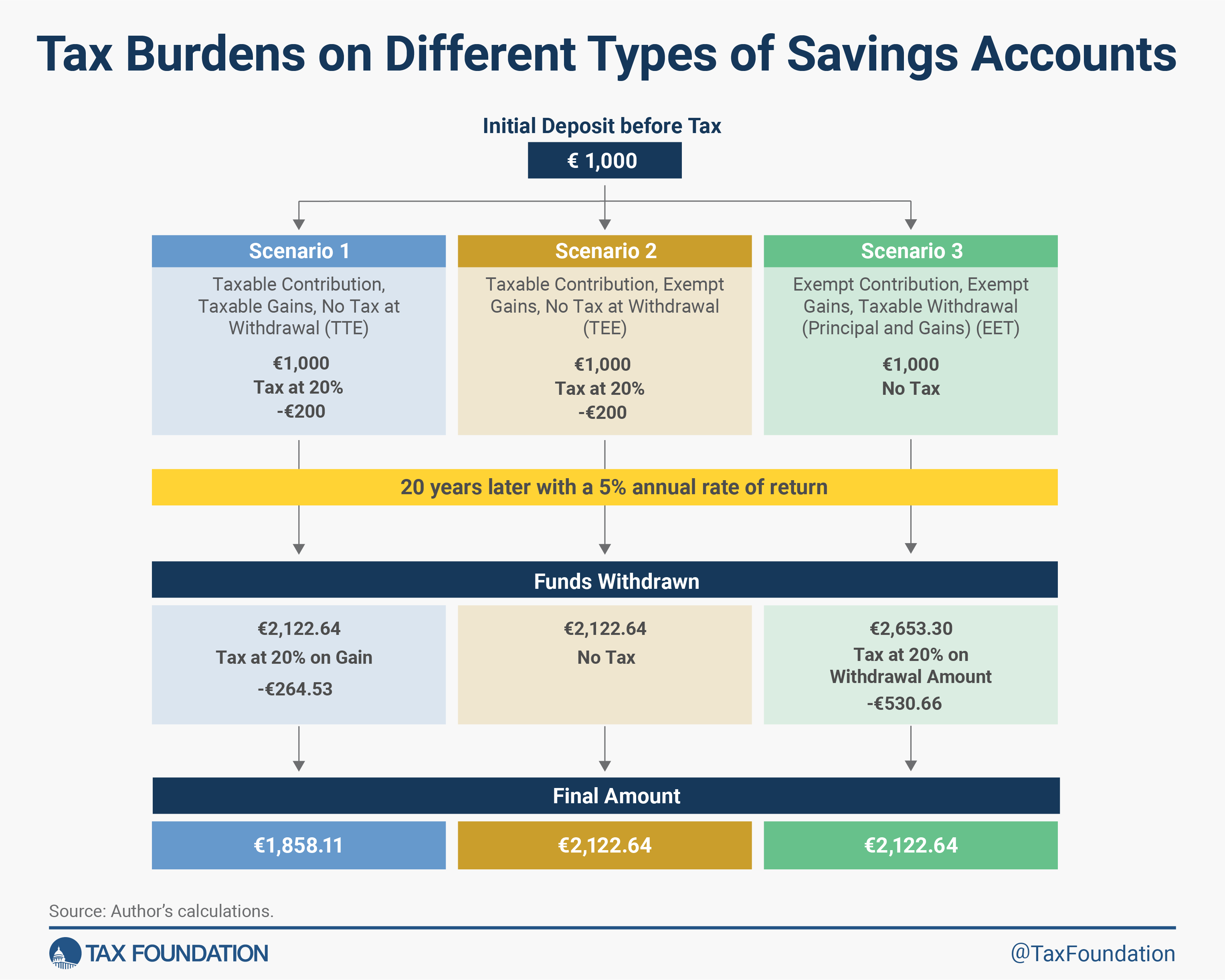
In every state of affairs, €1,000 is the preliminary deposit. Within the first and second eventualities, a 20 p.c tax applies to that preliminary deposit. Consider this as a tax on the wages which might be getting used to fund the funding.
