In at the moment’s day and age, organizations have monumental quantities of knowledge and they’re keen to put money into analyzing it since it could convey them many advantages. It may possibly enhance decision-making, enhance income, enhance inside processes, diagnose what doesn’t carry out nicely, or just have a complete overview of the entire group. Though organizations need to put money into knowledge evaluation, it often isn’t an easy job.
Varied knowledge sources, knowledge high quality points, and inconsistent terminology result in confusion, redundant efforts, and poor data distribution. Usually, corporations want knowledge engineers and knowledge instruments (for instance dremio, airbyte, dbt, or airflow) to resolve these points, however even then, there’s a lot knowledge the organizations need to cope with. That is the place automation turns into a useful software for analyzing your knowledge. This text particulars why and how you can automate knowledge engineering duties, so-called data-ops.
Why Automate Knowledge Analytics?
Knowledge engineers have already got many duties they need to full, due to this fact any automation of routine duties would assist to ease their workload. We see an analogous development on the earth of infrastructure — infrastructure as code. The high-level thought is to automate routine duties in UI. It means you don’t have to click on a number of buttons to start out a brand new occasion of your utility. The identical logic applies to knowledge analytics; everytime you need to deploy a brand new dashboard or configure an information supply, you often don’t need to click on a number of buttons. Ideally, you wish to do it simply as soon as and combine it together with your atmosphere. We name this course of analytics as a code.
How To Automate Knowledge Analytics?
Let’s have a more in-depth have a look at three instruments that automate knowledge evaluation: Dagger, GitLab, and GoodData. The mix of those instruments permits for complete automated knowledge evaluation, and every of those instruments performs an vital function within the course of.
Dagger
The benefit of this software is that I can check my pipeline regionally after which I can simply push my pipeline to pipeline distributors (for instance to GitLab or GitHub), which suggests Dagger is agnostic to pipeline distributors. Suppose you resolve to maneuver from one vendor to a different as a result of they supply a greater function set. You do not want to rewrite the whole lot, you simply push the pipeline to a unique vendor.
GitLab
GitLab is the first DevOps platform that permits me to run a quick and free pipeline (for demo functions).
GoodData and GoodData Python SDK
GoodData permits me to create constant metrics and dashboards and entry them utilizing GoodData Python SDK. It suits completely with my analytics as code strategy. Additionally, the so-called Logical Knowledge Mannequin (LDM) is a large advantage of GoodData. With a predefined LDM, you outline the mapping and relations solely as soon as — you may reuse the identical objects many occasions for numerous knowledge visualizations with out setting it up from scratch each time.
Why not attempt our 30-day free trial?
Absolutely managed, API-first analytics platform. Get instantaneous entry — no set up or bank card required.
5 Key Components of Knowledge Analytics Automation
Step one is to create a GoodData trial. If you’re within the particulars, verify the documentation. For the sake of brevity, I cannot go into particulars right here, however please let me know if you wish to hear extra. The objective of this automation is to have an atmosphere the place I can create insights, metrics, and dashboards. Why? You often are not looking for the purchasers to see the dashboard earlier than it’s prepared. Ideally, you create a dashboard, seek the advice of your coworkers, after which use CI/CD pipeline to publish the ready atmosphere within the manufacturing. Your clients will see the tuned dashboard and you do not want to repeat and paste metrics or insights manually, which is each error-prone and time-consuming. Let’s discover how you can obtain this objective!
1. Put together Staging Surroundings
First, I must create an atmosphere the place I’ll arrange, analyze, and current knowledge. For this function, I’ll create a workspace in GoodData with an API name as a result of I don’t must create a brand new workspace each time the pipeline runs.
