In my article 5 Causes Why to Write Your Semantic Layer in YAML I expressed my concepts about writing a semantic layer in YAML.
This time, I wish to broaden on the thought of utilizing YAML for analytics. I wish to envision what an analytics interface centered on Analytics Engineers ought to appear like.
Listed here are my 5 explanation why I consider we’re heading in the right direction with Analytics as Code:
1. It feels acquainted
Okay, that is form of a no brainer, however let’s give it some thought for a second. Nowadays, most BI/analytics interfaces comply with the drag & drop paradigm, however is that this actually the most effective interface for Analytics Engineers?
In accordance with dbt, who launched the time period Analytics Engineers, these individuals search to:
- Present clear information units to finish customers, modeling information in a method that empowers finish customers to reply their questions
- Apply software program engineering greatest practices like model management and steady integration to the analytics code base
That undoubtedly doesn’t sound like a drag-and-drop sort of individual. That is confirmed additionally by our personal expertise and analysis. These persons are extra accustomed to IDE-type instruments. They like readability and productiveness over astonishing animations and eye-candy results.
2. It gives a unified person expertise
These days, analytics/BI instruments depend on a layered abstraction mannequin. That is in core, a good suggestion and it jogs my memory of the OSI communication mannequin with its bodily, community, presentation, and software layer.
Nevertheless, even a good suggestion can shortly change into a nightmare when every layer has its distinctive person interface, and a single individual makes use of all of them. Such jacks-of-all-trades are Analytics Engineers. They work with information, information fashions, metrics, and typically even information visualizations.
Present BI platforms provide utterly totally different interfaces for every of those layers. Let’s take Tableau for example:
- There’s a list-style UI for the administration of workbooks and tasks.
- Then there’s a UI for information preparation and modeling.
- Then a visualization builder UI.
- Then a dashboard builder UI.
If you need to test it for your self, check out Tableau’s Get Began with Net Authoring information for creators.
All of those interfaces closely make the most of drag & drop, but on the identical time all of them feel and appear fairly totally different. I really feel sorry for everybody who has to change forwards and backwards between these interfaces in a speedy method.