So, proper off the bat, Eventualities 1 and a pair of have €800 for investing. State of affairs 3 doesn’t embrace a tax on wages used for contributing to a retirement account and permits the total €1,000 to be invested as a result of it’s an EET method (that means that contributions are tax-exempt).
In every state of affairs, the investor leaves the funds of their funding account for 20 years and earns a 5 p.c annual return. On the finish of this era, each Eventualities 1 and a pair of have the identical sum of money of their funding account, €2,122.64. As a result of State of affairs 3 began off with a bigger preliminary deposit, that state of affairs has €2,653.30 of their funding account.
Now, when funds are withdrawn, taxes apply each to quantities withdrawn in State of affairs 1 and State of affairs 3, however not State of affairs 2. State of affairs 2 operates as a TEE account, so withdrawals are exempt from tax.
Upon withdrawal, State of affairs 1 pays a 20 p.c tax on the beneficial properties (ultimate quantity minus the €800 preliminary funding). This ends in ultimate, after-tax earnings of €1,858.11. State of affairs 2 doesn’t owe taxes on beneficial properties or principal upon withdrawal; the ultimate earnings are €2,122.64. State of affairs 3 owes a 20 p.c tax on the withdrawn quantity which incorporates each the principal and beneficial properties—so the overall withdrawal quantity—and has ultimate earnings of €2,122.64, the identical as in State of affairs 2.
This instance exhibits two issues. First, as a result of absolutely taxable accounts have multiple layer of taxes, they lead to decrease after-tax funding earnings. Second, if the tax price on the principal in State of affairs 2 and the tax price on principal and achieve upon withdrawal in State of affairs 3 is identical, then the earnings from each will likely be equal.
The tax charges on deposit and withdrawal could not at all times be the identical, nevertheless. Many tax programs have a progressive price construction for wages which can imply a person will likely be in a special tax bracketA tax bracket is the vary of incomes taxed at given charges, which generally differ relying on submitting standing. In a progressive particular person or company earnings tax system, charges rise as earnings will increase. There are seven federal particular person earnings tax brackets; the federal company earnings tax system is flat.
when the funding is made than after they have retired and start making withdrawals.
If a person faces a 30 p.c tax price after they make investments, however a 15 p.c tax price after they withdraw their earnings, it might be advantageous to make use of an funding account as in State of affairs 3.
Different Sorts of Tax-Most popular Financial savings Accounts
Along with retirement accounts, some nations provide tax preferences for different financial savings functions. Examples embrace financial savings for future training and health-related prices.
For instance, america affords so-called “certified tuition plans” for future training prices, often known as “529 plans.”[4] Relying on the U.S. state and kind of 529 plan, savers might be able to deduct contributions from state earnings taxes or obtain matching grants; beneficial properties usually are not topic to tax; and withdrawals are exempt from state and federal earnings taxes.
Equally, Canada affords a registered training financial savings plan (RESP), which exempts earnings as they accrue, and a authorities financial savings bonus (earnings and bonus are taxed on the pupil’s tax price upon withdrawal).
In america, there may be additionally a well being financial savings account (HSA), which can be utilized to pay for certified medical bills. As proven in Desk 1, contributions are created from pre-tax earnings, beneficial properties are tax-exempt, and withdrawals usually are not taxed both.
Survey of Capital Good points Taxes, Dividend Taxes, and Retirement Financial savings in OECD International locations
Whereas most nations levy some type of tax on financial savings and funding, the tax remedy differs not solely between nations but in addition between kinds of funding earnings and financial savings functions.
For instance, the typical high long-term capital beneficial properties tax price within the OECD and choose EU nations is eighteen.78 p.c, whereas dividends face an common tax priceThe typical tax price is the overall tax paid divided by taxable earnings. Whereas marginal tax charges present the quantity of tax paid on the following greenback earned, common tax charges present the general share of earnings paid in taxes.
of 23.85 p.c. In relation to non-public retirement financial savings, the tax remedy in addition to contribution limits additionally range considerably.