curl --location --request POST 'https://cicd.anyplace.gooddata.com/api/entities/workspaces'
--header 'Authorization: <Bearer API Token>'
--header 'Content material-Kind: utility/vnd.gooddata.api+json'
--data-raw '{
"knowledge": {
"attributes": {
"title": "staging"
},
"id": "staging",
"sort": "workspace"
}
}'
The results of this motion is the next created workspace staging:
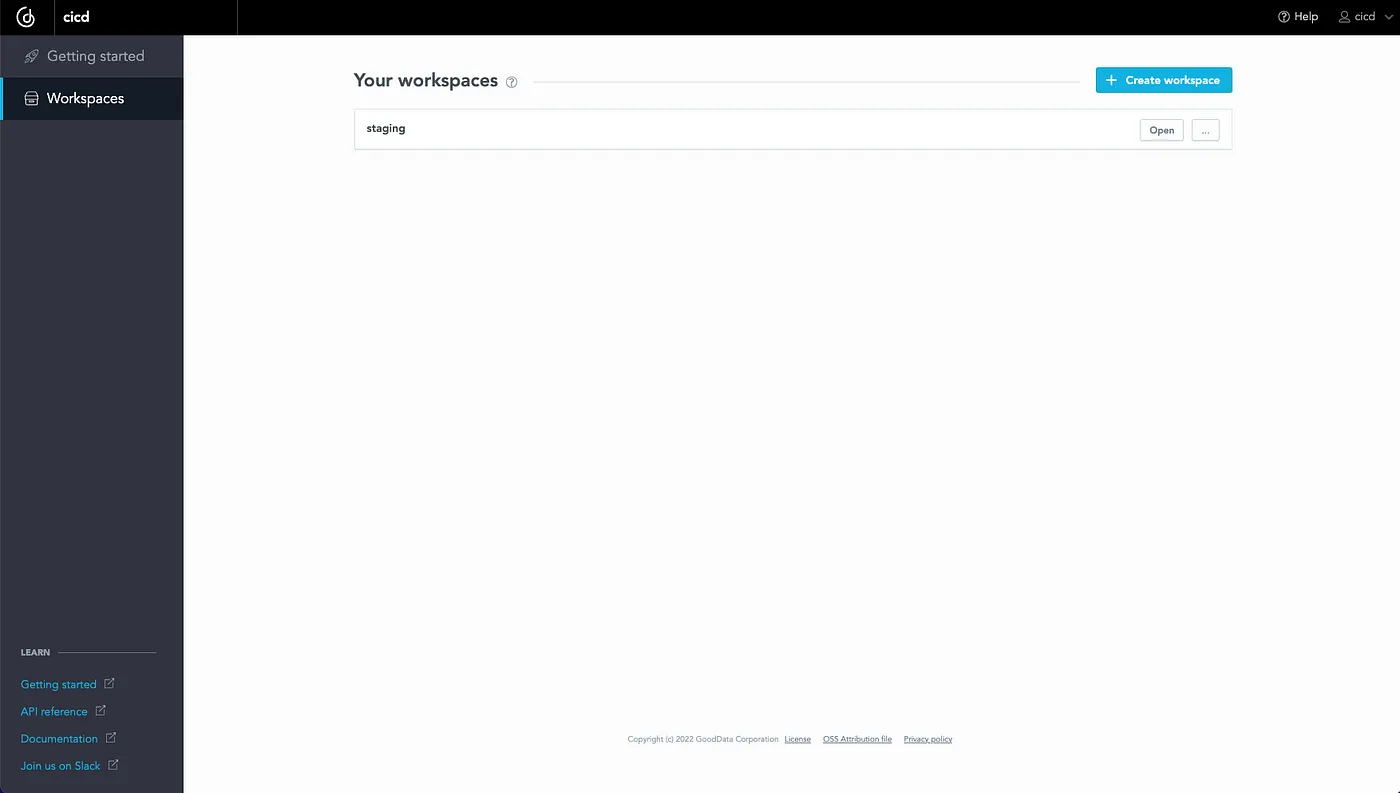
You may also create a workspace utilizing GoodData Python SDK, it’s only a few strains of code. It may be used as part of your pipeline (as a result of create_or_update technique is idempotent):