However what would such a unified expertise appear like? Would it not be doable to maintain the layered method whereas having a unified person expertise? After all, that’s what software program builders are used to anyway. Once more, they use IDEs which accurately means built-in improvement setting.
3. It’s comprehensible at first look
So now we have now applicable tooling (IDE) that feels acquainted and gives a unified expertise. Nevertheless, we shouldn’t cease there. To make the expertise actually clean and unified, we have to give attention to find out how to declare every of the analytics layers.
Happily, I’ve already accomplished some work in my different article 5 Causes Why to Write Your Semantic Layer in YAML.
Now let’s test a couple of examples on a real-life analytics challenge I’ve ready for an Analytic as code webinar. The challenge maps some fundamental statistics in regards to the well-known film character James Bond.
Information mannequin (semantic layer)
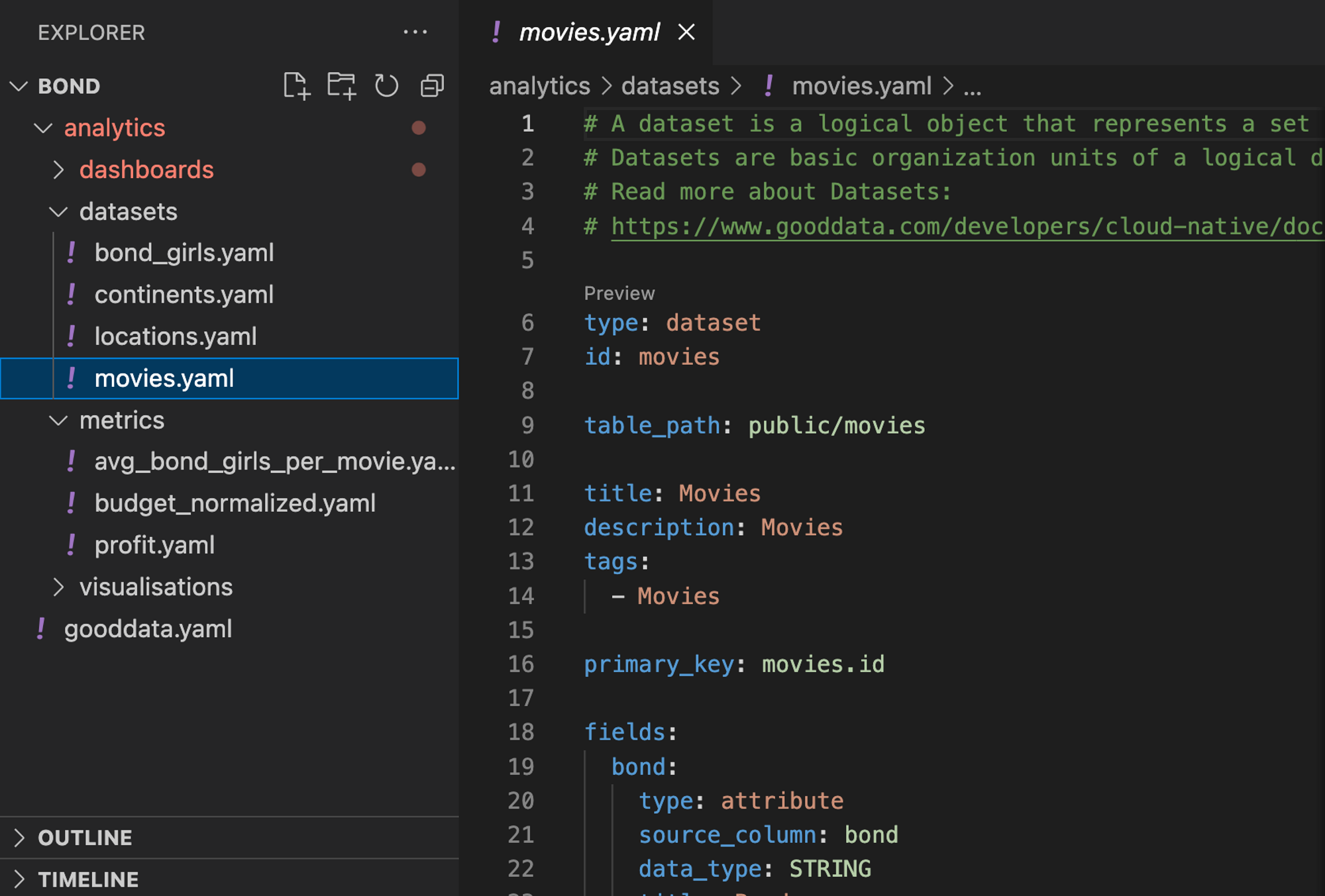
The logical information mannequin is a cornerstone of any maintainable analytics challenge. The James Bond mannequin could be very easy and consists of simply three datasets. Under is a shortened instance of a dataset in its code kind.
sort: dataset
id: motion pictures
table_path: public/motion pictures
title: Films
primary_key: motion pictures.id
fields:
bond:
sort: attribute
source_column: bond
data_type: STRING
title: Bond
bond_car:
sort: attribute
source_column: bond_car
data_type: STRING
title: Bond automotive
director:
sort: attribute
source_column: director
data_type: STRING
title: Director
…
Metrics
In 2023 Gartner launched a metric retailer as a brand new vital functionality for Analytics and Enterprise Intelligence (ABI) Platforms. Gartner describes it as a virtualized layer that enables customers to create and outline metrics as code. That is precisely what GoodData has provided for fairly a while. Under is an instance of metric’s code illustration. The metric consists of a question (maql) and a few metadata round it.
sort: metric
id: revenue
title: revenue
maql: SELECT sum({truth/worldgross}) - SUM({metric/budget_normalized})
format: "#,##0.00"Visualizations
Each visualization comprises a question half that feeds the visualization with information. Consider it as a SQL question that represents the uncooked information.
The following noticeable a part of visualization are buckets. These management how the uncooked information is translated into its visible kind. We tried our greatest to not make the buckets visualization-specific and thus a lot of the visualizations include buckets for metrics, slicing, and segmentation.