Capital Good points Tax Charges
Many nations tax capital beneficial properties at varied charges relying on the holding interval, the person’s earnings stage, and the kind of asset bought.
Recognizing the significance of long-term financial savings, some nations tax the beneficial properties from long-term financial savings at a decrease capital beneficial properties tax price than these from short-term financial savings. For instance, in Slovenia, capital beneficial properties on the disposition of immovable property, shares, or different capital participations are taxed at 25 p.c if held for as much as 5 years, at 20 p.c if held between 5 and 10 years, at 15 p.c if held between 10 and 15 years, and at 0 p.c if held for greater than 15 years.
Whereas some nations levy flat capital beneficial properties tax charges no matter a person’s earnings stage, others embrace capital beneficial properties when calculating private earnings taxes—which in most nations ends in the progressive taxation of capital beneficial properties. Nonetheless, different nations have a separate progressive capital beneficial properties tax construction. Some nations have an annual exempt quantity for capital beneficial properties. For instance, within the United Kingdom, the primary £6,000 ($7,532) of realized capital beneficial properties are tax-free (this exemption will likely be diminished to £3,000 beginning April 6, 2024).
Many nations exempt owner-occupied residential property from capital beneficial properties tax.
Desk 2 exhibits the highest marginal capital beneficial properties tax charges levied on people within the OECD and choose EU nations, bearing in mind exemptions and surtaxes. If a rustic has multiple capital beneficial properties tax price, the desk exhibits the tax price making use of to the sale of listed shares after an prolonged time period.
Denmark levies the best high marginal capital beneficial properties tax on long-held shares within the OECD, at a price of 42 p.c. Chile’s high capital beneficial properties tax price is the second highest, at 40 p.c, adopted by Norway at 37.48 p.c and Finland and France at 34 p.c every.
Roughly one-fourth of all nations analyzed don’t levy capital beneficial properties taxes on the sale of long-held shares. These are Belgium, the Czech Republic, Korea, Luxembourg, New Zealand, Slovakia, Slovenia, Switzerland, and Turkey.
On common, long-term capital beneficial properties from the sale of shares are taxed at a high marginal price of 18.78 p.c within the OECD and choose EU nations.
Dividend Tax Charges
Whereas some nations tax dividends on the identical price as capital beneficial properties, different nations differentiate between the 2 types of earnings. As well as, as beforehand talked about, a number of nations have built-in their taxation of company income and dividends paid. Desk 3 exhibits the highest marginal dividends tax charges levied in every nation, bearing in mind credit and surtaxes.
As with capital beneficial properties taxes, some nations levy private earnings taxes on dividend earnings, whereas others levy a flat, separate dividends tax. Exemption thresholds are additionally comparatively widespread. For instance, the UK gives a £1,000 ($1,255.35) dividend allowance, above which a progressive dividend tax is levied (this dividend allowance will likely be diminished to £500 beginning April 6, 2024).
On common, the OECD and choose EU nations levy a high marginal tax priceThe marginal tax price is the quantity of further tax paid for each further greenback earned as earnings. The typical tax price is the overall tax paid divided by whole earnings earned. A ten p.c marginal tax price signifies that 10 cents of each subsequent greenback earned can be taken as tax.
of 23.85 p.c on dividend earnings. Nevertheless, as with capital beneficial properties, there may be important variation. Eire’s high dividend tax price is the best, at 51 p.c.
Estonia and Latvia are the one OECD nations that don’t levy a tax on dividend earnings. This is because of their cash-flow-based company tax system. As a substitute of levying a dividend tax, Estonia and Latvia impose a company earnings tax of 20 p.c when a enterprise distributes its income to shareholders.
Of the OECD and choose EU nations with a tax on dividend earnings, Greece’s is the bottom, at 5 p.c. Second and third are Slovakia and Croatia, at 7 p.c and 12 p.c, respectively.