import gooddata_sdk
from gooddata_sdk.catalog.workspace.entity_model.workspace import CatalogWorkspace
host = <GOODDATA_HOST>
token = <GOODDATA_API_TOKEN>
workspace = "new_workspace"
sdk = gooddata_sdk.GoodDataSdk.create(host, token)
sdk.catalog_workspace.create_or_update(CatalogWorkspace(workspace, workspace))
2. Create Staging Analytics
Right here, I’m utilizing demo knowledge, which implies that the mannequin is comparatively easy:
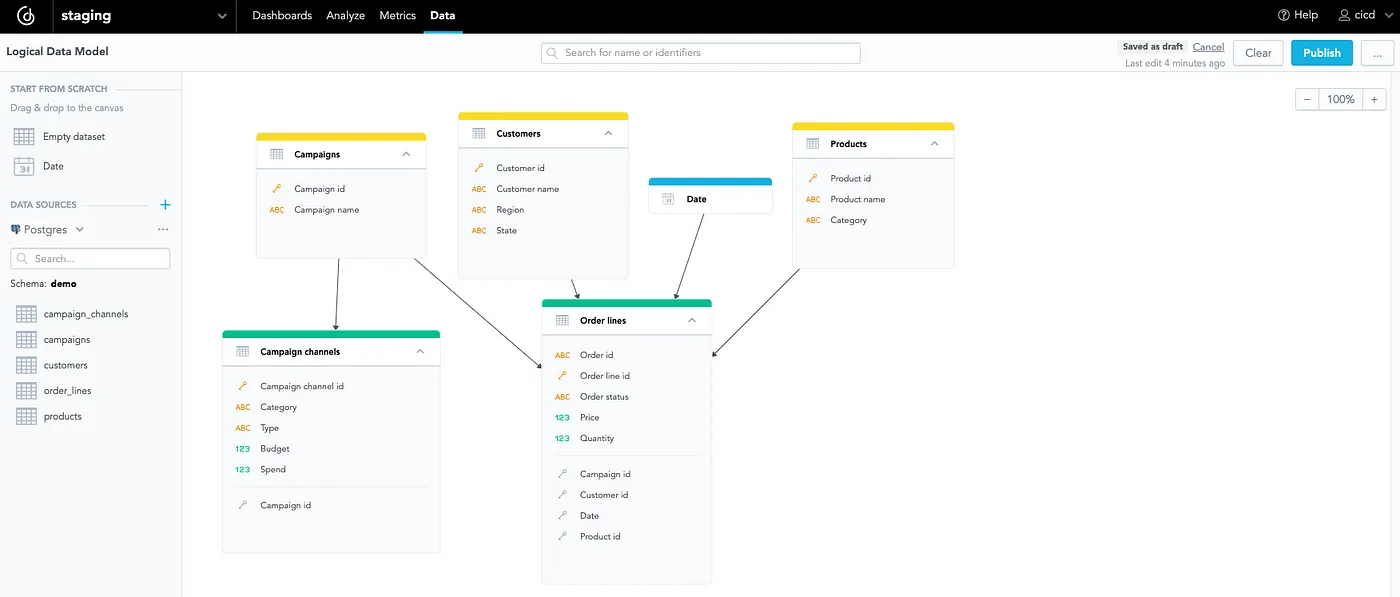