The emphasis on the excellence between uncooked information and buckets is aligned with GoodData’s composability efforts. Think about that an Analytics Engineer prepares a uncooked information question that’s later utilized by a number of Information Analysts in a number of visualizations.
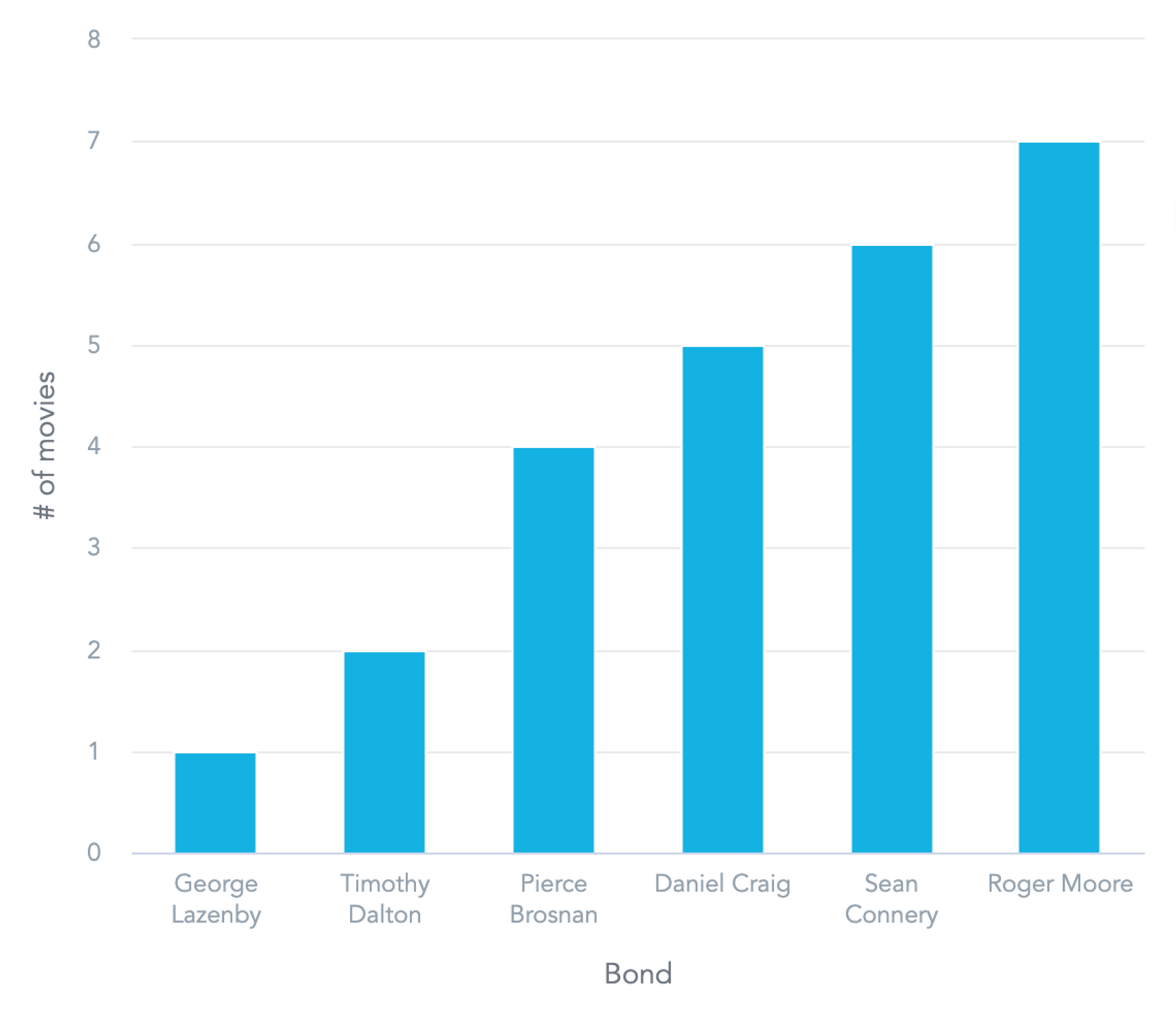
id: actors__number-of-motion pictures
sort: column_chart
title: In what number of motion pictures did every actor play?
question:
fields:
number_of_movies:
title: "# of flicks"
aggregation: COUNT
utilizing: label/motion pictures.id
bond: label/bond
sort_by:
- sort: attribute_sort
by: bond
route: ASC
aggregation: SUM
metrics:
- discipline: number_of_movies
format: "#,##0"
view_by:
- bondAnd the identical visualization in its visible kind.