Built-in Charges
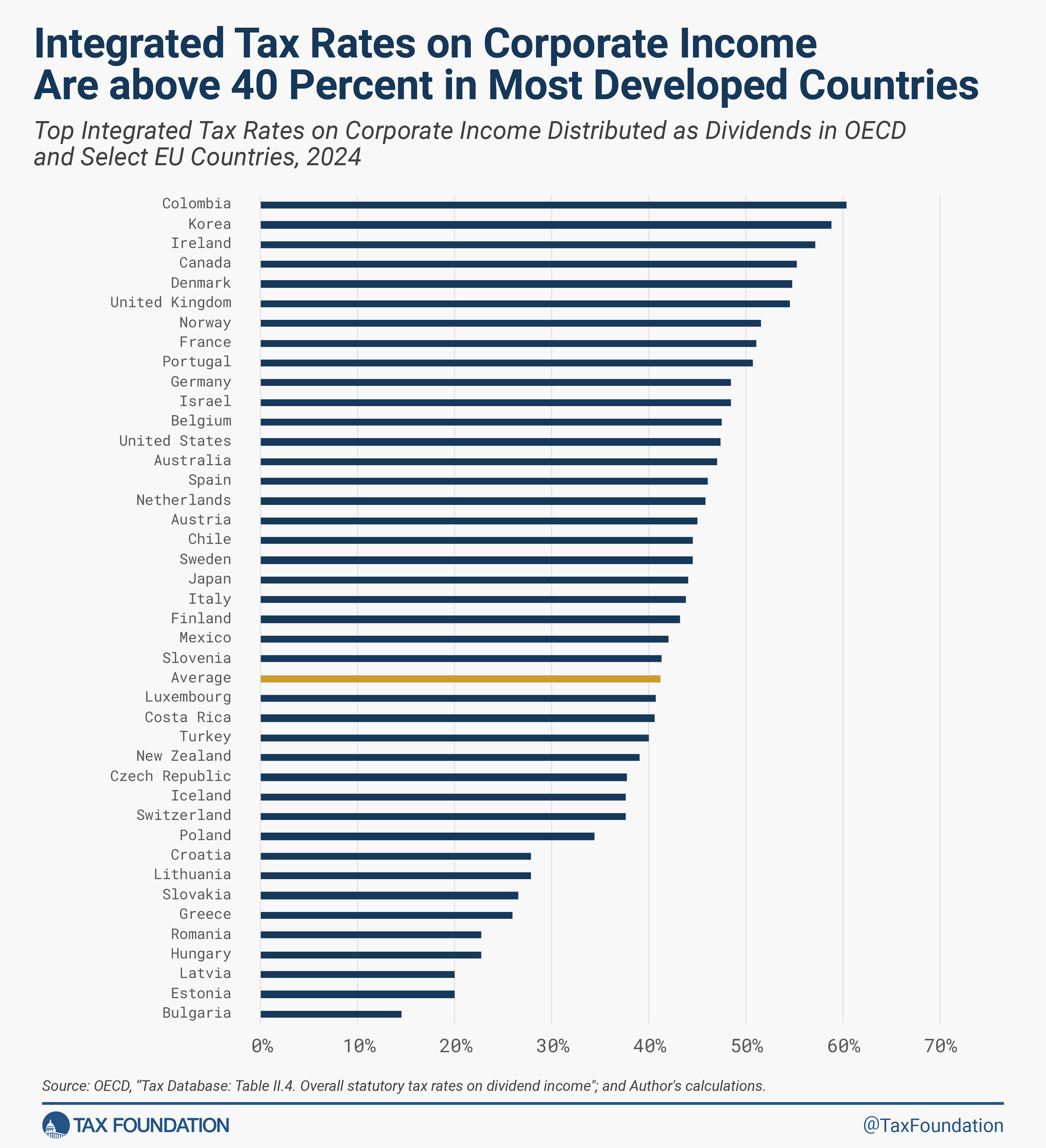
Most nations double tax company earnings by taxing it on the entity and on the shareholder ranges. On common, OECD and choose EU nations tax company earnings distributed as dividends at a price of 41.16 p.c and capital beneficial properties derived from company earnings at 37.38 p.c.