You may see that it consists solely of six tables. I can create priceless insights as a result of I’ve knowledge about orders and clients. Initially, let’s create a dashboard for all these insights — for instance, the dashboard will function an outline of the final seven days:
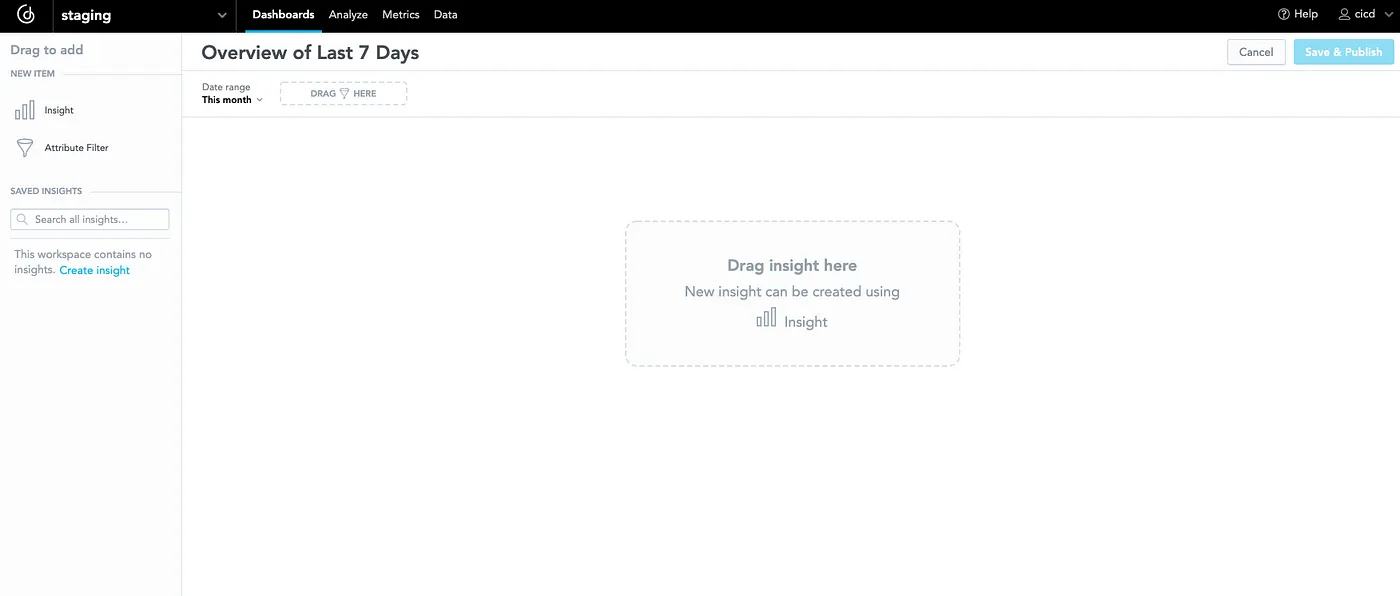
I can instantly put the primary perception onto the dashboard — for instance, an perception that might present me which state did most orders come from:
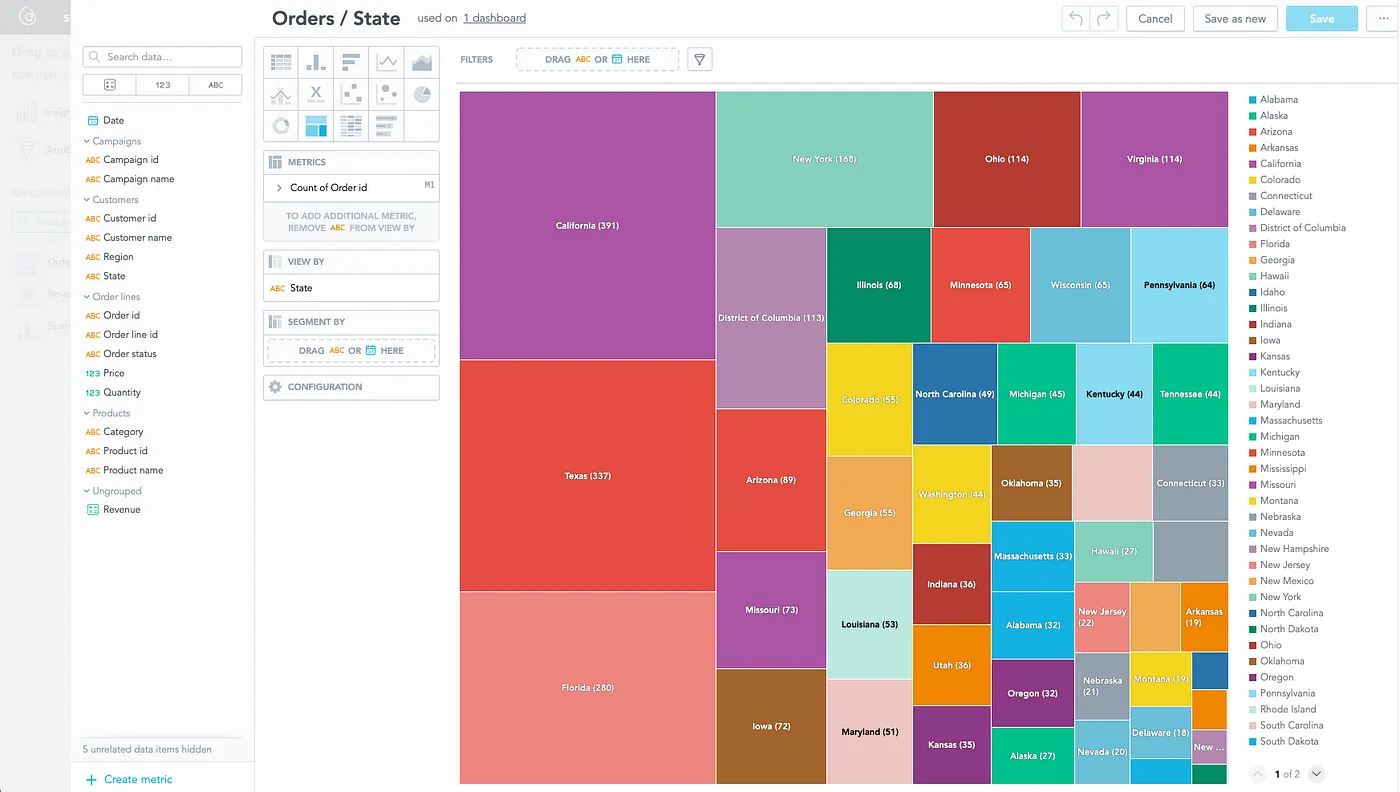
To complete the dashboard, I’ll add a number of extra insights and save the dashboard with the “Final 7 Day” filter:
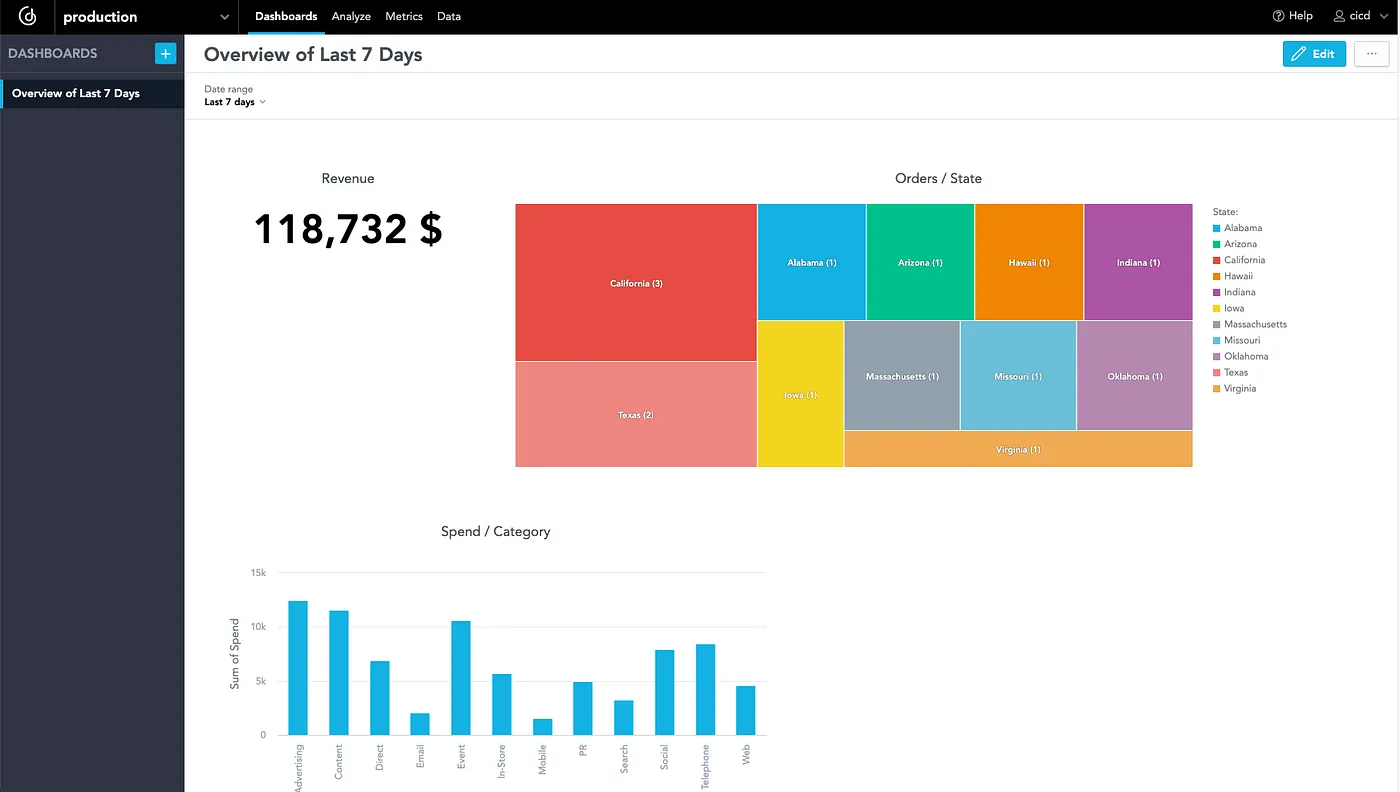
3. Create a Python Script for Pipeline Run
Within the earlier two steps, I’ve created a staging workspace and staging analytics. The following step is to create a easy script that can generate the manufacturing workspace (or replace) and that can put the entire staging analytics there. Declarative API is named behind the scenes; by atomic calls, the manufacturing workspace’s content material is changed by the brand new model each time. This may be simply reverted and older variations might be delivered if wanted, due to declarative API.