Dashboards
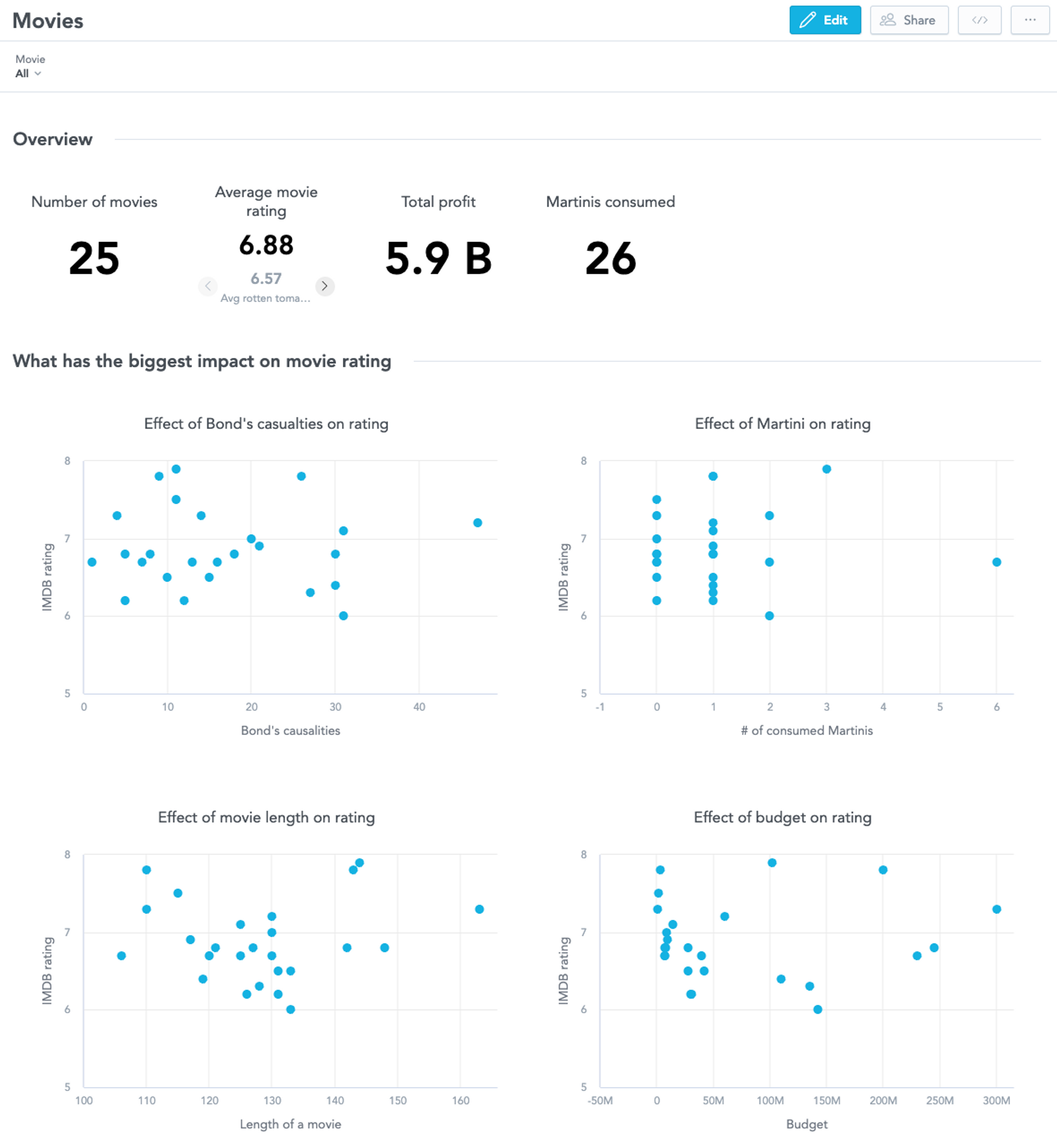
The ultimate instance pertains to dashboards. The dashboard code seems to be pretty easy given the quantity of displayed visualizations. That’s due to GoodData’s excessive degree of composability, the place Analytics Engineers are in a position to reuse a single visualization in a number of locations. Does it sound just like the well-known DRY precept?