For capital beneficial properties, Chile (56.2 p.c), Denmark (54.76 p.c), Norway (51.52 p.c), and France (51.04 p.c) have the best built-in charges within the OECD, whereas Bulgaria (19 p.c), the Czech Republic (19 p.c), Slovenia (19 p.c), Switzerland (19.65 p.c), and Slovakia (21 p.c) levy the bottom charges. A number of nations—particularly Belgium, the Czech Republic, Luxembourg, New Zealand, Slovakia, Slovenia, South Korea, Switzerland, and Turkey—don’t levy capital beneficial properties taxes on long-term capital beneficial properties, making the company tax the one layer of tax on company earnings realized as long-term capital beneficial properties.
For dividends, Colombia’s high built-in tax price of 60.35 p.c was highest within the OECD and choose EU nations, adopted by South Korea (58.8 p.c), Eire (57.13 p.c), and Canada (55.24 p.c). Bulgaria (14.5 p.c) Estonia (20 p.c), Latvia (20 p.c), Hungary (22.65 p.c), and Romania (22.72 p.c) levy the bottom charges. Estonia and Latvia’s dividend exemption system signifies that the company earnings tax is the one layer of taxation on company earnings distributed as dividends.
Tax Remedy of Retirement Financial savings within the OECD
Along with common pension programs, most OECD nations present tax preferences for personal retirement financial savings. As defined above, the commonest tax remedy of retirement financial savings accounts is TEE (contributions are taxed, however beneficial properties are tax-exempt and there’s no tax upon withdrawal) and EET (contributions and beneficial properties are tax-exempt, however withdrawals—principal plus beneficial properties—are taxed).
OECD and choose EU nations usually restrict the quantity of financial savings one can place in tax-preferred retirement accounts. That is completed by way of annual contribution caps. For instance, in Spain, whole employer and worker contributions made to non-public and occupational pension plans are restricted to €8,500 ($9,121) per yr. Eire and the UK are the one two OECD nations that even have a lifetime contribution restrict for tax-preferred retirement financial savings accounts, at €2 million ($2.15 million) and £1,073,100 ($1.35 million), respectively.
Some nations impose penalty charges on withdrawals made earlier than a sure age is reached. For instance, in america, early withdrawal from an IRA previous to age 59½ is topic to being included in gross earnings plus a ten p.c further tax penalty.
Particulars on the tax remedy of personal retirement financial savings in every OECD nation could be present in Appendix Desk 2.
Simplifying the Tax Remedy for Financial savings and Investments
Lengthy-term financial savings and investments play an vital function in people’ monetary stability and the economic system general. Lawmakers have acknowledged the necessity to incentivize saving by way of tax- and non-tax-related insurance policies. Nevertheless, in lots of circumstances, tax-preferred financial savings accounts include a myriad of complicated guidelines and limitations, which in the end could deter people from opening such tax-preferred financial savings accounts and doubtlessly decrease the quantity of whole financial savings.