import gooddata_sdk
from gooddata_sdk.catalog.workspace.entity_model.workspace import CatalogWorkspace
import os
host = os.getenv('GOODDATA_HOST')
token = os.getenv('GOODDATA_API_TOKEN')
staging_workspace_id = os.getenv('GOODDATA_STAGING_WORKSPACE_ID')
production_workspace_id = os.getenv('GOODDATA_PRODUCTION_WORKSPACE_ID')
sdk = gooddata_sdk.GoodDataSdk.create(host, token)
sdk.catalog_workspace.create_or_update(CatalogWorkspace(production_workspace_id, production_workspace_id))
declarative_ldm = sdk.catalog_workspace_content.get_declarative_ldm(staging_workspace_id)
declarative_analytics_model = sdk.catalog_workspace_content.get_declarative_analytics_model(staging_workspace_id)
sdk.catalog_workspace_content.put_declarative_ldm(production_workspace_id, declarative_ldm)
sdk.catalog_workspace_content.put_declarative_analytics_model(production_workspace_id, declarative_analytics_model)
print("completed")
You may see that I exploit the GoodData Python SDK to work together simply with GoodData utilizing code. In a nutshell, the script does two issues: it creates the brand new workspace manufacturing (if it doesn’t exist), and it takes analytics from the staging workspace and places it into the manufacturing workspace.
4. Setup Pipeline With the Assist of Dagger
I exploit Dagger to orchestrate the CI/CD pipeline. The pipeline generates the Dockerfile, builds a picture, and runs a container in response to the code beneath. It additionally defines which atmosphere variables it wants. Dagger is great as a result of I can debug it regionally and push it to GitLab or GitHub (I didn’t must push each code change to see the results of the pipeline).
bundle pipeline
import (
"dagger.io/dagger"
"universe.dagger.io/docker"
)
#StagingToProductionDeploy: docker.#Dockerfile & {
dockerfile: contents: """
FROM python:3.9
COPY . /src
RUN pip set up -r /src/necessities.txt
CMD python /src/staging_to_production_deploy.py
"""
}
dagger.#Plan & {
shopper: {
filesystem: "./src": learn: contents: dagger.#FS
env: {
GOODDATA_HOST: string
GOODDATA_API_TOKEN: string
GOODDATA_STAGING_WORKSPACE_ID: string
GOODDATA_PRODUCTION_WORKSPACE_ID: string
}
}
actions: {
construct: #StagingToProductionDeploy & {
supply: shopper.filesystem."./src".learn.contents
}
run: docker.#Run & {
all the time: true
enter: construct.output
env: {
GOODDATA_HOST: shopper.env.GOODDATA_HOST
GOODDATA_API_TOKEN: shopper.env.GOODDATA_API_TOKEN
GOODDATA_STAGING_WORKSPACE_ID: shopper.env.GOODDATA_STAGING_WORKSPACE_ID
GOODDATA_PRODUCTION_WORKSPACE_ID: shopper.env.GOODDATA_PRODUCTION_WORKSPACE_ID
}
}
}
}
5. Push All the pieces to GitLab
The ultimate step is to push the whole lot to GitLab and create a .gitlab-ci.yaml file to run the pipeline. I used the file within the Dagger documentation; mainly, it would merely allow you to copy and paste the file and instantly run the pipeline. You will discover the file within the GitLab repository, in addition to the opposite recordsdata from the earlier steps.
Automated Knowledge Analytics Demo
Now plainly the whole lot is prepared. Let’s run the pipeline! In GitLab, you may run the pipeline from the CI/CD part. The created pipeline runs for ~2 minutes (in the course of the first run), and in that point, it would deploy the staging workspace to the manufacturing workspace.