id: dashboard__movies
sort: dashboard
title: Films
sections:
- title: Overview
widgets:
- visualization: movies__count
title: Variety of motion pictures
columns: 2
rows: 10
- visualization: movies__avg_rating
title: Common film score
columns: 2
rows: 10
- visualization: universal__profit
title: Whole revenue
columns: 2
rows: 10
- visualization: universal__martinis-consumed
title: Martinis consumed
columns: 2
rows: 10
…And right here is the dashboard in its visible kind. Discover the second part was omitted from the code instance.
Did these samples catch your consideration? Then go and test the whole reference information.
4. It scales nicely
To be sincere, the standard drag-and-drop sort of person interface works really fairly nicely till you get into scalability points. When you hit that wall, administration of your analytics turns into a nightmare. I already spoke about IDE and the way it was initially constructed for the productiveness of software program builders.
Guess what, production-quality software program tasks often contain a whole lot of interconnected information and software program builders want a simple technique to handle all of them. That’s why an IDE gives functionalities like good search, project-scoped refactoring, or go to references/definitions.
After all, not all of this stuff come out of the field, however we have now developed an IDE plugin that brings them even to the analytics information.
5. It helps cooperation
Cooperation is more and more necessary in at this time’s world of analytics. Silos are gone and modifications have to be delivered in hours or days, not weeks or months.
Software program builders have confronted points with collaboration and cooperation for a few years. Let’s encourage and reuse what works nicely, equivalent to varied model management techniques like Git. Fortunately at this time’s IDEs provide high quality out-of-the-box assist for these techniques, which suggests all of the heavy lifting has already been accomplished.
Collaboration between a number of Analytics Engineers to ship a curated analytics expertise:
The cornerstone of the curated expertise is a Git repository that’s thought of as a single supply of fact. Optionally this repository is related to a CI/CD pipeline which validates every change and deploys it to manufacturing. Let’s take a look at how it will go in follow:
- Alice creates a brand new metric. She doesn’t do it in manufacturing, however slightly in her native setting.
- Alice commits her new metric and creates a pull request.
- Bob critiques her modifications and accepts the pull request. Alice’s modifications are actually within the grasp department.
- CI/CD pipeline routinely validates Alice’s modifications and pushes the modifications to manufacturing.
Cooperation between Analytics Engineers and enterprise customers:
Enterprise finish customers attempt for self-service, however in lots of conditions, they nonetheless want help from Analytics Engineers. Let’s take a look at an instance:
- Carol (enterprise finish person) desires to create a brand new visualization. Nevertheless, she wants new information for it.
- Carol contacts Taylor (analytical engineer) with a request so as to add the required information into the semantic layer.
- Taylor pushes the modifications into Git and provides a commit message explaining the modifications.
- After Taylor’s modifications get promoted to manufacturing, Carol creates her desired visualization.
- Different enterprise customers begin to request the exact same visualization Carol has already created.
- Taylor doesn’t have to recreate the visualization from scratch, as a substitute, he merely fetches and accepts Carol’s visualization as part of the curated expertise.
Conclusion
On this article, I attempted to stipulate a imaginative and prescient for another person interface to writer analytics. It is perhaps tempting to ditch the drag-and-drop sort of person interface at this level, however I received’t try this. I nonetheless consider it has its place within the analytics ecosystem, primarily for self-service analytics and enterprise customers.
Analytics Engineers as we all know them nonetheless attempt for productiveness and see that software program improvement greatest practices will ease their every day jobs. I consider the analytics as code sort of interface will cowl their wants.
Nonetheless not satisfied? Would you wish to strive it? The best method to take action is to strive our GoodData for VS Code.