Common financial savings accounts can considerably simplify a rustic’s tax-preferred financial savings system. These accounts usually are not restricted to a sure sort of financial savings (e.g., retirement financial savings) and haven’t any earnings limitations or withdrawal penalties. Returns to the account wouldn’t be topic to tax, mirroring the tax remedy of most tax-preferred non-public retirement financial savings accounts within the OECD. Annual contribution limits could possibly be set to make sure that the tax advantages are capped at a sure stage.[5]
Since 2009, Canada has had a sort of common financial savings account—the tax-free financial savings account (TFSA). The annual contribution restrict in 2024 is CAD 7,000 ($5,166). Contributions are made with after-tax {dollars}, earnings develop tax-free, and withdrawals could be made for any cause with out triggering further taxes or penalties. If somebody makes lower than the utmost contribution one yr, the remaining contribution eligibility is added to the following yr’s most contribution.[6]
The UK has had an analogous program of particular person financial savings accounts (ISAs) since 1999. ISAs have an annual contribution restrict of £20,000 ($25,115). As with TFSAs, contributions are made with after-tax {dollars}, and earnings develop tax-free; not like TFSAs, nevertheless, the rollover choice isn’t allowed.[7]
U.S. lawmakers have made a number of proposals to introduce a common financial savings account, although none have been enacted.[8] Establishing a common financial savings account in america that has an annual contribution restrict of $2,500 per yr, makes use of after-tax contributions, and permits earnings to develop tax-free would cut back federal income by about $15.1 billion over the following 10 years. Because of the annual contribution restrict of $2,500, the losses in federal tax income can be comparatively small. Nevertheless, it might barely enhance the after-tax return to saving, resulting in small will increase in output and after-tax incomes.[9]
Conclusion
Because of the significance of long-term financial savings and funding for people and the economic system general, dividend and capital beneficial properties taxes ought to be stored at a comparatively low stage—significantly when bearing in mind the company taxes paid on the entity stage. On common, within the OECD and choose EU nations, long-term capital beneficial properties from the sale of shares are taxed at a high price of 18.78 p.c, and dividends are taxed at a high price of 23.85 p.c. Nevertheless, since company earnings is taxed twice, on common, OECD and choose EU nations tax company earnings distributed as dividends at a price of 41.16 p.c and capital beneficial properties derived from company earnings at 37.38 p.c.
To encourage non-public retirement saving, nations generally present tax-preferred retirement accounts. Nevertheless, in lots of nations, the system of tax-preferred retirement accounts is complicated, which can deter savers from utilizing such accounts—and doubtlessly decrease general financial savings. Canada and the UK have applied common financial savings accounts, and thus present an instance for the way the system of tax-preferred retirement accounts could be simplified whereas offering extra flexibility for what the funds can be utilized for. Policymakers might simplify the tax system and encourage saving with the purpose of constructing monetary safety for low and middle-income households.
Keep knowledgeable on the tax insurance policies impacting you.
Subscribe to get insights from our trusted specialists delivered straight to your inbox.
Appendix
[1] Usually, the tax remedy of shares or possession shares of personal firms or different tradeable properties obtain related tax remedy to that of publicly traded shares.
[2] Steve Rosenthal and Theo Burke, “Who’s Left to Tax? US Taxation of Firms and Their
Shareholders,” New York College College of Regulation, Oct. 27, 2020, https://www.regulation.nyu.edu/websites/default/recordsdata/WhopercentE2percent80percent99spercent20Leftpercent20topercent20Taxpercent3Fpercent20USpercent20Taxationpercent20ofpercent20Corporationspercent20andpercent20Theirpercent20Shareholders-%20Rosenthalpercent20andpercent20Burke.pdf.
[3] Named for the late Senator William Roth (R-DE).
[4] Named for the related part of the U.S. tax code.
[5] For extra particulars on common financial savings accounts, see Robert Bellafiore, “The Case for Common Financial savings Accounts,” Tax Basis, Feb. 26, 2019, https://www.taxfoundation.org/case-for-universal-savings-accounts/.
[6] Authorities of Canada, “The Tax-Free Financial savings Account,” https://www.canada.ca/en/revenue-agency/companies/tax/people/subjects/tax-free-savings-account.html.
[7] Gov.uk, “Particular person Financial savings Accounts (ISAs),” https://www.gov.uk/individual-savings-accounts.
[8] See H.R. 937, H.R. 6757, and S. 232 from the 115th Congress and Alex Durante, William McBride, and Garrett Watson, “Dwindling Financial savings and Rising Monetary Stress Highlights Want for Tax Reforms,” Tax Basis, Nov. 9, 2023, https://taxfoundation.org/weblog/personal-saving-retirement-taxes/.
[9] See Choice 63 in Tax Basis, “Choices for Reforming America’s Tax Code 2.0,” Apr. 19, 2021, https://taxfoundation.org/analysis/federal-tax/tax-reform-options/?choice=63.
Share