The result’s the next (you may see the brand new workspace manufacturing in GoodData):
Once I open the workspace, it incorporates the identical dashboards with insights because the staging workspace:
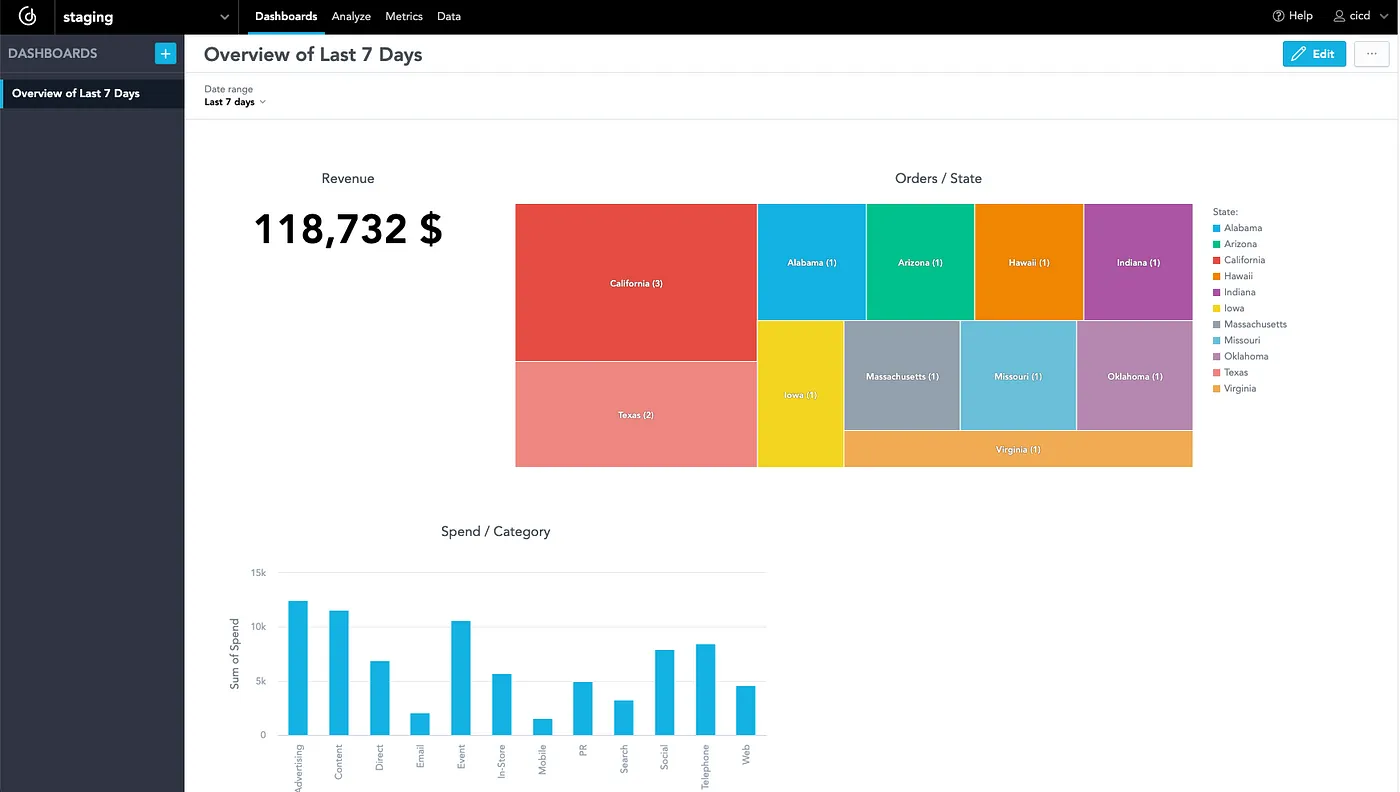
Think about I make some adjustments within the staging workspace. For instance — I’ll add a brand new dashboard with new insights. Delivering new analytics to manufacturing might be a matter of only one click on in GitLab and it’ll pace up the supply of analytics to clients or stakeholders!
Abstract
Thanks for studying the article! On this article, I described why the automation of analytics is vital and confirmed you an instance of such automation in motion. The issue with conflicts in UI isn’t talked about on this temporary article. Think about that somebody makes adjustments within the manufacturing workspace, and subsequently, you run the pipeline. In that case, all adjustments made within the UI are gone within the manufacturing workspace and they’re changed with the staging workspace. On this case, the pipeline doesn’t check if all insights are executable. What if one of many insights doesn’t work? It is going to go unnoticed and you’ll ship the adjustments to the manufacturing workspace. Due to GoodData Python SDK, you may remedy all of those points! If you’re involved in how you can remedy these issues, please comply with me, I’ll cowl these situations within the following articles. I additionally encourage you to learn different articles about analytics, resembling How To Automate Your Statistical Knowledge Evaluation or Construct a Device for Knowledge Evaluation.
Why not attempt our 30-day free trial?
Absolutely managed, API-first analytics platform. Get instantaneous entry — no set up or bank card required.
